The Main Difference Between Ponds And Lakes Is That Ponds Are Shallower: A Complete Guide
Have you ever wondered why some bodies of water are called ponds while others are referred to as lakes? The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are typically shallower and smaller in size, which significantly impacts the ecosystems they support. This distinction might seem subtle at first glance, but it plays a crucial role in how these water bodies interact with their surroundings. Understanding the nuances between ponds and lakes can help us better appreciate their ecological importance and the unique characteristics they bring to the environment.
While both ponds and lakes are freshwater ecosystems, their depth, size, and biodiversity differ in fascinating ways. Ponds are often small enough to allow sunlight to penetrate through to the bottom, fostering a rich variety of plant and animal life. Lakes, on the other hand, are deeper and larger, creating distinct zones where different organisms thrive. These differences not only affect the flora and fauna but also influence how humans interact with these bodies of water for recreation, agriculture, and conservation.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll uncover the science behind these differences, explore their ecological significance, and address common questions about ponds and lakes. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what sets ponds apart from lakes and why these distinctions matter. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a student, or simply curious, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of freshwater ecosystems.
Read also:Exploring The Most Dangerous Cities In The World Risks Realities And Resilience
Table of Contents
- What Makes a Pond Different from a Lake?
- How Do Ponds and Lakes Support Life?
- Why Are Ponds Shallower Than Lakes?
- Can You Really Tell a Pond from a Lake?
- What Are the Ecological Roles of Ponds?
- How Do Human Activities Impact Ponds and Lakes?
- What Are Some Fascinating Facts About Ponds?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Ponds and Lakes
What Makes a Pond Different from a Lake?
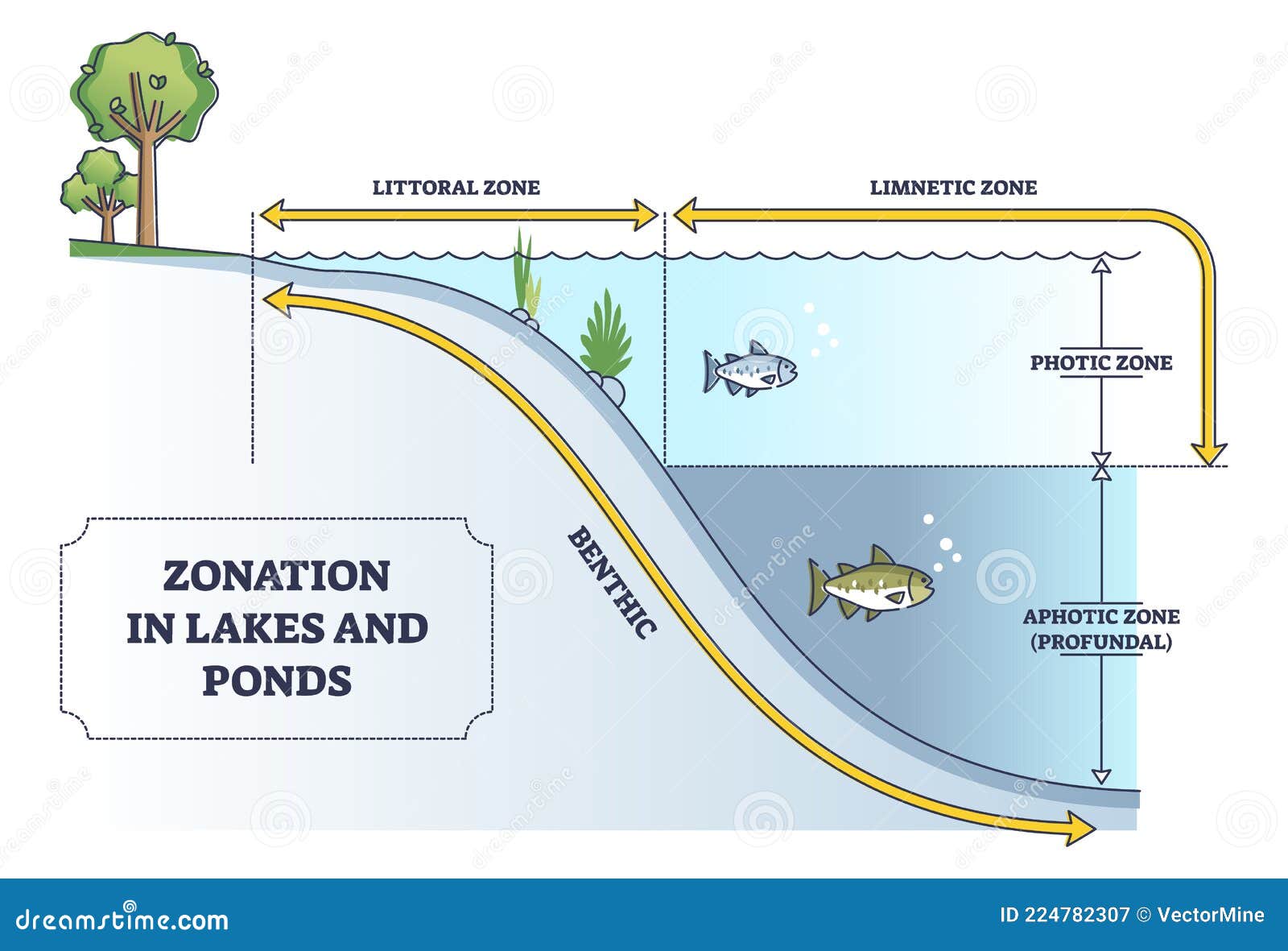
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are shallower and often smaller, which influences their temperature, light penetration, and biodiversity. While lakes can reach depths of hundreds of feet, ponds are typically less than 15 feet deep. This shallow depth allows sunlight to reach the bottom, creating an environment where aquatic plants can grow throughout the water body. In contrast, lakes have deeper zones where sunlight cannot penetrate, leading to distinct layers of temperature and oxygen levels.
Another key distinction lies in the way these ecosystems support life. Ponds are often teeming with plant life, from algae to rooted vegetation, due to their shallow nature. These plants provide food and shelter for a variety of animals, including fish, amphibians, and insects. Lakes, being larger and deeper, support a broader range of species, including those adapted to colder, darker waters. The biodiversity in lakes is often more complex, with different species occupying specific zones based on depth and temperature.
Understanding these differences is essential for conservation efforts. Ponds, for instance, are more vulnerable to pollution and changes in water quality because of their smaller size and shallower depth. Lakes, while more resilient, are still susceptible to issues like eutrophication and invasive species. By recognizing the unique characteristics of ponds and lakes, we can develop better strategies to protect these vital ecosystems.
How Do Ponds and Lakes Support Life?
Both ponds and lakes are teeming with life, but the types of organisms they support differ due to their unique characteristics. In ponds, the abundance of sunlight and plant life creates a thriving ecosystem for amphibians, insects, and small fish. Frogs, turtles, and dragonflies are commonly found in ponds, where they rely on the dense vegetation for shelter and food. The shallow waters also make ponds ideal breeding grounds for many species, contributing to their role as biodiversity hotspots.
What Types of Plants Thrive in Ponds?
Ponds are home to a variety of aquatic plants, including water lilies, duckweed, and cattails. These plants not only provide oxygen and food for aquatic life but also help stabilize the pond’s ecosystem by preventing erosion and filtering pollutants. Water lilies, for example, float on the surface and offer shade, which helps regulate water temperature. Duckweed, on the other hand, grows rapidly and serves as a food source for fish and birds.
How Do Lakes Differ in Supporting Aquatic Life?
Lakes, being larger and deeper, support a wider range of species, including larger fish like bass and trout. The deeper zones of lakes, known as the profundal zone, are home to organisms adapted to low-light conditions, such as certain types of algae and bacteria. Additionally, lakes often serve as habitats for migratory birds, which rely on them as stopover points during long journeys. The diverse ecosystems in lakes make them crucial for maintaining global biodiversity.
Read also:What Kind Of Cancer Did Melanie Olmstead Have A Comprehensive Guide
Why Are Ponds Shallower Than Lakes?
The shallow nature of ponds is one of their defining features and plays a significant role in their ecological dynamics. Ponds are typically formed in depressions on the Earth’s surface, often as a result of glacial activity, tectonic shifts, or human intervention. Their shallowness allows sunlight to penetrate the entire water column, promoting photosynthesis and supporting a rich variety of plant life. This, in turn, creates a habitat that is highly productive and biodiverse.
In contrast, lakes are usually formed by more complex geological processes, such as volcanic activity or the melting of glaciers. These processes often result in deeper basins that can hold larger volumes of water. The depth of lakes creates distinct thermal layers, such as the epilimnion (upper layer), metalimnion (middle layer), and hypolimnion (bottom layer). These layers influence the distribution of oxygen and nutrients, shaping the types of organisms that can survive in each zone.
The shallow depth of ponds also makes them more susceptible to environmental changes. For instance, temperature fluctuations in ponds are more pronounced due to their smaller volume of water. This can affect the organisms living in them, making ponds both highly productive and vulnerable to external pressures like pollution and climate change.
Can You Really Tell a Pond from a Lake?
Distinguishing between a pond and a lake isn’t always straightforward, as the definitions can vary depending on regional and scientific criteria. However, there are some general guidelines that can help. Ponds are typically smaller and shallower, with sunlight reaching the bottom and supporting rooted vegetation throughout. Lakes, on the other hand, are larger and deeper, often with areas where sunlight cannot penetrate, leading to zones with little to no plant life.
What Are the Visual Differences?
Visually, ponds often appear more uniform, with clear visibility of the bottom in many areas. Lakes, due to their size and depth, often have a darker appearance and may exhibit wave action on the surface. Additionally, lakes are more likely to have distinct shorelines and surrounding vegetation, while ponds may blend seamlessly into their surroundings.
How Do Scientists Classify Ponds and Lakes?
Scientists use a combination of factors to classify water bodies, including depth, surface area, and the presence of certain plant and animal species. For example, a water body might be classified as a pond if it is less than 15 feet deep and supports rooted vegetation throughout. Lakes, in contrast, are typically deeper and may have areas where sunlight does not reach the bottom. These classifications help researchers study and manage freshwater ecosystems more effectively.
What Are the Ecological Roles of Ponds?
Ponds play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance, serving as habitats for a wide range of species and acting as natural water filters. Their shallow depth and abundant plant life make them ideal for supporting amphibians, insects, and small fish, many of which are crucial for food webs. Additionally, ponds help regulate water flow in the surrounding landscape, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion.
How Do Ponds Contribute to Biodiversity?
- Ponds provide breeding grounds for amphibians like frogs and salamanders.
- They support a variety of insect species, including dragonflies and mosquitoes.
- Ponds act as stopover points for migratory birds, offering food and rest.
What Are the Benefits of Ponds for Humans?
Beyond their ecological importance, ponds offer numerous benefits to humans. They are often used for irrigation, aquaculture, and recreation, such as fishing and boating. Additionally, ponds can improve water quality by filtering pollutants and sediments, making them valuable for both urban and rural communities.
How Do Human Activities Impact Ponds and Lakes?
Human activities have a significant impact on both ponds and lakes, often leading to pollution, habitat destruction, and the introduction of invasive species. Runoff from agriculture and urban areas can introduce excess nutrients into these water bodies, causing issues like algal blooms and oxygen depletion. Additionally, deforestation and land development can increase sedimentation, further degrading water quality.
Efforts to mitigate these impacts include implementing sustainable land-use practices, restoring damaged ecosystems, and educating communities about the importance of freshwater conservation. By taking proactive measures, we can ensure that ponds and lakes continue to thrive and support the diverse life forms that depend on them.
What Are Some Fascinating Facts About Ponds?
Ponds are more than just small bodies of water; they are dynamic ecosystems with a wealth of intriguing features. Did you know that some ponds are temporary, forming only during certain seasons and drying up completely in others? These ephemeral ponds are vital for species that have adapted to their cyclical nature. Additionally, ponds are often home to rare and endangered species, making their conservation even more critical.
Another fascinating fact is that ponds can serve as natural laboratories for scientists studying climate change and biodiversity. Their small size and sensitivity to environmental changes make them ideal for monitoring shifts in ecosystems. By studying ponds, researchers can gain valuable insights into the health of larger water bodies and the planet as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ponds and Lakes
What Is the Main Difference Between Ponds and Lakes?
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are shallower and smaller, allowing sunlight to penetrate to the bottom and support rooted vegetation throughout. Lakes, on the other hand, are deeper and larger, often with areas where sunlight cannot reach.
Are Ponds More Vulnerable to Pollution Than Lakes?
Yes, ponds are generally more vulnerable to pollution due to their smaller size and shallower depth. Changes in water quality can have a more immediate and pronounced impact on pond ecosystems.
Can Ponds Turn Into Lakes Over Time?
While ponds can grow larger over time due to natural processes like sedimentation, they typically remain distinct from lakes in terms of depth and ecological characteristics. However, human intervention, such as damming or excavation, can transform a pond into a lake.
In conclusion, understanding the main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds are shallower provides valuable insights into their ecological roles and the challenges they face. By appreciating these distinctions, we can better protect and conserve these vital freshwater ecosystems for future generations. For more information on freshwater ecosystems, you can explore resources like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Water Page.
How Much Is Gucci Mane Worth In 2023? A Deep Dive Into His Net Worth And Career
What Size Wire For 40 Amp: A Complete Guide To Electrical Wiring
Moneybagg Yo Net Worth: A Comprehensive Guide To His Wealth And Success

Lakes+Ponds Housatonic Heritage
Pictures Of Lakes And Ponds