What Size Wire Is Rated For 100 Amps? A Complete Guide For Electrical Safety
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100-amp electrical circuit is critical for safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Whether you’re upgrading your home’s electrical panel, installing a subpanel, or working on an industrial project, understanding what size wire is rated for 100 amps ensures that your system can handle the load without overheating or causing hazards. Electrical systems are complex, and using the wrong wire gauge can lead to dangerous situations like fires, equipment damage, or power failures. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about wire sizing, including factors that influence your choice, common mistakes to avoid, and practical tips for selecting the right wire for your needs.
When it comes to electrical wiring, the size of the wire is determined by its gauge, which indicates the thickness of the conductor. Thicker wires have lower resistance, allowing them to carry higher currents safely. For a 100-amp circuit, the wire must be able to handle the current without overheating, which requires careful consideration of materials, insulation, and environmental factors. While copper is the most commonly used material due to its excellent conductivity, aluminum is also an option for certain applications. Understanding the nuances of these materials, along with the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, will empower you to make informed decisions.
Beyond safety, selecting the right wire size also impacts the long-term performance and cost-effectiveness of your electrical system. Using an undersized wire can lead to energy losses, increased operating costs, and frequent maintenance issues. On the other hand, oversizing the wire might unnecessarily inflate expenses. To help you navigate these considerations, this article will break down the technical aspects into easy-to-understand sections, answer common questions like "What size wire is rated for 100 amps?" and provide actionable advice to ensure your electrical installations are both safe and efficient.
Read also:Exploring Adam Savages Children A Glimpse Into Their Lives And Influence
Table of Contents
- What Factors Determine the Right Wire Size for 100 Amps?
- Why Does Wire Material Matter for 100-Amp Circuits?
- How Do Distance and Voltage Drop Affect Wire Sizing?
- What Are the NEC Guidelines for 100-Amp Wire Sizing?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire for 100 Amps
- What Size Wire Is Rated for 100 Amps? A Practical Guide
- How to Install and Maintain 100-Amp Wiring Safely
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100-Amp Wire Sizing
What Factors Determine the Right Wire Size for 100 Amps?
When determining what size wire is rated for 100 amps, several factors come into play. These include the type of material used, the length of the wire run, the ambient temperature, and the insulation rating. Each of these elements can significantly impact the performance and safety of your electrical system. Let’s break them down in detail:
Wire Material: Copper vs. Aluminum
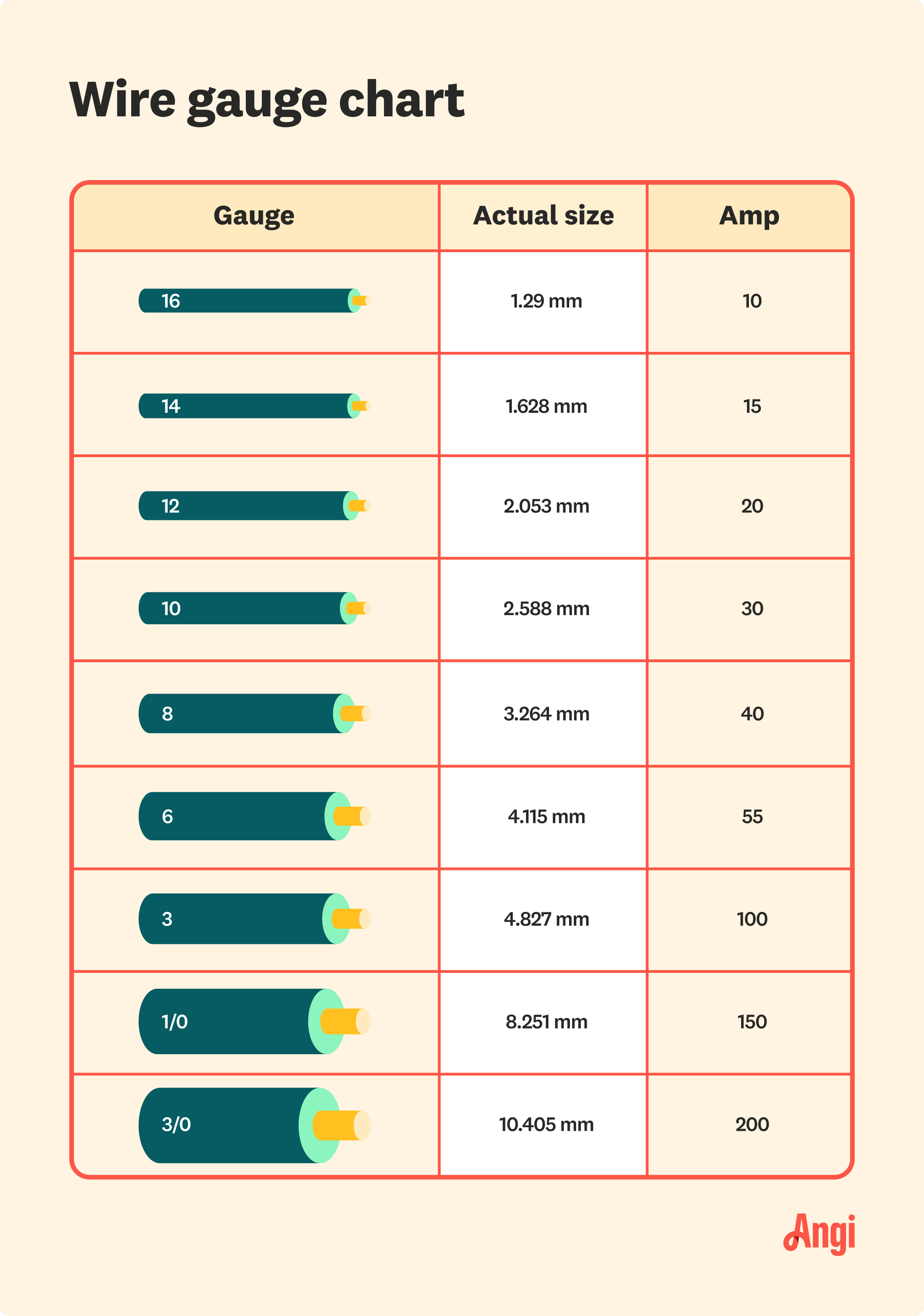
The material of the wire is one of the most critical factors. Copper wires are preferred for their superior conductivity and durability. They can carry more current than aluminum wires of the same gauge, making them ideal for high-load applications like 100-amp circuits. However, copper is more expensive, which is why some opt for aluminum as a cost-effective alternative. Aluminum wires are lighter and less costly but require larger gauges to handle the same current. For instance, a 100-amp circuit typically requires a 3 AWG copper wire, whereas a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is needed to achieve the same capacity.
Ambient Temperature and Insulation Rating
Temperature plays a vital role in wire sizing. Wires are rated for specific temperature ranges, and exceeding these limits can compromise their performance. Most wires are insulated with materials like THHN or XHHW, which have temperature ratings of 90°C or higher. However, if your installation is in a hot environment, such as an attic or industrial setting, you may need to adjust the wire size to account for the increased heat. Always check the insulation rating to ensure it matches the conditions of your project.
Additional Considerations
- Conduit Fill: If the wire is run through a conduit, the number of wires and their sizes must comply with fill capacity regulations to prevent overheating.
- Future Expansion: Planning for potential upgrades or additional loads can save you from costly rewiring in the future.
Why Does Wire Material Matter for 100-Amp Circuits?
The material of the wire is a fundamental consideration when determining what size wire is rated for 100 amps. Copper and aluminum are the two primary materials used in electrical wiring, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right wire for your specific application.
Copper Wires: The Gold Standard
Copper is widely regarded as the best material for electrical wiring due to its high conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It can carry more current than aluminum for the same gauge, making it an excellent choice for high-load circuits like those rated for 100 amps. For example, a 3 AWG copper wire is typically sufficient for a 100-amp service, provided the run length is within acceptable limits. Copper wires are also more flexible and easier to work with, which simplifies installation.
Aluminum Wires: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Aluminum wires are a popular choice for larger installations due to their lower cost and lighter weight. However, they require a larger gauge to match the current-carrying capacity of copper wires. For a 100-amp circuit, a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is generally recommended. While aluminum is a viable option, it is more prone to oxidation and requires special anti-oxidant compounds during installation to ensure a secure connection. Additionally, aluminum wires are stiffer and harder to bend, which can make installation more challenging.
Read also:What Kind Of Cancer Did Melanie Olmstead Have A Comprehensive Guide
Key Takeaways
- Copper wires are more conductive and durable but come at a higher cost.
- Aluminum wires are cost-effective but require larger gauges and careful installation.
How Do Distance and Voltage Drop Affect Wire Sizing?
Distance and voltage drop are critical factors when determining what size wire is rated for 100 amps. As the length of the wire increases, so does the resistance, which can lead to voltage drop. Excessive voltage drop can cause appliances and equipment to underperform or even fail. To mitigate this, it’s essential to select a wire size that minimizes resistance over the entire run.
Understanding Voltage Drop
Voltage drop occurs when electrical current encounters resistance in the wire, resulting in a loss of voltage along the circuit. The NEC recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeder circuits to ensure optimal performance. For a 100-amp circuit, this means selecting a wire size that can maintain voltage levels within these limits, even over long distances.
Calculating Wire Size for Long Runs
To calculate the appropriate wire size for a long run, you’ll need to consider the circuit’s voltage, the load in amps, and the distance in feet. For example, a 100-amp circuit running 100 feet may require a larger gauge wire, such as 1/0 AWG copper, to compensate for the increased resistance. Using a voltage drop calculator or consulting a professional electrician can help ensure accurate sizing.
Practical Tips
- Always account for voltage drop when planning long wire runs.
- Use larger gauges than the minimum requirement for added safety and efficiency.
What Are the NEC Guidelines for 100-Amp Wire Sizing?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides standardized guidelines for wire sizing to ensure safety and compliance. These guidelines are essential for determining what size wire is rated for 100 amps and should be followed rigorously to avoid violations and hazards.
NEC Requirements for 100-Amp Circuits
According to the NEC, a 100-amp service typically requires a minimum of 3 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire. These sizes are based on the assumption of standard conditions, such as a 75°C temperature rating and a short wire run. If your installation deviates from these conditions, adjustments may be necessary. For example, longer runs or higher ambient temperatures may require larger wire gauges.
Importance of Compliance
Adhering to NEC guidelines not only ensures safety but also helps avoid legal and financial consequences. Non-compliant installations can result in fines, insurance claims being denied, or even catastrophic failures. Always consult the latest NEC edition and work with a licensed electrician to ensure compliance.
Additional Considerations
- Check local codes, as they may have additional requirements beyond the NEC.
- Use wires with appropriate insulation ratings for your environment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire for 100 Amps
Selecting the wrong wire size for a 100-amp circuit can lead to serious consequences. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Underestimating Wire Size
Using a wire that’s too small for the load can cause overheating, leading to fires or equipment damage. Always choose a wire size that meets or exceeds the current requirements.
Ignoring Environmental Factors
Failure to account for temperature, conduit fill, and voltage drop can compromise the performance of your electrical system. Always consider these factors during planning.
Best Practices
- Consult a professional electrician for complex installations.
- Use high-quality materials and components to ensure reliability.
What Size Wire Is Rated for 100 Amps? A Practical Guide
For most residential and commercial applications, a 3 AWG copper wire or 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is rated for 100 amps. These sizes provide a safe and efficient solution for standard conditions. However, always verify your specific requirements based on distance, temperature, and other factors.
Installation Tips
Proper installation is just as important as selecting the right wire size. Use anti-oxidant compounds for aluminum wires, secure all connections tightly, and follow NEC guidelines to ensure safety.
Final Recommendations
- Double-check your calculations before purchasing materials.
- Label wires clearly to avoid confusion during installation.
How to Install and Maintain 100-Amp Wiring Safely
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for the longevity and safety of your 100-amp wiring. Follow these steps to ensure a successful project:
Installation Steps
1. Turn off the power at the main breaker before starting work.
2. Use the correct tools and equipment for cutting, stripping, and connecting wires.
3. Secure wires in conduits or raceways to prevent damage.
Maintenance Tips
Regularly inspect connections for signs of corrosion or overheating. Tighten loose connections and replace damaged wires promptly to prevent hazards.
Additional Advice
- Schedule periodic inspections by a licensed electrician.
- Keep a record of all electrical work for future reference.
Exploring Diddy's Net Worth 2023: A Deep Dive Into His Success Story
Understanding What’s Half Of 1/3 Cup: A Comprehensive Guide
Comprehensive Guide To Sewer Repair Insurance: What You Need To Know
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi

What Size Copper Wire For 40 Amps