What Size Wire For A 100 Amp Panel: A Complete Guide
Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical panel or installing a new one, understanding the correct wire gauge is essential. Using an incorrect wire size can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or insufficient power delivery. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about selecting the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp panel, ensuring compliance with electrical codes and maximizing safety. Proper wire sizing is determined by several factors, including the distance between the panel and the power source, the material of the wire (copper or aluminum), and the specific requirements of your electrical setup. For instance, copper wires are more conductive and can carry more current than aluminum wires of the same gauge, meaning you may need a larger gauge for aluminum. Additionally, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines to ensure safe installations, and local building codes may impose further restrictions. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision and avoid costly mistakes. In this article, we’ll explore the technical details of wire sizing, answer common questions like "What size wire for a 100 amp panel is best for long-distance runs?" and provide practical advice for homeowners and electricians alike. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of the wire size requirements for a 100 amp panel and how to ensure your installation is both safe and efficient.
Table of Contents
- Why Is Wire Size Important for a 100 Amp Panel?
- What Size Wire for a 100 Amp Panel Is Recommended by the NEC?
- How Does Distance Affect the Wire Size for a 100 Amp Panel?
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Which Is Better for a 100 Amp Panel?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for a 100 Amp Panel?
- Tools and Resources for Selecting the Right Wire Size
- FAQ About Wire Size for a 100 Amp Panel
Why Is Wire Size Important for a 100 Amp Panel?
Selecting the correct wire size for a 100 amp panel is critical for maintaining the safety and functionality of your electrical system. The wire gauge determines how much current the wire can safely carry without overheating. If the wire is too small for the load, it can overheat, melt the insulation, and potentially cause a fire. On the other hand, using a wire that is unnecessarily large can lead to wasted materials and higher costs.
Several factors contribute to the importance of wire size. First, the electrical load of your home or building must match the capacity of the wire. For example, a 100 amp panel requires a wire size that can handle up to 100 amps of current without exceeding the safe temperature threshold. Second, local building codes and the NEC set standards to ensure that installations are safe and reliable. These codes specify minimum wire sizes for different applications, and failing to comply can result in fines or unsafe conditions.
Read also:Unlock The Fun Infinite Craft Unblocked Ndash The Ultimate Guide
Another key consideration is the material of the wire. Copper and aluminum have different conductivity levels, which affect the required wire gauge. Copper wires are more efficient and can carry more current than aluminum wires of the same size. Therefore, the choice of material directly impacts the wire size you need. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions and avoid potential hazards.
What Size Wire for a 100 Amp Panel Is Recommended by the NEC?
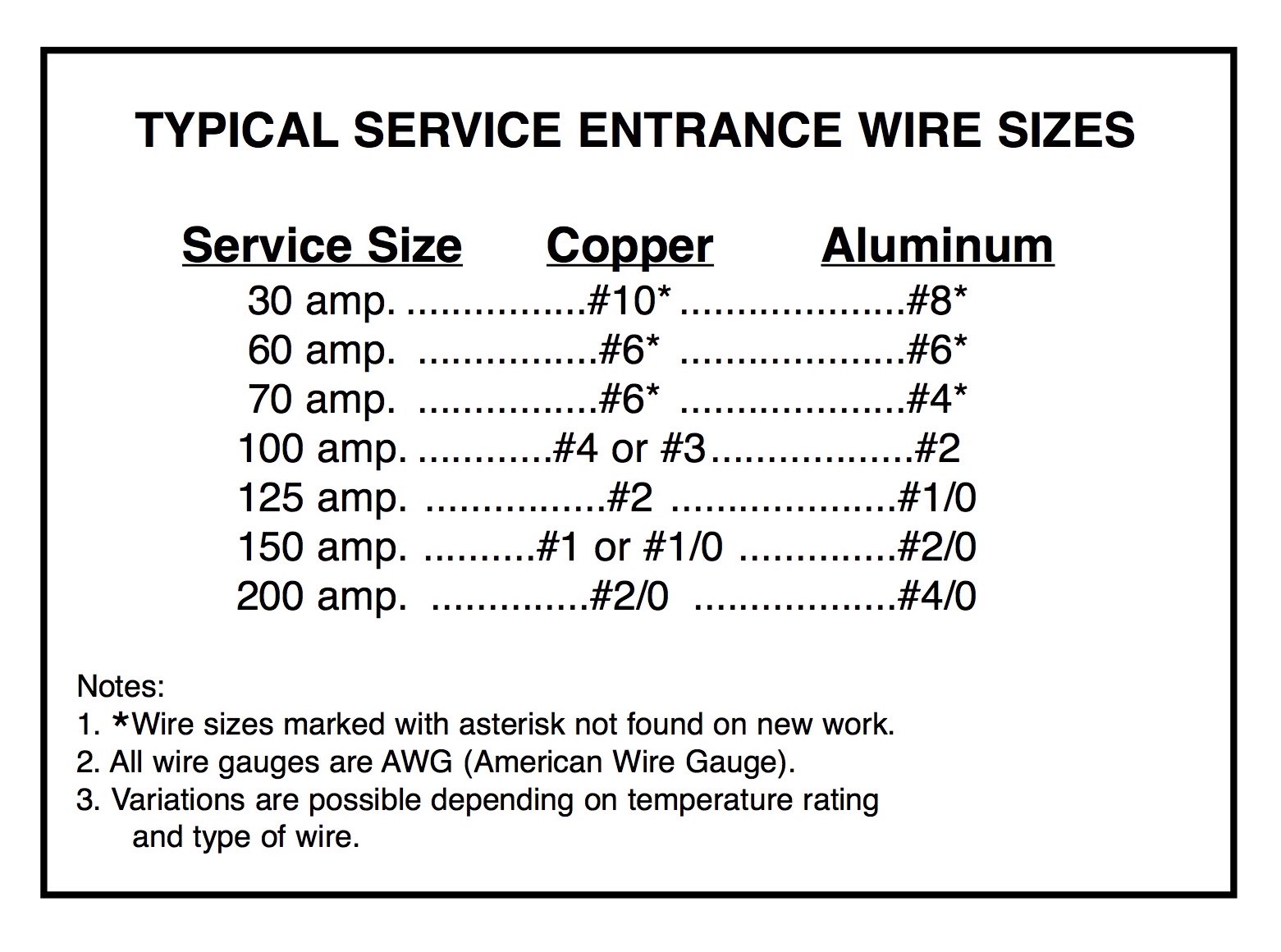
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides clear guidelines for wire sizing to ensure safe electrical installations. For a 100 amp panel, the NEC typically recommends using a #3 AWG copper wire or a #1 AWG aluminum wire. These recommendations are based on the wire's ability to carry the required current without overheating, assuming standard conditions such as a maximum ambient temperature of 30°C (86°F).
How Does the NEC Determine Wire Size?
The NEC uses a combination of factors to determine wire size, including the ampacity (current-carrying capacity) of the wire, the type of insulation, and the installation environment. Ampacity tables in the NEC provide specific guidelines for different wire materials and insulation types. For example, a #3 AWG copper wire has an ampacity of 100 amps when used with THHN/THWN insulation, which is common for residential wiring.
Why Does Insulation Matter?
Insulation plays a crucial role in determining the safe operating temperature of a wire. Different types of insulation, such as THHN, XHHW, and UF, have varying temperature ratings. Using a wire with the wrong insulation for your environment can lead to overheating or reduced performance. For instance, UF (Underground Feeder) cables are designed for direct burial and have different temperature ratings compared to THHN wires used in conduits.
How Does Distance Affect the Wire Size for a 100 Amp Panel?
Distance is a critical factor when determining the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp panel. As the distance between the power source and the panel increases, so does the resistance in the wire. This resistance leads to voltage drop, which can reduce the efficiency of your electrical system and cause appliances to underperform.
What Is Voltage Drop and Why Does It Matter?
Voltage drop occurs when electrical energy is lost as heat due to the resistance in the wire. The NEC recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders to ensure optimal performance. For a 100 amp panel, this means you may need to increase the wire gauge if the distance between the panel and the power source exceeds 100 feet.
Read also:Who Is Patricia Brights Husband A Deep Dive Into Her Personal Life And Influence
How to Choose the Right Wire Size for Long Distances?
For long-distance runs, you may need to upgrade to a larger wire gauge to compensate for voltage drop. For example, if you're running a 100 amp circuit 150 feet, you might need to use a #1 AWG copper wire instead of a #3 AWG. Using a voltage drop calculator can help you determine the exact wire size needed for your specific setup.
Copper vs. Aluminum: Which Is Better for a 100 Amp Panel?
When selecting wire for a 100 amp panel, you have two primary material options: copper and aluminum. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice often depends on budget, application, and personal preference.
Why Choose Copper Wire?
Copper is the preferred material for most residential applications due to its superior conductivity and durability. A #3 AWG copper wire can safely carry 100 amps, making it ideal for most home electrical panels. Copper is also more resistant to corrosion and has a longer lifespan compared to aluminum.
Why Choose Aluminum Wire?
Aluminum is a cost-effective alternative to copper, but it requires a larger gauge to carry the same current. For a 100 amp panel, you would typically use a #1 AWG aluminum wire. While aluminum is less expensive, it is more prone to oxidation and requires special connectors to ensure a secure connection.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size?
Selecting the wrong wire size can lead to serious safety hazards and inefficiencies. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Ignoring Distance: Failing to account for voltage drop over long distances can result in underperforming appliances.
- Using Incorrect Insulation: Choosing the wrong insulation type for your environment can lead to overheating.
- Overlooking Local Codes: Always check local building codes, as they may have additional requirements beyond the NEC.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for a 100 Amp Panel?
Calculating voltage drop is essential for ensuring your electrical system operates efficiently. The formula for voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 × Length × Current × Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length is the distance in feet.
- Current is the amperage (100 amps).
- Resistance is the resistance per 1,000 feet of wire (available in NEC tables).
Tools and Resources for Selecting the Right Wire Size
Several tools and resources can help you determine the correct wire size for a 100 amp panel:
- NEC Ampacity Tables: These tables provide guidelines for wire sizes based on current and insulation type.
- Voltage Drop Calculators: Online tools that simplify the process of calculating voltage drop.
- Local Building Codes: Always consult local codes for specific requirements.
FAQ About Wire Size for a 100 Amp Panel
What Happens If I Use the Wrong Wire Size for a 100 Amp Panel?
Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or insufficient power delivery.
Can I Use a Smaller Wire for a 100 Amp Panel If the Distance Is Short?
Yes, but only if the distance is very short and voltage drop is not a concern. Always consult the NEC guidelines.
Is It Safe to Use Aluminum Wire for a 100 Amp Panel?
Yes, but you must use the correct gauge and ensure proper installation with compatible connectors.
In conclusion, selecting the right wire size for a 100 amp panel is a critical step in ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls. Always consult a licensed electrician for complex installations or if you're unsure about any aspect of the process.
External Resource: For more information on electrical codes, visit the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
Exploring The Intricacies Of A Line Of Symmetry Heptagon: A Comprehensive Guide
Why Is Enter Sandman Called Enter Sandman: Unveiling The Origins And Legacy
What Gauge Wire For 150 Amp Service: A Complete Guide

What Size Wire 100 Amp Subpanel
What Size Ground Wire For 100 Amp Sub Panel