What Size Wire Do You Need For 100 Amps? A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100-amp electrical service is crucial for safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Whether you're planning a new installation or upgrading an existing system, understanding the factors that influence wire selection can save you from costly mistakes and potential hazards. Wires that are too small can overheat, leading to fires, while oversized wires can unnecessarily increase costs without providing additional benefits. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about selecting the right wire size for 100-amp service, ensuring your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
When it comes to electrical systems, the size of the wire directly affects its ability to carry current safely. For a 100-amp service, the wire gauge must be carefully chosen based on factors like the distance of the run, the material of the wire (copper or aluminum), and the ambient temperature. Copper wires are generally preferred for their superior conductivity, but aluminum wires are a cost-effective alternative in certain scenarios. Understanding these variables will help you make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls.
Additionally, local building codes and the National Electrical Code (NEC) provide guidelines that must be followed to ensure safety and compliance. These codes specify minimum wire sizes for different amperage levels, but they also allow for adjustments based on specific conditions. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of what size wire you need for 100 amps, empowering you to tackle your electrical projects with confidence.
Read also:Exploring The Legacy Of Norma Strait A Journey Through Time
Table of Contents
- What Size Wire Do You Need for 100 Amps?
- Why Is Wire Size Important for Electrical Safety?
- How Does Distance Affect Wire Size Selection?
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Which Is Better for 100 Amps?
- What Are the Local Codes and Standards to Follow?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Service?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Size for 100 Amps
What Size Wire Do You Need for 100 Amps?
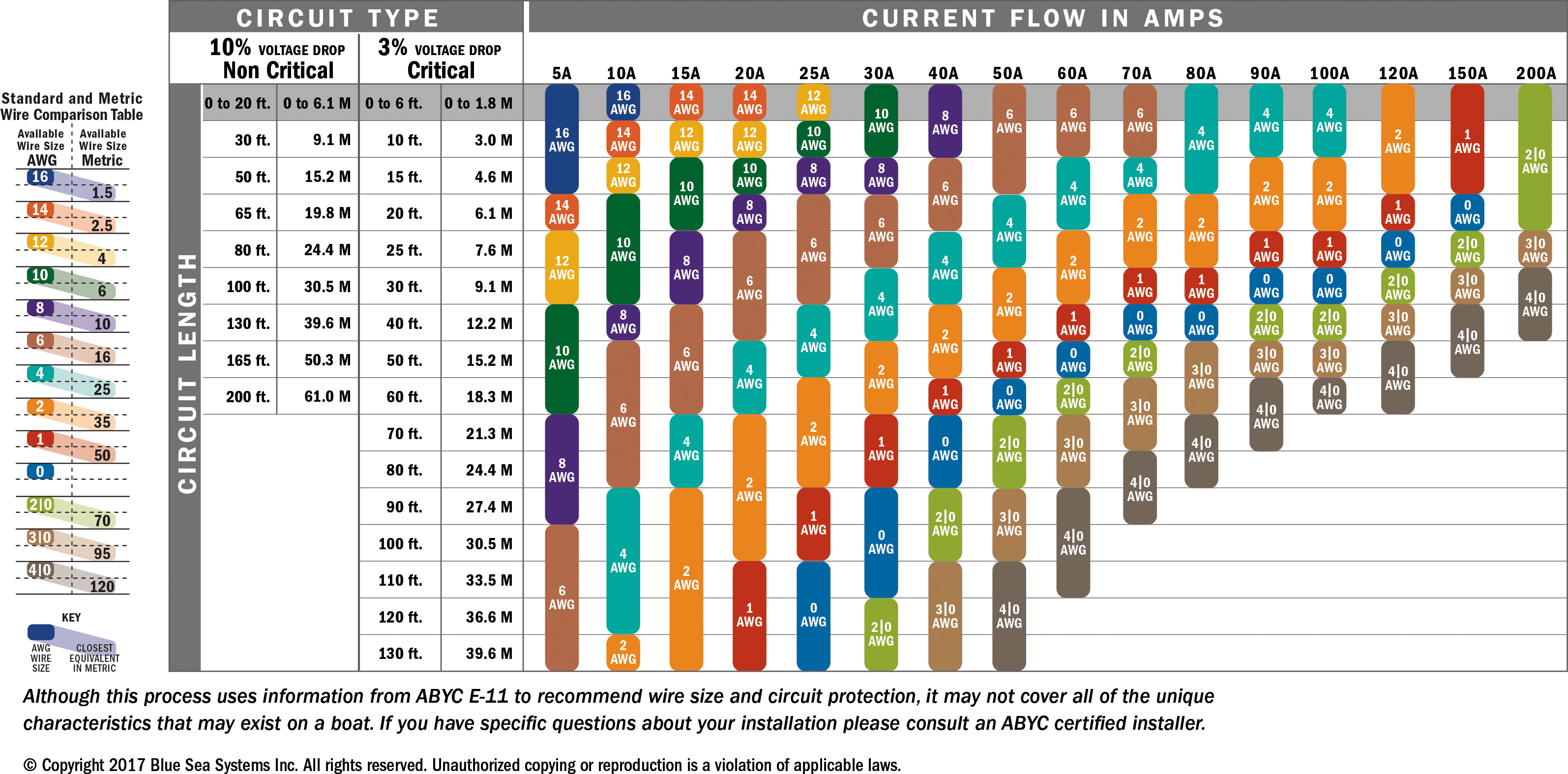
Selecting the appropriate wire size for a 100-amp service is a decision that requires careful consideration. For most residential applications, a 100-amp service is common, and the wire size typically falls within a specific range. According to the NEC, a 100-amp service generally requires a minimum of 3 AWG copper wire or 1 AWG aluminum wire. These sizes ensure that the wire can safely handle the current without overheating.
However, the actual wire size you need may vary depending on several factors. For example, if your electrical panel is located far from the meter, you may need to increase the wire size to compensate for voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels through the circuit. To minimize this, thicker wires are often used for longer runs.
Another consideration is the type of insulation on the wire. Wires with higher temperature ratings (such as THHN or XHHW) can carry more current than those with lower ratings. This means you might be able to use a slightly smaller wire if it has a high-temperature rating. Always consult the NEC or a licensed electrician to ensure compliance with local codes and safety standards.
Why Is Wire Size Important for Electrical Safety?
Wire size plays a critical role in maintaining electrical safety. When a wire is too small for the current it needs to carry, it can overheat, melt its insulation, and potentially cause a fire. This is why selecting the correct wire size for 100 amps is not just a matter of efficiency but also a matter of safety.
Overheating occurs because electrical resistance generates heat. The smaller the wire, the higher the resistance, and the more heat it produces. For a 100-amp service, using a wire that is too small can lead to a dangerous situation where the wire becomes a fire hazard. This is why the NEC mandates specific wire sizes for different amperage levels.
Besides preventing overheating, proper wire sizing also ensures that your electrical system operates efficiently. Undersized wires can lead to voltage drop, which can cause appliances and devices to underperform or fail. On the other hand, oversized wires, while safer, can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with. Striking the right balance is key to a safe and efficient electrical system.
Read also:Who Is Patricia Brights Husband A Deep Dive Into Her Personal Life And Influence
How Does Distance Affect Wire Size Selection?
One of the most overlooked factors when selecting wire size is the distance between the power source and the load. For a 100-amp service, longer runs require larger wires to compensate for voltage drop. Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage as electricity travels through a conductor, and it becomes more significant over longer distances.
What Is Voltage Drop and Why Does It Matter?
Voltage drop occurs because all wires have some level of resistance. As electricity flows through the wire, this resistance causes a loss of voltage. For a 100-amp service, even a small voltage drop can affect the performance of appliances and devices. The NEC recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders to ensure optimal performance.
How to Choose the Right Wire Size for Long Runs?
To choose the right wire size for long runs, you need to calculate the voltage drop based on the distance, current, and wire material. For example, if you're running a 100-amp service 100 feet from the meter to the panel, you may need to upgrade from 3 AWG copper to 1 AWG copper to maintain acceptable voltage levels. Using an online voltage drop calculator or consulting a professional electrician can help you make the right choice.
Copper vs. Aluminum: Which Is Better for 100 Amps?
When selecting wire for a 100-amp service, you'll need to decide between copper and aluminum. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice often comes down to cost, application, and personal preference.
Copper is the preferred material for most residential applications due to its superior conductivity. It can carry more current than aluminum of the same size, making it ideal for 100-amp services. Copper wires are also more resistant to corrosion and have a longer lifespan, which adds to their appeal.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is a more cost-effective option. While it is less conductive than copper, aluminum wires are lighter and easier to work with in certain situations. However, they require larger sizes to carry the same current as copper, and they are more prone to oxidation, which can lead to connection issues over time. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial when using aluminum wires.
What Are the Local Codes and Standards to Follow?
Local building codes and the NEC provide the framework for safe and compliant electrical installations. These codes specify the minimum wire sizes for different amperage levels, including 100-amp services. However, they also allow for adjustments based on specific conditions, such as distance and temperature.
Why Should You Always Check Local Codes?
Local codes may vary from the NEC, so it's essential to check with your local building authority before starting any electrical project. Some areas may have stricter requirements, while others may allow for exceptions. Failing to comply with local codes can result in fines, delays, and even the need to redo the work.
What Are the Key NEC Guidelines for 100-Amp Service?
The NEC provides a table of wire sizes for different amperage levels, including 100 amps. For copper wires, the minimum size is typically 3 AWG, while for aluminum, it's 1 AWG. These guidelines are designed to ensure safety and efficiency, but they should be viewed as a starting point rather than the final word.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Service?
Calculating voltage drop is an essential step in selecting the right wire size for a 100-amp service. Voltage drop can affect the performance of your electrical system, so it's important to keep it within acceptable limits.
The formula for calculating voltage drop is straightforward: Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000. The length is the distance of the run in feet, the current is the amperage, and the resistance is based on the wire material and size. Online calculators are available to simplify this process.
For example, if you're running a 100-amp service 150 feet with 3 AWG copper wire, the voltage drop might exceed the recommended 3%. In this case, upgrading to 1 AWG copper would reduce the voltage drop and ensure optimal performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size
Even experienced DIYers and electricians can make mistakes when selecting wire size for a 100-amp service. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Ignoring Voltage Drop: Failing to account for voltage drop can lead to underperforming appliances and devices.
- Using Undersized Wires: Undersized wires can overheat and pose a fire hazard.
- Overlooking Local Codes: Always check local building codes to ensure compliance.
- Choosing the Wrong Material: Copper and aluminum have different properties, so choose the right one for your application.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Size for 100 Amps
What Happens If You Use the Wrong Wire Size for 100 Amps?
Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and even fire hazards. Always consult the NEC or a licensed electrician to ensure safety.
Can You Use Aluminum Wire for 100-Amp Service?
Yes, but aluminum wires require larger sizes to carry the same current as copper. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to avoid connection issues.
How Do You Know If Your Wire Size Is Correct?
Check the NEC guidelines, calculate voltage drop, and consult a professional electrician to ensure your wire size is appropriate for your 100-amp service.
In conclusion, selecting the correct wire size for a 100-amp service is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of several factors. By understanding the importance of wire size, calculating voltage drop, and following local codes, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical system. Always consult a licensed electrician if you're unsure about any aspect of your electrical project.
For more information on electrical safety, visit the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
Who Is Larry Ellison's Wife? A Deep Dive Into Her Life And Influence
Discovering The Talent Of Benicio Del Toro: A Journey Through His Life And Career
Rafe Cameron Haircut: The Ultimate Guide To Style And Inspiration

Wire Size Chart For Amps And Volts
Wire Size For 90 Amps