Choosing The Right Wire For 10 Amps: A Comprehensive Guide
Whether you're working on a DIY project or planning an industrial setup, understanding the basics of electrical wiring can save you from costly mistakes and potential hazards. Wires designed to handle 10 amps must meet specific standards to prevent overheating and electrical fires. This article dives deep into everything you need to know about selecting the appropriate wire gauge, understanding its applications, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. By the end of this guide, you’ll feel confident in making informed decisions about wiring for your electrical needs. When it comes to electrical projects, the stakes are high. Faulty wiring can lead to power outages, equipment damage, or even fires. That’s why it’s essential to understand the role of wire gauge, material, and insulation when selecting wire for 10 amps. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical wiring, each with its own advantages and limitations. Additionally, insulation plays a vital role in protecting the wire from environmental factors such as heat, moisture, and abrasion. This guide will walk you through the key considerations, ensuring that your project not only functions efficiently but also adheres to safety standards. Finally, it’s important to recognize that the right wire for 10 amps isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Different applications, such as residential wiring, automotive systems, or industrial machinery, may require specific types of wires. Understanding these nuances can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure your project runs smoothly. From deciphering wire gauge charts to exploring the latest innovations in wiring technology, this article is your ultimate resource for mastering the art of selecting wire for 10 amps. Let’s dive in and explore the details that will empower you to make the best choices for your electrical needs.
Table of Contents
- What Is the Right Wire Gauge for 10 Amps?
- How Does Wire Material Affect Performance?
- Why Is Insulation Important for Wire Safety?
- Applications of Wire for 10 Amps
- What Are the Safety Standards for Wiring?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire
- How Can You Test the Wire for 10 Amps?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire for 10 Amps
What Is the Right Wire Gauge for 10 Amps?
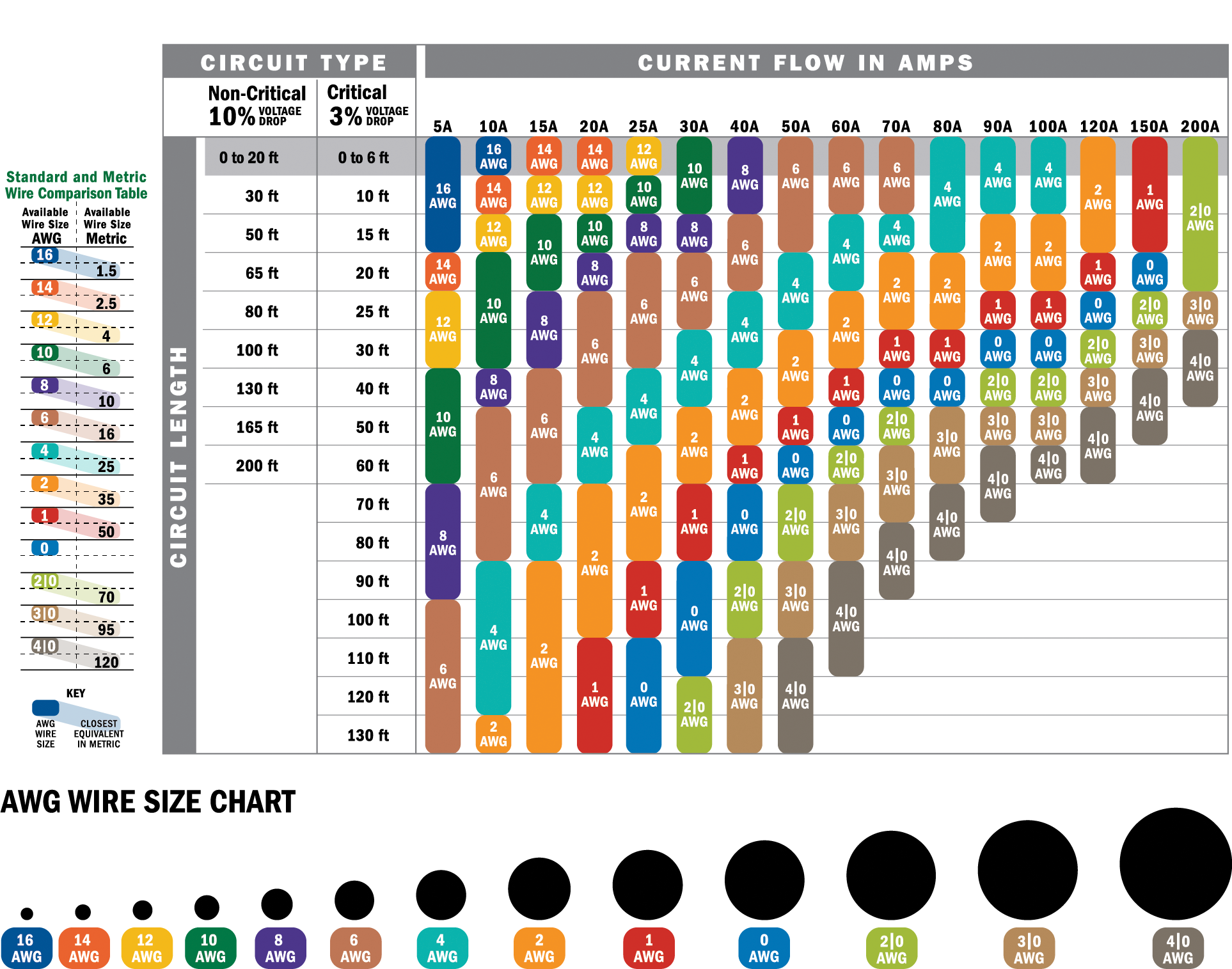
Choosing the correct wire gauge is the first step in ensuring your electrical system operates safely and efficiently. For wire for 10 amps, a 16-gauge wire is typically recommended for most applications. However, the exact gauge may vary depending on factors such as the length of the wire, the type of material used, and the environment in which it will be installed. Understanding these variables is essential for making the right choice.
Factors Influencing Wire Gauge Selection
Several factors influence the appropriate wire gauge for 10 amps. First, consider the distance over which the wire will carry the current. Longer distances require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop, which can affect the performance of your electrical devices. For instance, a 16-gauge wire is suitable for short runs, but for distances exceeding 50 feet, you may need to upgrade to a 14-gauge wire to maintain efficiency.
Read also:Rick Moranis A Comprehensive Look At The Comedy Legends Life And Legacy
Material Matters
The material of the wire also plays a significant role in determining the appropriate gauge. Copper wires are more conductive than aluminum, meaning they can carry the same current with a smaller diameter. If you're using aluminum wire for 10 amps, you may need to choose a thicker gauge to compensate for its lower conductivity. Always consult a wire gauge chart to ensure accuracy.
Practical Examples of Wire Gauge Usage
To better understand the practical applications of wire gauge selection, consider the following examples:
- Residential Wiring: For household appliances like lamps or small kitchen gadgets, a 16-gauge wire is sufficient.
- Automotive Systems: In cars, where space is limited, 18-gauge wires are often used for low-power applications like dashboard lights.
- Industrial Machinery: For heavy-duty equipment, thicker wires like 14-gauge may be necessary to handle the load without overheating.
How Does Wire Material Affect Performance?
The material of the wire is a critical factor in determining its performance and suitability for specific applications. When selecting wire for 10 amps, copper and aluminum are the two primary materials to consider. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to weigh these factors carefully before making a decision.
Advantages of Copper Wire
Copper is widely regarded as the gold standard for electrical wiring due to its superior conductivity. It can carry more current than aluminum of the same gauge, making it ideal for applications where space is limited. Additionally, copper is more resistant to corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan for your wiring system. These qualities make copper the preferred choice for residential and commercial wiring.
Why Choose Aluminum Wire?
While aluminum is less conductive than copper, it is significantly lighter and more cost-effective. This makes it a popular choice for large-scale applications like power transmission lines. However, aluminum wire requires special connectors and terminations to prevent oxidation and ensure a secure connection. If you're considering aluminum wire for 10 amps, consult a professional to ensure proper installation.
Comparing Conductivity and Cost
To better understand the trade-offs between copper and aluminum, consider the following comparison:
Read also:Dawn Wells Measurements A Complete Guide To Her Life And Career
- Conductivity: Copper is approximately 60% more conductive than aluminum, meaning it can carry more current with less resistance.
- Cost: Aluminum is about 30% cheaper than copper, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
- Weight: Aluminum is lighter, which is advantageous for applications where weight is a concern, such as aerospace or automotive wiring.
Why Is Insulation Important for Wire Safety?
Insulation is a critical component of any electrical wire, providing protection against environmental factors and ensuring safe operation. For wire for 10 amps, choosing the right insulation material is just as important as selecting the correct gauge and material. Insulation not only prevents electrical leakage but also protects the wire from heat, moisture, and abrasion.
Types of Insulation Materials
There are several types of insulation materials available, each suited to specific applications. Common options include:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A versatile and cost-effective choice, PVC is widely used in residential wiring.
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Known for its high heat resistance, XLPE is ideal for industrial applications.
- Teflon: Offers excellent resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures, making it suitable for specialized environments.
How Insulation Prevents Hazards
Proper insulation prevents electrical hazards by containing the current within the wire. Without adequate insulation, wires can short-circuit, leading to sparks, fires, or electrical shocks. Insulation also protects the wire from external factors like moisture, which can cause corrosion and reduce the wire's lifespan. Always choose insulation that matches the environmental conditions of your application.
Testing Insulation Integrity
To ensure the insulation is performing as intended, regular testing is recommended. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and insulation resistance. If the insulation shows signs of wear or damage, replace the wire immediately to prevent potential hazards.
Applications of Wire for 10 Amps
Wire for 10 amps finds its use in a wide range of applications, from residential wiring to automotive systems and industrial machinery. Understanding these applications can help you choose the right wire for your specific needs. Let’s explore some of the most common uses of wire for 10 amps and how it contributes to the efficiency and safety of various systems.
Residential Wiring
In residential settings, wire for 10 amps is often used for lighting circuits, small appliances, and outlets. For example, a 16-gauge copper wire is commonly used for ceiling fans, lamps, and other low-power devices. Properly sized wires ensure that these devices operate safely without overheating or causing voltage drops.
Automotive Systems
In vehicles, wire for 10 amps is used for lighting, audio systems, and dashboard controls. Due to space constraints, thinner wires like 18-gauge are often employed. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the wire can handle the load without exceeding its capacity, as overheating in automotive systems can lead to malfunctions or fires.
Industrial Machinery
Industrial applications often require more robust wiring solutions. For machinery that operates at 10 amps, thicker wires like 14-gauge are used to handle the load efficiently. These wires are typically insulated with materials like XLPE to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions.
What Are the Safety Standards for Wiring?
Adhering to safety standards is essential when working with wire for 10 amps. These standards ensure that your wiring system is safe, reliable, and compliant with regulations. Whether you're working on a DIY project or a professional installation, understanding these guidelines can prevent accidents and ensure long-term performance.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Guidelines
The NEC provides comprehensive guidelines for electrical wiring, including recommendations for wire gauge, material, and insulation. For wire for 10 amps, the NEC specifies the minimum gauge required for various applications and environments. Always consult the latest edition of the NEC to ensure compliance.
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards
For projects outside the United States, the IEC provides international standards for electrical wiring. These standards cover everything from wire sizing to insulation materials, ensuring global consistency in safety practices.
Local Building Codes
In addition to national and international standards, local building codes may impose additional requirements. These codes often address specific environmental conditions, such as humidity or temperature extremes, which can affect wire performance. Always check with your local authorities to ensure your project meets all applicable regulations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire
Selecting the wrong wire for 10 amps can lead to inefficiencies, safety hazards, and costly repairs. By understanding common mistakes, you can avoid these pitfalls and ensure your wiring system performs optimally. Let’s explore some of the most frequent errors and how to prevent them.
Underestimating Wire Gauge
One of the most common mistakes is using a wire that’s too thin for the load. This can cause overheating, voltage drops, and even fires. Always consult a wire gauge chart to ensure you’re using the appropriate size for your application.
Ignoring Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions like heat, moisture, and abrasion can affect wire performance. Failing to account for these factors can lead to premature wear and reduced lifespan. Choose insulation materials that are suited to the specific environment in which the wire will be installed.
Overlooking Material Differences
Using aluminum wire without proper connectors or terminations can lead to oxidation and poor connections. Always consider the material of the wire and its compatibility with your application. If in doubt, consult a professional for guidance.
How Can You Test the Wire for 10 Amps?
Testing wire for 10 amps is an essential step in ensuring its performance and safety. Regular testing can identify potential issues before they become serious problems. Let’s explore the tools and techniques you can use to test your wire effectively.
Using a Multimeter
A multimeter is a versatile tool for testing electrical wires. Use it to check for continuity, insulation resistance, and voltage drop. If the wire shows signs of wear or damage, replace it immediately to prevent hazards.
Conducting a Voltage Drop Test
A voltage drop test measures the difference in voltage between two points in a circuit. Excessive voltage drop can indicate that the wire is too thin or damaged. Use this test to ensure your wire is performing optimally.
Visual Inspection
A simple visual inspection can reveal signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Look for cracks, fraying
Buddy Ebsen: The Versatile Entertainer Who Left A Lasting Legacy
Understanding The 40 Amp Wire Gauge: Everything You Need To Know
Jill Vedder: A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Achievements

Wire Ratings For Amps
20 Gauge Wire Amps