White Bread Nutrition Facts: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Its Impact On Your Diet
White bread is a staple food found in households worldwide, but its nutritional profile often sparks debate among health-conscious consumers. While it is a convenient and versatile option, many people question whether it aligns with their dietary goals. White bread is made from refined wheat flour, which undergoes a milling process that strips away much of the grain's natural nutrients. This raises concerns about its nutritional value and potential health effects. However, enriched white bread is fortified with essential vitamins and minerals, making it a more balanced choice than many realize. Understanding the nutritional facts of white bread can help you make informed decisions about incorporating it into your diet.
White bread has been a part of human diets for centuries, evolving from ancient bread-making techniques to modern industrial production. Its widespread availability and affordability have made it a go-to option for sandwiches, toast, and snacks. Despite its popularity, white bread has faced criticism for its high glycemic index and potential contribution to weight gain. On the flip side, it also provides quick energy and essential nutrients like iron and B vitamins when enriched. By delving into the details of white bread nutrition facts, you can uncover its pros and cons and determine whether it fits into your lifestyle.
Whether you're a health enthusiast or someone simply looking for a convenient meal option, this article will guide you through everything you need to know about white bread nutrition facts. From its calorie content to its impact on blood sugar levels, we'll explore the science behind this everyday food. Additionally, we'll address common misconceptions and provide practical tips for making healthier choices. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how white bread can fit into a balanced diet while meeting your nutritional needs.
Read also:What Are Examples A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Using Examples Effectively
Table of Contents
- What Are the Nutritional Components of White Bread?
- How Does White Bread Affect Your Health?
- Is White Bread a Good Source of Energy?
- What Are the Drawbacks of Consuming White Bread?
- How Can You Make Healthier White Bread Choices?
- What Are the Alternatives to White Bread?
- How Does White Bread Compare to Whole Grain Bread?
- Frequently Asked Questions About White Bread Nutrition
What Are the Nutritional Components of White Bread?
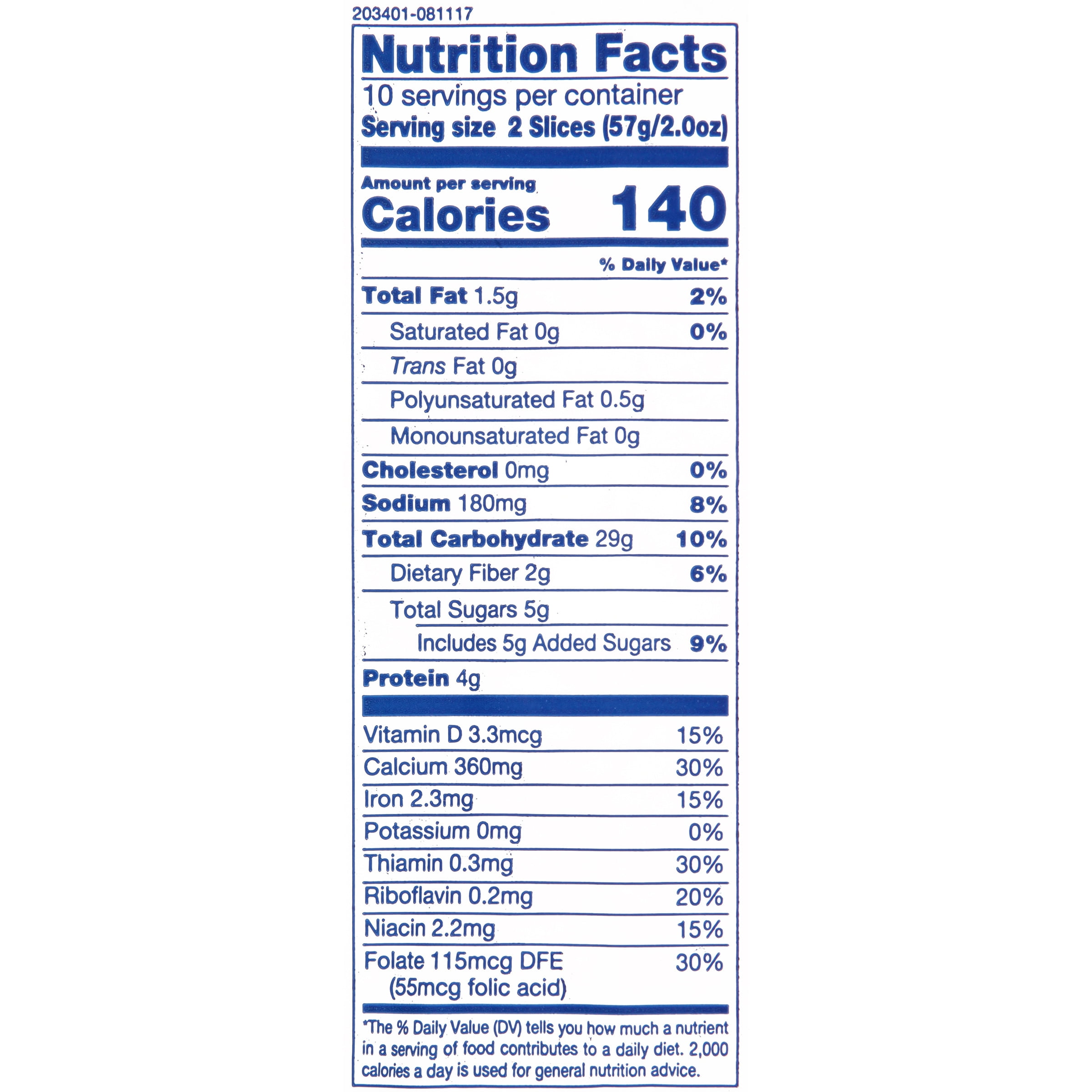
White bread is primarily made from refined wheat flour, water, yeast, and salt. During the refining process, the bran and germ layers of the wheat grain are removed, leaving behind the starchy endosperm. This results in a softer texture and longer shelf life but also reduces the bread's fiber content. To compensate for the loss of nutrients, many manufacturers enrich white bread with added vitamins and minerals, such as iron, folic acid, and B vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin.
Caloric Content and Macronutrients
A typical slice of white bread contains around 70-80 calories, depending on the brand and size. It is predominantly composed of carbohydrates, with about 15 grams per slice, making it a high-carb food. The carbohydrate content provides quick energy, which is why white bread is often included in pre-workout meals. However, it contains minimal protein and fat, with less than 2 grams of each per slice. This macronutrient profile makes white bread a low-satiety food, meaning it may not keep you full for long.
Vitamins and Minerals in Enriched White Bread
Enriched white bread is fortified with essential nutrients to replace those lost during processing. For instance, it is a good source of iron, which is crucial for red blood cell production, and B vitamins, which support energy metabolism. Additionally, some brands add calcium and vitamin D to further enhance its nutritional value. These additions make white bread a convenient way to meet your daily nutrient requirements, especially if you consume it regularly.
How Does White Bread Affect Your Health?
The impact of white bread on health largely depends on the quantity consumed and the overall diet. While it provides essential nutrients, excessive consumption can lead to negative health outcomes. One concern is its high glycemic index, which means it can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This can be problematic for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes, as it may lead to unstable energy levels and increased cravings.
Does White Bread Contribute to Weight Gain?
White bread is often criticized for its potential role in weight gain. Its low fiber content and high carbohydrate levels can lead to overeating, as it doesn't promote satiety as effectively as whole-grain options. Additionally, frequent consumption of refined carbs has been linked to an increased risk of obesity. However, moderation is key. Including white bread in a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can mitigate its negative effects.
Can White Bread Support Digestive Health?
While white bread is not a significant source of dietary fiber, some enriched varieties include added fiber to improve digestive health. Fiber is essential for maintaining regular bowel movements and supporting a healthy gut microbiome. If you're concerned about fiber intake, consider pairing white bread with high-fiber toppings like avocado, hummus, or leafy greens. This combination can enhance its nutritional profile and provide additional health benefits.
Read also:Discovering Kevin Beets A Journey Through His Life And Achievements
Is White Bread a Good Source of Energy?
White bread is an excellent source of quick energy due to its high carbohydrate content. The refined carbs in white bread are rapidly broken down into glucose, which serves as the body's primary energy source. This makes it a popular choice for athletes and individuals needing a quick energy boost before physical activity. However, relying solely on white bread for energy may not be sustainable in the long term, as it lacks the complex carbs found in whole grains.
When Is the Best Time to Consume White Bread?
The timing of white bread consumption can influence its effects on your body. Eating it in the morning can provide the energy needed to kickstart your day, especially when paired with protein-rich foods like eggs or peanut butter. However, consuming it late at night may lead to unwanted weight gain, as the body is less active and more likely to store excess carbs as fat. Planning your meals strategically can help you maximize the benefits of white bread while minimizing its drawbacks.
What Role Does Portion Control Play?
Portion control is crucial when incorporating white bread into your diet. Eating one or two slices per meal is generally acceptable, but consuming large quantities can lead to excessive calorie intake. To practice portion control, consider using smaller slices or opting for open-faced sandwiches. This approach allows you to enjoy white bread without overindulging.
What Are the Drawbacks of Consuming White Bread?
While white bread has its benefits, it also comes with several drawbacks that should be considered. One major concern is its low nutrient density compared to whole-grain alternatives. The refining process removes fiber, vitamins, and minerals, leaving behind mostly empty calories. This can contribute to nutrient deficiencies if white bread is a staple in your diet without other nutrient-rich foods to compensate.
How Does White Bread Impact Blood Sugar Levels?
White bread's high glycemic index means it can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, followed by a sharp decline. This rollercoaster effect can leave you feeling fatigued and hungry shortly after eating. For individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, this can be particularly problematic, as it may lead to poor blood sugar control. Choosing whole-grain or low-GI bread options can help stabilize blood sugar levels and provide sustained energy.
Does White Bread Increase the Risk of Chronic Diseases?
Research suggests that a diet high in refined carbs, such as those found in white bread, may increase the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. The lack of fiber and antioxidants in white bread can contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are risk factors for these conditions. To reduce your risk, aim to balance your intake of refined carbs with nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
How Can You Make Healthier White Bread Choices?
Making healthier choices doesn't mean you have to give up white bread entirely. Instead, focus on selecting high-quality options and pairing them with nutritious toppings. Look for bread labeled as "enriched" or "fortified," as these contain added vitamins and minerals. Additionally, consider opting for sprouted or artisanal white bread, which may retain more nutrients than mass-produced varieties.
What Are Some Healthy Toppings for White Bread?
Choosing nutrient-rich toppings can enhance the nutritional value of white bread. Some healthy options include:
- Avocado slices for healthy fats and fiber
- Grilled chicken or turkey for lean protein
- Hummus or nut butter for added flavor and nutrients
- Leafy greens like spinach or arugula for vitamins and minerals
Should You Consider Homemade White Bread?
Making white bread at home allows you to control the ingredients and reduce additives like preservatives and excess sugar. You can also experiment with adding whole grains or seeds to boost its fiber content. While homemade bread may require more effort, it can be a rewarding way to enjoy a healthier version of this classic food.
What Are the Alternatives to White Bread?
If you're looking to diversify your bread choices, several alternatives can provide more nutrients and health benefits. Whole-grain bread, rye bread, and sourdough are popular options that offer higher fiber content and a lower glycemic index. These alternatives can help you meet your dietary goals while still enjoying the convenience of bread.
Why Choose Whole-Grain Bread Over White Bread?
Whole-grain bread retains the bran and germ layers of the wheat grain, making it a richer source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It also has a lower glycemic index, which helps stabilize blood sugar levels. Switching to whole-grain bread can improve your overall nutrient intake and support better health outcomes.
What Are the Benefits of Sourdough Bread?
Sourdough bread undergoes a fermentation process that enhances its digestibility and nutritional profile. The natural bacteria and yeast used in fermentation break down phytic acid, a compound that can inhibit nutrient absorption. This makes sourdough a more gut-friendly option compared to traditional white bread.
How Does White Bread Compare to Whole Grain Bread?
Comparing white bread to whole-grain bread highlights the nutritional differences between the two. While white bread provides quick energy and essential nutrients when enriched, whole-grain bread offers a more balanced profile with higher fiber content and lower glycemic index. Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices based on your dietary needs and health goals.
Which Is Better for Weight Management?
Whole-grain bread is generally a better option for weight management due to its higher fiber content, which promotes satiety and reduces overeating. However, white bread can still be included in a weight-loss diet if consumed in moderation and paired with nutrient-dense foods.
Which Is More Suitable for Athletes?
Athletes may benefit from white bread's quick energy release, especially before or after intense workouts. However, incorporating whole-grain bread into their diet can provide sustained energy and additional nutrients to support recovery and overall performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About White Bread Nutrition
Is White Bread Bad for You?
White bread is not inherently bad, but its nutritional value depends on how it's consumed. When eaten in moderation and paired with healthy toppings, it can be part of a balanced diet. However, excessive consumption of refined carbs may lead to health issues.
Can White Bread Fit into a Low-Carb Diet?
White bread is not ideal for low-carb diets due to its high carbohydrate content. If you're following a low-carb plan, consider alternatives like almond flour bread or lettuce wraps.
Does Toasting White Bread Change Its Nutritional Value?
Toasting white bread slightly reduces its moisture content but does not significantly alter its nutritional profile. However, it can enhance flavor and texture, making it a more satisfying option.
In conclusion, understanding white bread nutrition facts can empower
Ricky Wilde Net Worth: A Comprehensive Guide To His Earnings And Career
Understanding The Security Code On Amex: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring The Charm Of The Three Blind Mice Shrek: A Timeless Tale Reimagined
White Wonder Bread Nutrition Facts Besto Blog

Wonder Plus Bread Nutrition Facts Nutrition Ftempo