Comprehensive Guide To Wire Chart For Amperage: Everything You Need To Know
When it comes to electrical safety and efficiency, understanding the wire chart for amperage is critical for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. Electrical systems rely on wires to carry current, and selecting the correct wire gauge is essential to prevent overheating, fires, or system failures. The wire chart for amperage serves as a guide to determine the appropriate wire size based on the current load and application. Without this knowledge, even a small error can lead to significant risks, making it vital to grasp the fundamentals of wire sizing and amperage.
Whether you're wiring a new home, installing appliances, or working on an industrial project, the wire chart for amperage ensures that your electrical setup is safe and compliant with standards. This guide will delve into the intricacies of wire charts, explaining how they work, why they matter, and how to use them effectively. We'll also explore practical tips, FAQs, and expert advice to help you make informed decisions.
By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of wire charts for amperage, enabling you to tackle electrical projects with confidence. From decoding wire gauges to exploring the factors that influence amperage capacity, this guide is your go-to resource for mastering this essential aspect of electrical engineering.
Read also:Rick Moranis A Comprehensive Look At The Comedy Legends Life And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is a Wire Chart for Amperage and Why is it Important?
- How to Read a Wire Chart for Amperage?
- Factors Affecting Amperage Capacity
- How Do I Choose the Right Wire Gauge for My Project?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Wire Charts
- What Are the Safety Implications of Wrong Wire Gauge?
- Applications of Wire Charts in Different Industries
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Charts
What is a Wire Chart for Amperage and Why is it Important?
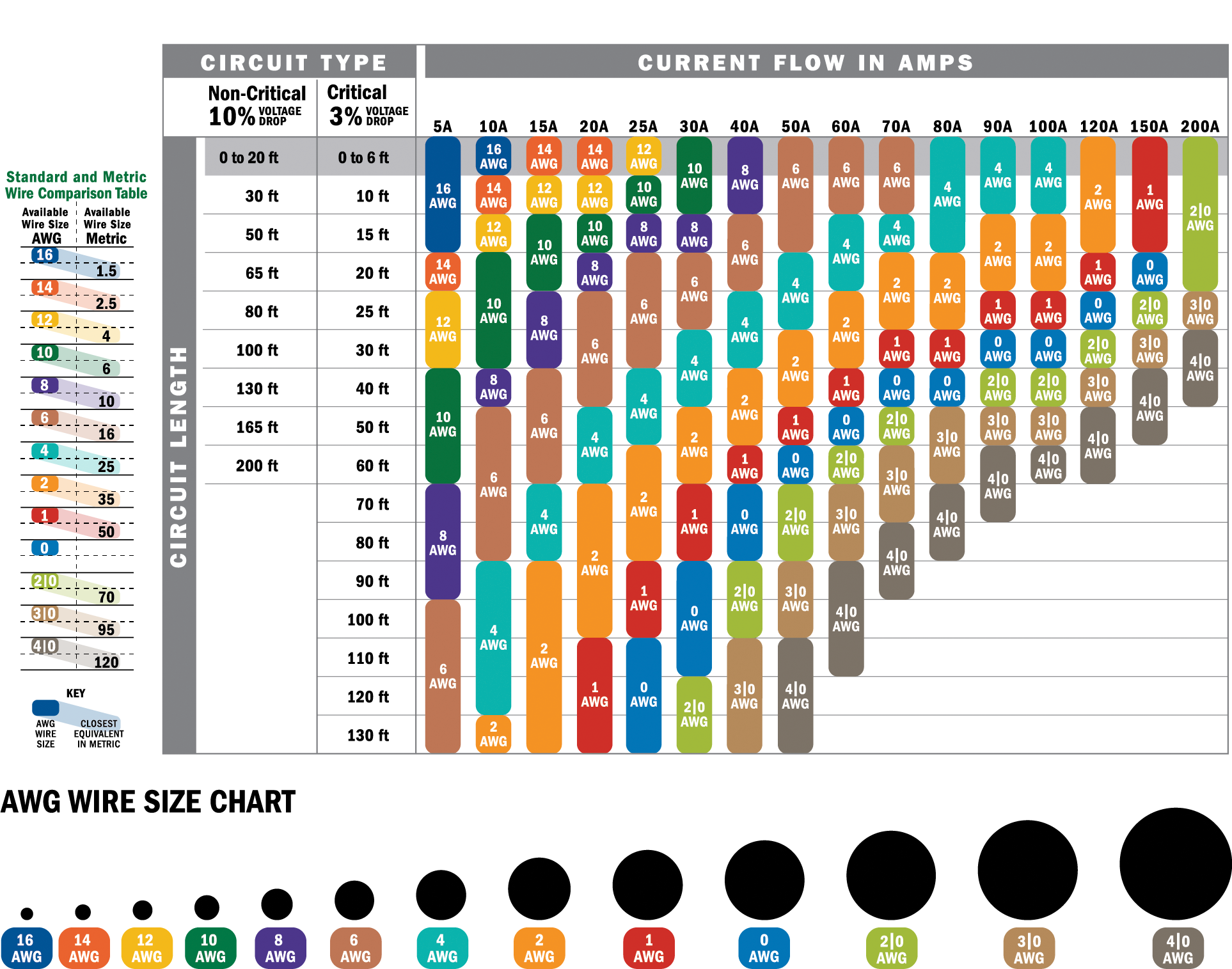
A wire chart for amperage is a standardized reference tool used to determine the appropriate wire gauge for a given electrical load. It provides a clear relationship between wire size, amperage capacity, and other factors such as voltage drop and temperature. This chart is essential for ensuring that electrical systems operate safely and efficiently, minimizing risks such as overheating, voltage drops, and potential fires.
The importance of a wire chart for amperage cannot be overstated. Electrical systems are designed to carry specific loads, and using the wrong wire gauge can lead to inefficiencies or catastrophic failures. For instance, a wire that is too thin for the current it carries will overheat, potentially causing insulation damage or even igniting a fire. Conversely, using a wire that is unnecessarily thick can lead to wasted resources and higher costs.
By consulting a wire chart for amperage, electricians and engineers can ensure that their projects meet safety standards and regulatory requirements. This tool is particularly useful in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, where electrical demands vary significantly. Understanding how to interpret and apply this chart is a foundational skill for anyone working with electrical systems.
How to Read a Wire Chart for Amperage?
Reading a wire chart for amperage may seem daunting at first, but with a little practice, it becomes second nature. The chart typically lists wire gauges (measured in AWG or American Wire Gauge) alongside their corresponding amperage capacities. Additional columns may include factors such as voltage drop, conductor material (copper or aluminum), and ambient temperature.
Key Components of a Wire Chart for Amperage
- Wire Gauge: The thickness of the wire, measured in AWG. Lower numbers indicate thicker wires, which can carry more current.
- Amperage Capacity: The maximum current a wire can safely carry without overheating.
- Conductor Material: Copper wires generally have higher amperage capacities compared to aluminum wires of the same gauge.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher temperatures reduce a wire's ability to carry current safely.
How Do I Interpret the Data?
To interpret the data, start by identifying the amperage requirement of your project. Next, locate the corresponding wire gauge that can handle this load while considering factors like conductor material and ambient temperature. For example, a 10 AWG copper wire can typically handle up to 30 amps in a standard environment, but this capacity decreases in hotter conditions.
Understanding these nuances ensures that you select the right wire for your application, balancing safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Read also:Dawn Wells Measurements A Complete Guide To Her Life And Career
Factors Affecting Amperage Capacity
Several factors influence the amperage capacity of a wire, and understanding these variables is crucial for making informed decisions. Below, we explore the key factors that affect how much current a wire can safely carry.
Conductor Material
The material of the conductor plays a significant role in determining amperage capacity. Copper is the most commonly used material due to its excellent conductivity and durability. Aluminum, while lighter and less expensive, has lower conductivity and requires larger gauges to carry the same current as copper.
Ambient Temperature
Higher ambient temperatures reduce the safe amperage capacity of a wire. For example, a wire rated for 20 amps at 75°C may only be safe for 15 amps at 90°C. This is why wire charts often include temperature correction factors.
Length of the Wire
The length of the wire affects voltage drop, which in turn impacts amperage capacity. Longer wires require thicker gauges to maintain the same level of performance, as resistance increases with length.
Insulation Type
Different insulation materials have varying temperature ratings, which influence the wire's amperage capacity. For instance, THHN insulation is rated for higher temperatures than PVC, allowing for greater current-carrying capacity.
How Do I Choose the Right Wire Gauge for My Project?
Selecting the correct wire gauge is a critical step in any electrical project. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the right choice.
Step 1: Determine the Amperage Requirement
Calculate the total current your circuit will carry. This information is usually available on the device or appliance you’re connecting. For example, a 15-amp circuit breaker requires a wire gauge that can handle at least 15 amps.
Step 2: Consult the Wire Chart for Amperage
Using the wire chart for amperage, find the gauge that matches your amperage requirement. Ensure you account for factors like conductor material and ambient temperature.
Step 3: Factor in Voltage Drop
For long runs, calculate the voltage drop to ensure it stays within acceptable limits (typically 3% for branch circuits). If the drop is too high, consider using a thicker wire gauge.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Wire Charts
While wire charts for amperage are invaluable tools, mistakes in their application can lead to serious consequences. Below are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
Ignoring Temperature Ratings
Many people overlook the impact of ambient temperature on wire capacity. Always check the temperature correction factors provided in the wire chart.
Underestimating Voltage Drop
Failing to account for voltage drop in long wire runs can result in inefficient performance. Use a voltage drop calculator or consult the wire chart for guidance.
Using the Wrong Conductor Material
Assuming aluminum wires have the same capacity as copper wires can lead to undersized wiring. Always specify the conductor material when consulting the chart.
What Are the Safety Implications of Wrong Wire Gauge?
Using the wrong wire gauge can have severe safety implications, ranging from overheating to electrical fires. Here’s a closer look at the risks involved.
Overheating and Fire Hazards
A wire that is too thin for the current it carries will overheat, potentially melting the insulation and causing a fire. This is why adhering to the wire chart for amperage is non-negotiable.
Equipment Damage
Undersized wires can lead to voltage drops, which may damage sensitive equipment or cause it to malfunction.
Regulatory Non-Compliance
Using incorrect wire gauges can result in violations of electrical codes, leading to fines or project shutdowns.
Applications of Wire Charts in Different Industries
Wire charts for amperage are used across various industries to ensure safe and efficient electrical systems. Below are some examples of their applications.
Residential Wiring
In homes, wire charts help electricians determine the correct gauge for outlets, lighting, and appliances.
Automotive Industry
Automotive wiring requires precise calculations to ensure reliability and safety, especially in electric vehicles.
Industrial Settings
In factories, wire charts are used to design circuits for heavy machinery and equipment, ensuring they operate safely under high loads.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Charts
What is the Difference Between AWG and SWG?
AWG (American Wire Gauge) and SWG (Standard Wire Gauge) are two systems for measuring wire thickness. AWG is more commonly used in the U.S., while SWG is prevalent in the U.K.
Can I Use a Higher Gauge Wire Than Recommended?
Yes, using a higher gauge wire (thicker) is safe and often recommended for long runs or high-temperature environments.
Where Can I Find a Reliable Wire Chart for Amperage?
Reliable wire charts are available from electrical manufacturers, industry standards organizations, and reputable online resources like the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Learn more about the National Electrical Code (NEC) here.
Conclusion
Understanding and utilizing a wire chart for amperage is essential for anyone involved in electrical work. From ensuring safety to optimizing performance, this tool is indispensable for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can confidently select the right wire gauge for your projects, avoiding common pitfalls and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Remember, electrical safety is not something to take lightly. Always consult a wire chart for amperage, and when in doubt, seek advice from a qualified electrician. With the right knowledge and tools, you can create electrical systems that are safe, efficient, and built to last.
What Is The Easiest Way To Identify Gold: A Comprehensive Guide
Stay Cool And Cozy: The Ultimate Guide To Summer Comforters Lightweight
Fortnite Default Outfit: Exploring The Iconic Look And Its Evolution

House Wiring Amperage Chart Wiring Flow Line
Wire Gauge Size Chart Actual Size Amperage