Choosing The Right Size Wire For 100 Amp: A Complete Guide
Electrical wiring isn’t just about connecting devices; it’s about ensuring that the power flows safely and efficiently. A 100-amp service is common in residential and small commercial settings, providing enough electricity to power appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems. However, the wire you choose must match the demands of your system. Copper and aluminum are the two primary materials used for wiring, each with its own advantages and limitations. Copper is more conductive but pricier, while aluminum is cost-effective but requires larger diameters to handle the same load. Understanding these differences is key to making informed decisions about your wiring needs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about choosing the right size wire for 100 amp applications. From understanding electrical codes to calculating voltage drop and exploring material options, we’ll cover all the bases. Whether you’re an electrician, a DIY enthusiast, or a homeowner planning an upgrade, this article will equip you with the knowledge to make safe and efficient choices. Let’s dive in and demystify the process of selecting the perfect wire size for your 100-amp electrical system.
Table of Contents
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for 100-Amp Systems?
- What Are the Different Materials Used for Wiring?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Wiring?
- What Are the National Electrical Code Requirements?
- How Far Can You Run a 100-Amp Wire?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size
- How to Choose the Right Size Wire for 100-Amp Subpanels?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Size Wire for 100 Amp
Why Does Wire Size Matter for 100-Amp Systems?
Choosing the correct size wire for 100 amp systems is not just a recommendation—it’s a necessity. The wire size directly impacts the safety and functionality of your electrical system. If the wire is too small, it can overheat due to excessive current flow, leading to insulation damage, short circuits, or even fires. On the other hand, using an oversized wire increases material costs without providing any additional benefits. Therefore, understanding why wire size matters is the first step toward making informed decisions.
Why Is Overheating a Concern with Incorrect Wire Sizes?
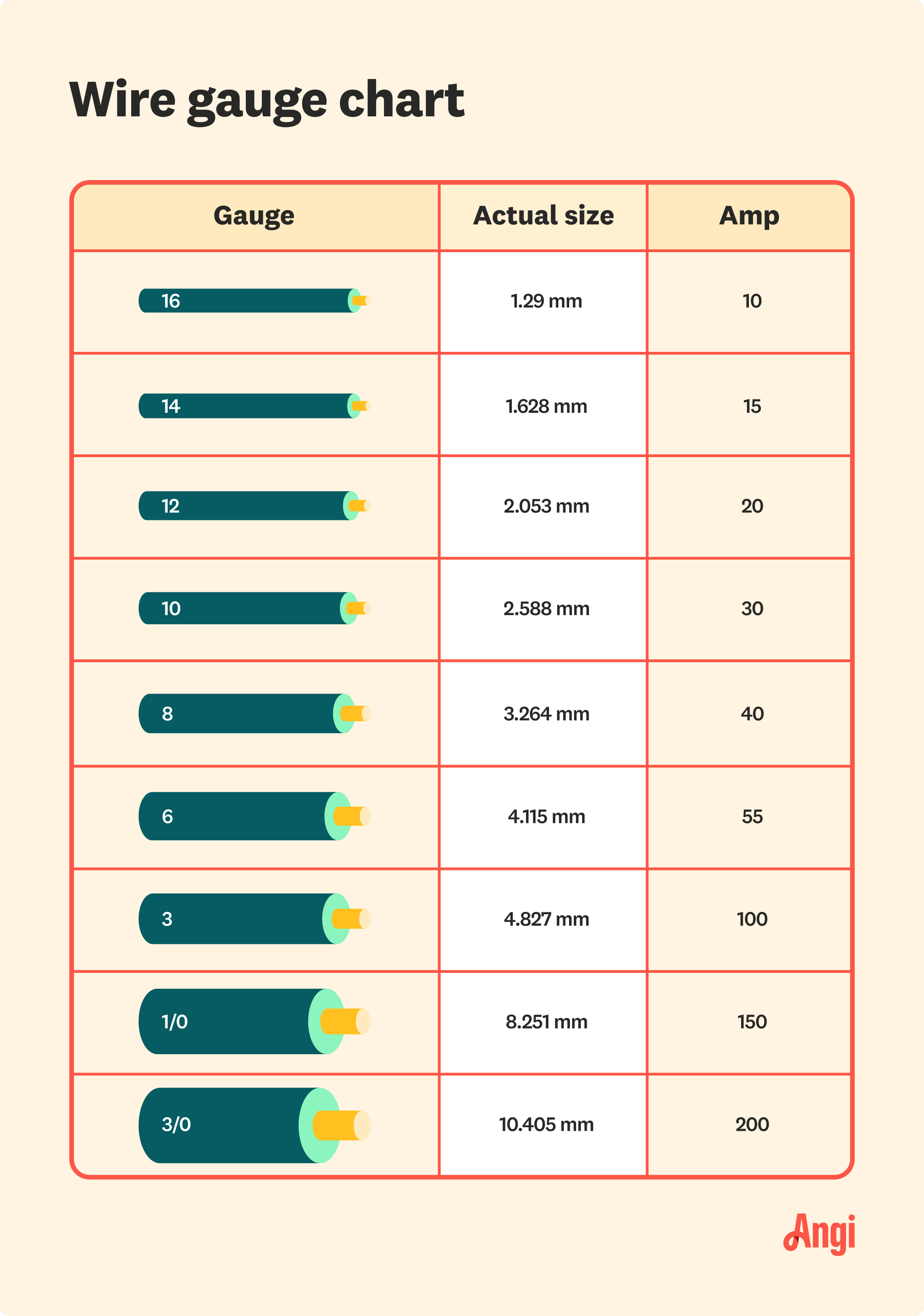
Overheating is one of the most significant risks associated with using undersized wires. When the current exceeds the wire’s capacity, the resistance in the wire generates heat. This heat can degrade the wire’s insulation, exposing the conductor and creating a fire hazard. For example, a 100-amp circuit requires a wire gauge that can handle the current without excessive resistance. Using a wire that’s too thin, such as 10 AWG instead of 2 AWG, can lead to overheating and catastrophic failures. Always consult the American Wire Gauge (AWG) chart to ensure your wire size aligns with the current load.
Read also:Mastering Remote Iot Vpc Ssh A Comprehensive Guide To Secure Connectivity
How Does Wire Size Affect Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop occurs when electrical energy is lost as it travels through a conductor, resulting in reduced efficiency and potential equipment damage. The size wire for 100 amp systems plays a critical role in minimizing voltage drop. Larger wires have lower resistance, which helps maintain consistent voltage levels across long distances. For instance, a 2 AWG copper wire is often recommended for 100-amp applications to ensure minimal voltage drop. Ignoring this factor can lead to dimming lights, malfunctioning appliances, and increased energy bills.
Key Factors Influencing Wire Size Selection
- Current Load: The wire must handle the maximum current without overheating.
- Distance: Longer runs require thicker wires to compensate for resistance.
- Material: Copper wires can be smaller than aluminum wires for the same current.
- Insulation Type: The wire’s insulation affects its temperature rating and durability.
What Are the Different Materials Used for Wiring?
When selecting the size wire for 100 amp systems, the material of the wire is a critical factor. The two most common materials used for electrical wiring are copper and aluminum. Each material has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to weigh these factors before making a decision. Understanding the differences between these materials will help you choose the best option for your specific needs.
Why Is Copper Preferred for High-Current Applications?
Copper is widely regarded as the gold standard for electrical wiring due to its superior conductivity and durability. It offers excellent performance in high-current applications, such as 100-amp circuits, because it has lower resistance compared to other materials. This means that a smaller gauge of copper wire, such as 2 AWG, can safely handle 100 amps without significant voltage drop or overheating. Additionally, copper wires are more resistant to corrosion and have a longer lifespan, making them a reliable choice for long-term installations. However, the higher cost of copper is a consideration for budget-conscious projects.
When Is Aluminum Wiring a Cost-Effective Alternative?
Aluminum wiring is a popular alternative to copper, especially for larger installations where cost is a primary concern. While aluminum is less conductive than copper, it is significantly lighter and more affordable. For a 100-amp circuit, you would typically need a thicker wire, such as 1/0 AWG aluminum, to achieve the same performance as a 2 AWG copper wire. Although aluminum is more susceptible to oxidation and requires special connectors to prevent corrosion, it remains a viable option for many applications. Proper installation techniques, such as using anti-oxidant compounds, can mitigate some of the challenges associated with aluminum wiring.
Comparison of Copper and Aluminum Wires
| Feature | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Fair (requires maintenance) |
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Wiring?
Voltage drop is a critical consideration when selecting the size wire for 100 amp systems. It refers to the loss of voltage as electricity travels through a conductor, which can affect the performance of your electrical devices. Understanding how to calculate voltage drop ensures that your wiring can maintain optimal voltage levels, even over long distances. This section will guide you through the process of calculating voltage drop and selecting the appropriate wire size to minimize it.
What Is the Formula for Calculating Voltage Drop?
The formula for calculating voltage drop is relatively straightforward: Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000. In this equation, the length represents the distance of the wire run in feet, the current is the amperage of the circuit (100 amps in this case), and the resistance is determined by the wire’s material and gauge. For example, a 2 AWG copper wire has a resistance of approximately 0.156 ohms per 1,000 feet. Plugging these values into the formula allows you to determine the voltage drop for your specific setup. Keeping the voltage drop below 3% is generally recommended for optimal performance.
Read also:Exploring Adam Savages Children A Glimpse Into Their Lives And Influence
Why Is Minimizing Voltage Drop Important?
Minimizing voltage drop is essential for maintaining the efficiency and safety of your electrical system. Excessive voltage drop can lead to dimming lights, reduced motor performance, and increased energy consumption. For instance, if the voltage at the end of a 100-amp circuit drops below the acceptable threshold, appliances may not function correctly, and sensitive electronics could be damaged. Using a larger wire size, such as 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum, helps reduce resistance and ensures consistent voltage levels across the circuit. This is particularly important for long wire runs or installations with high power demands.
Practical Tips for Reducing Voltage Drop
- Use Larger Wires: Thicker wires have lower resistance, minimizing voltage drop.
- Shorten Wire Runs: Reducing the distance between the power source and the load decreases voltage loss.
- Select High-Quality Materials: Copper wires offer better conductivity than aluminum, reducing resistance.
- Upgrade Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion to maintain optimal performance.
What Are the National Electrical Code Requirements?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides standardized guidelines to ensure the safe installation of electrical systems, including the selection of the size wire for 100 amp circuits. These requirements are designed to protect both property and people from electrical hazards. Adhering to NEC standards is not only a legal obligation but also a practical way to ensure your electrical system operates safely and efficiently. Understanding these requirements is essential for anyone involved in electrical installations.
What Does the NEC Say About Wire Sizing for 100-Amp Circuits?
According to the NEC, the size wire for 100 amp systems must be selected based on the current-carrying capacity, insulation type, and installation conditions. For example, a 2 AWG copper wire is typically recommended for 100-amp circuits in residential settings. The NEC also specifies that wires must be rated for the appropriate temperature and environment, such as wet or dry locations. Additionally, the code mandates the use of proper connectors and protection devices, such as circuit breakers, to prevent overloads and short circuits. Always consult the latest NEC edition to ensure compliance with current standards.
Why Is Compliance with NEC Standards Critical?
Compliance with NEC standards is critical for several reasons. First, it ensures the safety of your electrical system by minimizing the risk of fires, shocks, and other hazards. Second, it helps avoid legal issues and potential fines for non-compliance. Finally, adhering to NEC guidelines enhances the reliability and longevity of your electrical installation. For instance, using the correct size wire for 100 amp circuits as per NEC recommendations prevents overheating and voltage drop, ensuring smooth operation of your appliances and devices. Ignoring these standards can lead to costly repairs, insurance claims, and even legal liabilities.
Key NEC Requirements for 100-Amp Wiring
- Wire Gauge: Minimum 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum for 100 amps.
- Insulation Rating: Wires must be rated for the operating temperature and environment.
- Protection Devices: Install circuit breakers and fuses to prevent overloads.
- Grounding: Proper grounding is essential for safety and compliance.
How Far Can You Run a 100-Amp Wire?
The distance you can safely run a 100-amp wire depends on several factors, including the wire size, material, and
Understanding The Importance Of A Section Of Land Acres In Real Estate
Is Expired Bleach Harmful? Everything You Need To Know
Is Fungi A Autotroph? Exploring The Role Of Fungi In Ecosystems
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi

What Size Wire 100 Amp Subpanel