What You Need To Know About 100 Amp AWG Wire Size For Safe Electrical Installations
When working with a 100 amp circuit, it’s essential to consider factors such as the wire's material (copper or aluminum), the length of the wire run, and the specific application. Copper wires, for instance, are more conductive and can carry higher loads compared to aluminum wires of the same gauge. However, aluminum wires are often more cost-effective and lighter, making them suitable for certain applications. The 100 amp AWG wire size is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it requires careful calculation and adherence to the National Electrical Code (NEC) standards to ensure compliance and safety. The consequences of using an undersized wire for a 100 amp circuit can be severe. Undersized wires can overheat, melt insulation, or even cause a fire. On the other hand, oversized wires might seem like a safer option, but they can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with. Therefore, understanding the nuances of 100 amp AWG wire size is not just about meeting code requirements but also about ensuring long-term reliability and safety. This article will guide you through everything you need to know, from determining the correct wire size to addressing common questions and misconceptions.
Table of Contents
- What is 100 Amp AWG Wire Size and Why Does It Matter?
- How to Choose the Right Wire Size for 100 Amp Circuits?
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Which is Better for 100 Amp AWG Wire Size?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with 100 Amp Wire Sizes
- What Are the Legal Requirements for 100 Amp AWG Wire Size?
- How Does Wire Length Affect 100 Amp AWG Wire Size Selection?
- Is Upgrading to a Larger Wire Size Necessary for Future-Proofing?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp AWG Wire Size
What is 100 Amp AWG Wire Size and Why Does It Matter?
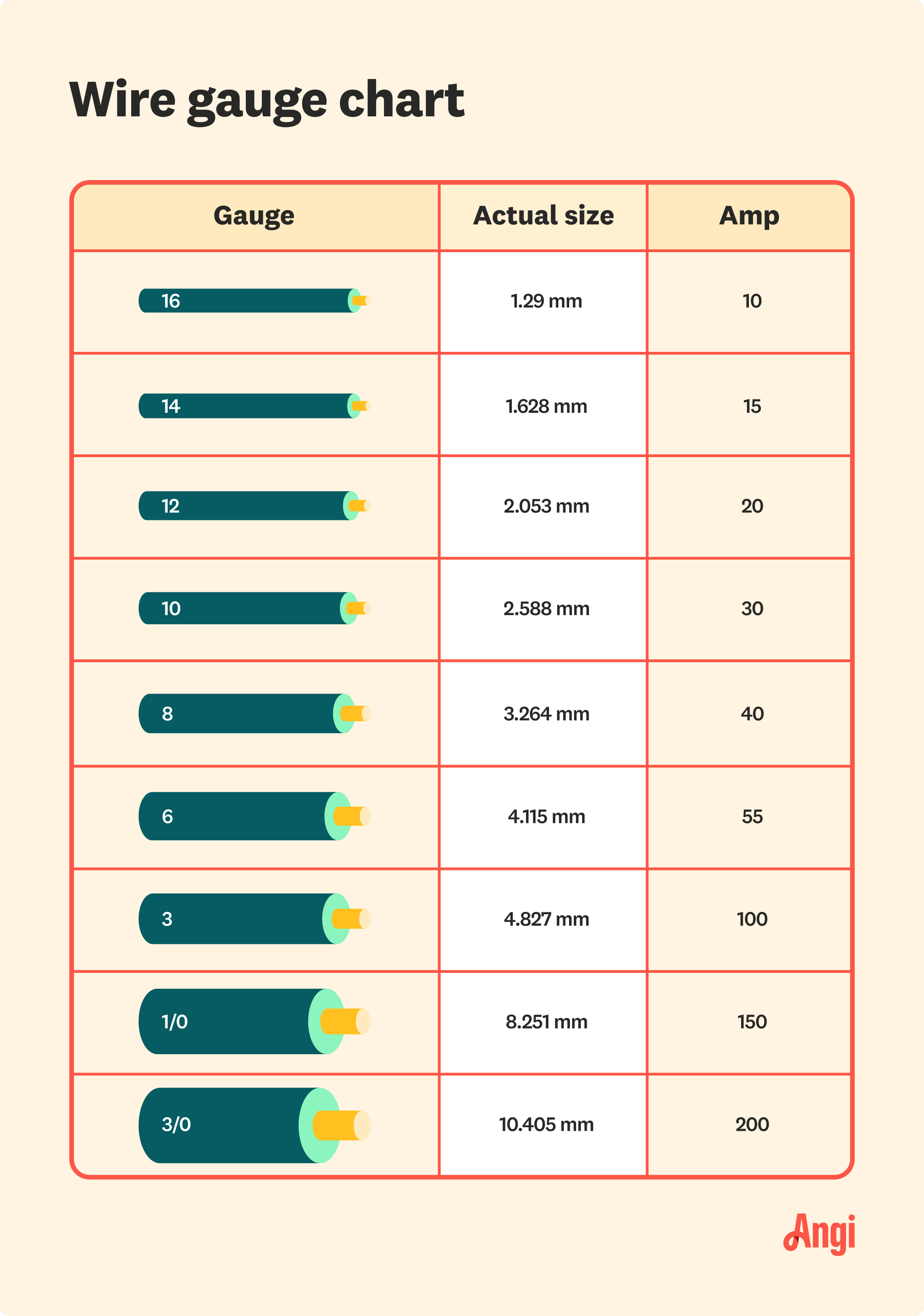
The term "100 amp AWG wire size" refers to the specific gauge of wire required to safely handle a 100 amp electrical load. AWG, or American Wire Gauge, is a standardized system used to measure the diameter of electrical conductors. The lower the AWG number, the thicker the wire and the higher its current-carrying capacity. For a 100 amp circuit, the recommended AWG wire size typically falls between 2 AWG and 4 AWG, depending on the wire material and other factors.
Why does this matter? The wire size directly impacts the safety and efficiency of an electrical system. If the wire is too thin for the amperage it needs to carry, it can overheat, leading to insulation breakdown and potential fire hazards. Conversely, if the wire is excessively thick, it may be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome to install. Understanding the relationship between wire size and amperage is essential for electricians, DIY enthusiasts, and homeowners alike.
Read also:Exploring Adam Savages Children A Glimpse Into Their Lives And Influence
Factors Influencing Wire Size Selection
Several factors influence the choice of 100 amp AWG wire size. These include:
- Wire Material: Copper wires are more conductive and require a smaller gauge compared to aluminum wires for the same amperage.
- Length of the Wire Run: Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- Environmental Conditions: High temperatures or exposure to moisture may necessitate adjustments in wire size.
Why Compliance with NEC Standards is Crucial
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for selecting the appropriate wire size for various applications. Adhering to these standards ensures not only compliance with local regulations but also the safety of the installation. For instance, the NEC specifies that copper wires for 100 amp circuits should typically be 2 AWG, while aluminum wires should be 1/0 AWG. Failure to follow these guidelines can result in failed inspections, legal liabilities, and safety hazards.
How to Choose the Right Wire Size for 100 Amp Circuits?
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100 amp circuit requires a systematic approach. Start by determining the wire material—copper or aluminum—as this significantly affects the AWG size. Copper wires are more efficient and can handle higher currents with a smaller gauge, while aluminum wires are bulkier but more cost-effective. For a 100 amp circuit, copper wires are generally 2 AWG, whereas aluminum wires are typically 1/0 AWG.
Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting the Right Wire Size
- Assess the Amperage: Confirm that the circuit requires exactly 100 amps. Overestimating or underestimating can lead to incorrect wire size selection.
- Check the Wire Material: Decide whether you’ll use copper or aluminum. Copper is more conductive and requires a smaller gauge.
- Measure the Wire Run Length: Longer runs necessitate thicker wires to prevent voltage drop. Use a voltage drop calculator to determine the appropriate size.
- Consider Environmental Factors: High temperatures, moisture, or exposure to chemicals may require adjustments in wire size or insulation type.
Why Voltage Drop Matters
Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in a wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels through it. For 100 amp circuits, excessive voltage drop can lead to inefficient appliance performance and potential damage to electrical devices. To minimize voltage drop, ensure the wire size is adequate for the length of the run. For example, a 100-foot run may require a thicker wire than a 50-foot run to maintain optimal performance.
Copper vs. Aluminum: Which is Better for 100 Amp AWG Wire Size?
When selecting a wire for a 100 amp circuit, the choice between copper and aluminum is a critical decision. Copper wires are renowned for their superior conductivity, making them ideal for high-amperage applications. For a 100 amp circuit, a 2 AWG copper wire is typically sufficient. Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are less conductive and require a larger gauge—usually 1/0 AWG—for the same amperage.
Advantages of Copper Wires
- Higher Conductivity: Copper wires can carry more current with a smaller diameter, reducing material costs and installation complexity.
- Longevity: Copper is more resistant to corrosion and wear, ensuring a longer lifespan for the electrical system.
- Flexibility: Copper wires are easier to bend and manipulate during installation.
Advantages of Aluminum Wires
- Cost-Effectiveness: Aluminum wires are generally cheaper than copper wires, making them a budget-friendly option.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is lighter, making it easier to handle during installation, especially for long runs.
- Availability: Aluminum wires are widely available and suitable for large-scale projects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with 100 Amp Wire Sizes
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when selecting or installing wires for a 100 amp circuit. These errors can compromise safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
Read also:Discover The Best Remote Iot Vpc Solutions For Your Business Needs
- Using Undersized Wires: This is one of the most dangerous mistakes, as undersized wires can overheat and cause fires.
- Ignoring Voltage Drop: Failing to account for voltage drop can lead to inefficient appliance performance and potential damage.
- Incorrect Insulation Type: Using wires with inadequate insulation for the environment can lead to premature failure.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
To avoid these common errors, always consult the NEC guidelines and use a voltage drop calculator when determining the appropriate 100 amp AWG wire size. Additionally, ensure that the wire insulation is suitable for the environmental conditions, such as heat or moisture exposure. Hiring a licensed electrician for complex installations can also help prevent costly mistakes.
What Are the Legal Requirements for 100 Amp AWG Wire Size?
Adhering to legal requirements is essential when selecting and installing wires for a 100 amp circuit. The NEC provides specific guidelines for wire size, insulation, and installation practices. For example, the NEC mandates that copper wires for 100 amp circuits should be 2 AWG, while aluminum wires should be 1/0 AWG. These standards are designed to ensure safety, prevent electrical hazards, and maintain compliance with local building codes.
Why Compliance is Non-Negotiable
Failure to comply with NEC standards can result in failed inspections, legal liabilities, and safety hazards. Additionally, non-compliant installations may void insurance policies, leaving homeowners or businesses financially vulnerable in the event of an electrical accident. Always consult a licensed electrician or local building authority to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
How to Stay Updated on NEC Guidelines
The NEC updates its guidelines periodically to reflect advancements in technology and safety standards. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for electricians, contractors, and DIY enthusiasts. Subscribe to industry publications, attend workshops, or consult online resources to ensure you’re always up-to-date.
How Does Wire Length Affect 100 Amp AWG Wire Size Selection?
The length of the wire run plays a significant role in determining the appropriate 100 amp AWG wire size. Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop and ensure efficient performance. For example, a 50-foot run may only require a 2 AWG copper wire, while a 100-foot run may necessitate a 1/0 AWG copper wire to maintain optimal voltage levels.
Understanding Voltage Drop in Long Runs
Voltage drop occurs when electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels through it. For 100 amp circuits, excessive voltage drop can lead to inefficient appliance performance and potential damage to electrical devices. To minimize voltage drop, ensure the wire size is adequate for the length of the run.
Practical Tips for Long Wire Runs
- Use a Voltage Drop Calculator: This tool helps determine the appropriate wire size based on the length of the run and the desired voltage drop percentage.
- Opt for Thicker Wires: When in doubt, choose a thicker wire to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Consult an Expert: For complex installations, hiring a licensed electrician can help ensure compliance and safety.
Is Upgrading to a Larger Wire Size Necessary for Future-Proofing?
As electrical demands increase, many homeowners and businesses consider upgrading their wire sizes to accommodate future needs. For a 100 amp circuit, upgrading to a larger wire size—such as moving from 2 AWG to 1/0 AWG copper—can provide additional capacity for future appliances or expansions.
Benefits of Future-Proofing
- Increased Capacity: Larger wires can handle higher amperages, making them suitable for future upgrades.
- Improved Efficiency: Thicker wires reduce voltage drop, ensuring optimal performance for all connected devices.
- Cost Savings: Upgrading now can prevent the need for costly rewiring in the future.
When Upgrading May Not Be Necessary
While future-proofing is beneficial, it may not always be necessary. If your current electrical demands are well within the capacity of your existing wire size, upgrading may be an unnecessary expense. Always assess your specific needs and consult a professional before making any changes.
Where Is The Security Code On An AmEx Card? A Comprehensive Guide
Discovering Jackie Witte Newman: A Journey Through Her Life And Achievements
Is Joey Merlino Still Married? Exploring His Life, Relationships, And More
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi

Silicone wire size vs withstand current (wire amp chart) esk8.news