Choosing The Right Wire Gauge For 100 Amp Service: A Comprehensive Guide
To answer this question, we must first consider the factors that influence wire gauge selection. Wire gauge refers to the diameter of the conductor, and it directly impacts the amount of current the wire can safely carry. For a 100 amp service, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines, but local regulations and specific installation conditions may also play a role. Copper and aluminum wires, for example, have different conductivity levels, which means their gauge requirements differ. Additionally, the length of the wire run, the type of insulation, and the ambient temperature can all affect the choice of wire gauge. By understanding these variables, you can make an informed decision that aligns with safety standards and your unique needs. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about selecting the right wire gauge for a 100 amp service. From understanding the basics of wire gauges to addressing common questions like "What gauge of wire for 100 amp service is best?" and "How does distance impact wire gauge selection?"—we’ve got you covered. We’ll also delve into practical tips, industry standards, and frequently asked questions to help you navigate this critical aspect of electrical work. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to make confident decisions about your electrical system.
Table of Contents
- What Is Wire Gauge and Why Does It Matter?
- How to Choose the Right Wire Gauge for 100 Amp Service?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Gauge?
- What Does the National Electrical Code Say About Wire Gauge for 100 Amp Service?
- How to Install Wires Safely for a 100 Amp Service?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge for 100 Amp Service
- Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Electrical Needs
What Is Wire Gauge and Why Does It Matter?
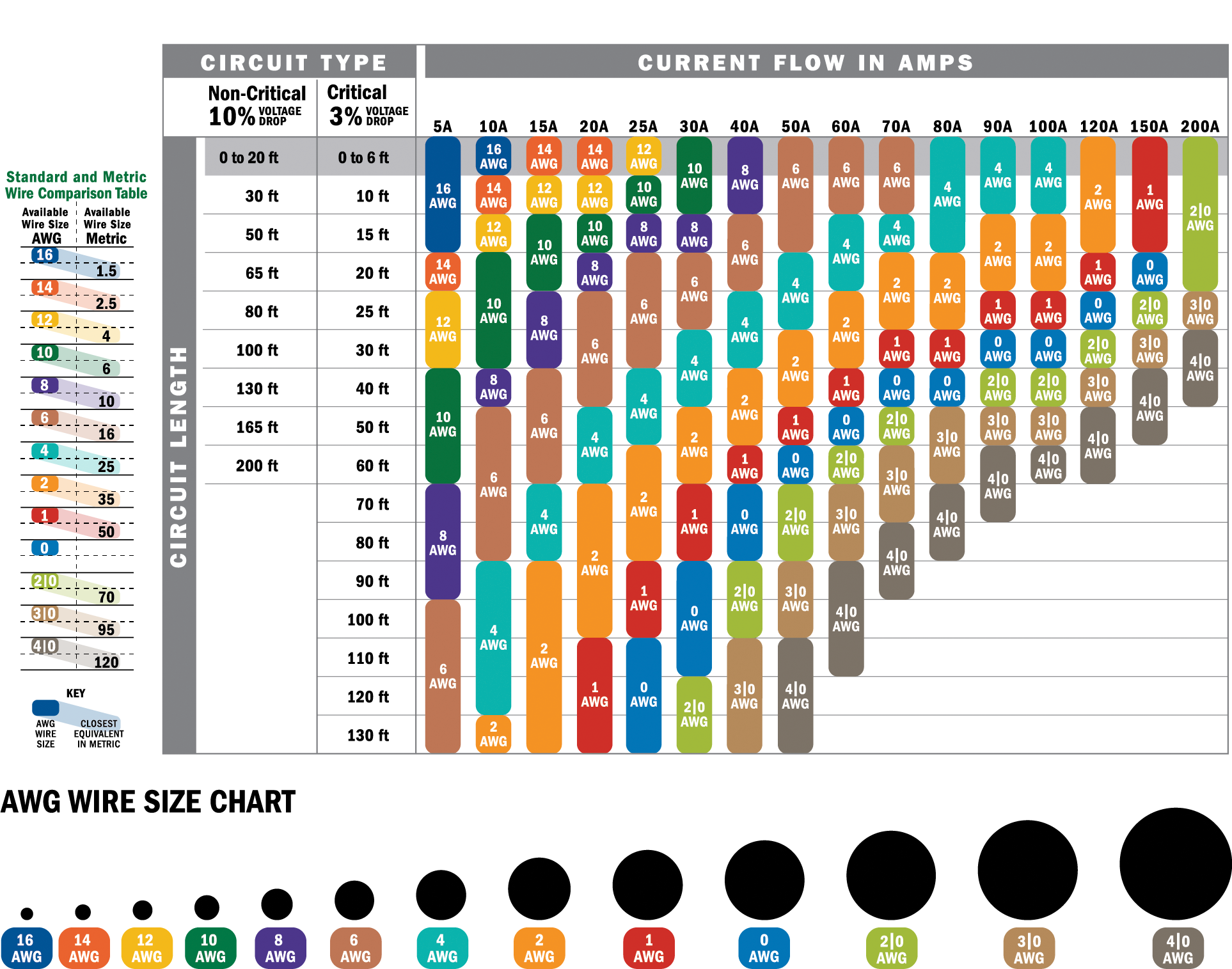
Wire gauge refers to the physical size of the wire's conductor, which determines its current-carrying capacity. Measured using the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire capable of handling more current. For instance, a 2 AWG wire is thicker and can carry more current than a 6 AWG wire. This is particularly important for a 100 amp service, where the wire must safely handle the electrical load without overheating or causing voltage drops.
Choosing the correct wire gauge is not just about meeting code requirements; it’s about ensuring long-term safety and performance. If the wire is too thin, it can overheat, leading to insulation damage or even fire. On the other hand, using a wire that’s excessively thick can be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome to install. Understanding the relationship between wire gauge, current capacity, and safety is essential for any electrical project.
Read also:Who Is Lakiha Spicer Discover The Inspiring Story Of A Rising Star
Several factors influence wire gauge selection, including the type of conductor material (copper or aluminum), the length of the wire run, and environmental conditions like temperature. Copper wires, for example, are more conductive than aluminum, meaning they can carry the same current with a smaller gauge. Similarly, longer wire runs require thicker gauges to compensate for voltage drop, which occurs when electrical resistance reduces the voltage available at the end of the line. By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that balances safety, efficiency, and cost.
How to Choose the Right Wire Gauge for 100 Amp Service?
Selecting the appropriate wire gauge for a 100 amp service involves understanding the specific requirements of your installation. For most residential applications, a 2 AWG copper wire or a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is recommended. These sizes are designed to handle the current load safely while minimizing the risk of overheating or voltage drop. However, the exact gauge may vary depending on factors such as the distance between the power source and the load, the type of insulation, and local building codes.
One of the first steps in choosing the right wire gauge is determining the material of the conductor. Copper wires are more conductive and require smaller gauges compared to aluminum wires, which are less conductive but often more affordable. Additionally, the length of the wire run plays a critical role. Longer runs necessitate thicker wires to prevent voltage drop, which can reduce the efficiency of your electrical system and cause appliances to underperform.
Local regulations and the National Electrical Code (NEC) also provide guidelines for wire gauge selection. These standards are designed to ensure safety and compliance, so it’s essential to consult them before making a decision. By combining technical knowledge with practical considerations, you can select a wire gauge that meets your needs and ensures a reliable electrical system.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which Is Better?
When choosing a wire for a 100 amp service, the debate between copper and aluminum often arises. Copper wires are highly conductive, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making them a popular choice for residential applications. They also require smaller gauges compared to aluminum, which can save space and simplify installation. However, copper wires are more expensive, which can be a limiting factor for some projects.
Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are lighter and more cost-effective. While they are less conductive than copper, they can still handle a 100 amp load if the correct gauge is used (typically 1/0 AWG for aluminum). Aluminum wires are often used in larger installations, such as commercial or industrial settings, where cost savings are a priority. However, they require special connectors and anti-oxidant compounds to prevent corrosion and ensure a secure connection.
Read also:Top Unblocked Car Games For Endless Fun And Thrills
Ultimately, the choice between copper and aluminum depends on your budget, the specific requirements of your project, and local regulations. Both materials can be safe and effective if installed correctly, so it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons before making a decision.
What Is the Impact of Wire Length on Gauge Selection?
The length of the wire run is a critical factor in determining the appropriate gauge for a 100 amp service. Longer wires experience greater electrical resistance, which can lead to voltage drop—a reduction in the voltage available at the end of the line. Voltage drop can cause appliances to operate inefficiently or even fail to function properly, so it’s essential to account for wire length when selecting a gauge.
For example, a 2 AWG copper wire may be sufficient for a short run of 50 feet, but a longer run of 150 feet may require a thicker gauge, such as 1/0 AWG, to compensate for the increased resistance. The NEC recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders to ensure optimal performance. By calculating the voltage drop based on wire length, load, and material, you can determine the appropriate gauge for your installation.
To minimize voltage drop, consider using thicker wires or reducing the length of the run whenever possible. Additionally, upgrading to copper wires can help mitigate resistance issues, as they are more conductive than aluminum. By addressing wire length and voltage drop early in the planning process, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical system.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Gauge?
Choosing the wrong wire gauge for a 100 amp service can lead to serious consequences, including overheating, voltage drop, and fire hazards. To avoid these issues, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes and how to prevent them. One frequent error is underestimating the importance of wire gauge, leading to the selection of a wire that’s too thin for the load. This can cause the wire to overheat, damaging insulation and posing a fire risk.
Another common mistake is ignoring the impact of wire length. Many homeowners assume that a standard gauge will suffice regardless of the distance between the power source and the load. However, longer runs require thicker wires to compensate for voltage drop, and failing to account for this can result in inefficient performance. Additionally, using aluminum wires without proper connectors or anti-oxidant compounds can lead to corrosion and poor connections, which compromise safety and reliability.
To avoid these pitfalls, always consult the NEC guidelines and local building codes. Use a wire gauge calculator to determine the appropriate size based on your specific needs, and consider hiring a licensed electrician if you’re unsure. By taking these precautions, you can ensure a safe and effective electrical installation.
What Does the National Electrical Code Say About Wire Gauge for 100 Amp Service?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides comprehensive guidelines for selecting wire gauges to ensure safety and compliance. For a 100 amp service, the NEC typically recommends a 2 AWG copper wire or a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire. These recommendations are based on the wire’s ability to handle the current load without overheating or causing voltage drop. However, it’s important to note that local regulations may impose additional requirements, so always check with your local building authority.
The NEC also emphasizes the importance of using wires with the appropriate insulation. For example, wires rated for 75°C or 90°C are often required for residential installations, as they can withstand higher temperatures without degrading. Additionally, the code specifies the use of proper connectors and grounding techniques to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
By adhering to NEC guidelines, you can ensure that your electrical system meets industry standards and operates safely. Always consult the latest edition of the NEC and seek professional advice if you’re unsure about specific requirements for your project.
How to Install Wires Safely for a 100 Amp Service?
Installing wires for a 100 amp service requires careful planning and execution to ensure safety and compliance. Start by selecting the appropriate wire gauge and material based on your load requirements, wire length, and local regulations. Once you’ve chosen the wire, gather the necessary tools and equipment, such as wire strippers, connectors, and a voltage tester, to complete the installation.
Before beginning the installation, turn off the power at the main breaker to prevent electrical shocks. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the circuit is de-energized, and follow all safety precautions outlined in the NEC. When running the wire, ensure it is properly supported and protected from physical damage, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Use conduit or raceways where necessary to safeguard the wire.
Finally, make all connections securely and use anti-oxidant compounds for aluminum wires to prevent corrosion. Double-check your work to ensure there are no loose connections or exposed wires. By following these steps, you can install wires safely and effectively for a 100 amp service.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Installation
Proper tools and equipment are essential for a successful wire installation. Some of the key tools include wire strippers, crimping tools, and a multimeter for testing connections. Additionally, conduit benders and fish tape can be helpful for running wires through tight spaces. Always use tools that are rated for electrical work to ensure safety and reliability.
Safety Tips to Keep in Mind
Safety should always be your top priority when working with electrical systems. Wear protective gear, such as insulated gloves and safety glasses, and ensure the power is turned off before starting any work. Use a voltage tester to confirm that circuits are de-energized, and follow all NEC guidelines for wiring and grounding.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge for 100 Amp Service
What gauge of wire for 100 amp service is recommended? For most residential applications,
Discover The Best Gift Ideas At Vanulla Gift.com
Who Is Buddy Ebsen's Son? Discovering The Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon
Who Is Misty Copeland Married To? Discovering The Life Of The Ballet Star
What Gauge Wire For 20 Amp Service

Wire Gauge Chart