Bread Nutrition Facts: Unveiling The Health Benefits And Nutritional Insights
From whole grain loaves to artisanal sourdough, bread comes in various forms and flavors, catering to diverse tastes and dietary needs. But how much do you really know about bread nutrition facts? Understanding the nutritional profile of bread can help you make informed decisions about what you eat, ensuring you’re fueling your body with the right nutrients. With its rich history and versatility, bread remains a cornerstone of many meals worldwide, but not all bread is created equal. It’s essential to delve into its nutritional composition to understand how it fits into a balanced diet. Bread nutrition facts are more than just numbers on a label; they tell a story about the ingredients, preparation methods, and health benefits associated with this beloved food. Whether you’re a fan of white, whole wheat, or gluten-free bread, each variety brings unique nutritional attributes to the table. For instance, whole grain bread is packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making it a healthier choice for those looking to maintain a balanced diet. On the other hand, refined bread might lack some of these nutrients but can still be a convenient source of energy. By exploring the nutritional content of bread, you can better understand how it impacts your overall health and well-being. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of bread nutrition facts, uncovering everything from its macronutrient breakdown to its role in supporting specific health goals. We’ll also address common questions like, “Is bread good for weight loss?” and “What are the healthiest bread options?” Along the way, we’ll provide practical tips for choosing the right bread for your dietary needs and lifestyle. Whether you’re a health enthusiast or simply curious about what’s in your sandwich, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make smarter choices about bread.
Table of Contents
- What Makes Bread a Nutritional Powerhouse?
- How Does Bread Nutrition Facts Support Your Daily Diet?
- Is Bread Good for Weight Loss?
- What Are the Healthiest Bread Options?
- How Can You Identify High-Quality Bread?
- What Are the Key Nutrients in Bread?
- How Does Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
- What Role Does Bread Play in Global Diets?
What Makes Bread a Nutritional Powerhouse?
Bread is often misunderstood as a simple carbohydrate source, but its nutritional profile can vary significantly depending on the type and ingredients used. At its core, bread is made from grains, which are naturally rich in essential nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Whole grain bread, in particular, is a nutritional powerhouse due to its high fiber content and abundance of B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and zinc. These nutrients play vital roles in maintaining energy levels, supporting immune function, and promoting overall health. One of the standout features of bread nutrition facts is its versatility. For example, whole wheat bread provides complex carbohydrates that release energy slowly, keeping you fuller for longer. On the other hand, enriched white bread is fortified with additional nutrients like folic acid and iron, making it a convenient option for those who may not consume enough of these essential vitamins through other foods. By understanding the differences between bread varieties, you can choose options that align with your health goals and dietary preferences. Moreover, bread’s nutritional value extends beyond its macronutrient content. Many types of bread contain antioxidants, phytonutrients, and prebiotics that support gut health and reduce inflammation. For instance, sourdough bread undergoes a fermentation process that enhances its digestibility and increases its bioavailability of nutrients. This makes it a great choice for individuals with sensitive stomachs or those looking to boost their gut microbiome. By incorporating nutrient-dense bread into your diet, you can enjoy both its taste and its health benefits.
How Does Bread Nutrition Facts Support Your Daily Diet?
Bread nutrition facts play a crucial role in supporting a balanced and nutritious diet. Whether you’re aiming to meet your daily fiber intake or boost your energy levels, bread can be a valuable addition to your meal plan. For starters, bread is an excellent source of carbohydrates, which serve as the body’s primary energy source. Complex carbohydrates found in whole grain bread are particularly beneficial because they provide sustained energy without causing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. In addition to carbohydrates, bread is rich in essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall well-being. For example, many bread varieties are fortified with B vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin, which are vital for converting food into energy and supporting brain function. Iron, another key nutrient found in bread, plays a critical role in transporting oxygen throughout the body and preventing fatigue. By including bread in your diet, you can ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements for these essential nutrients. Another way bread nutrition facts support your daily diet is through its fiber content. Fiber is essential for maintaining digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and promoting feelings of fullness. Whole grain and multigrain breads are particularly high in fiber, making them ideal choices for those looking to improve their gut health or manage their weight. Furthermore, fiber-rich bread can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By choosing the right type of bread, you can enjoy both its taste and its health-promoting properties.
Read also:Baryshnikov The Legendary Dancer Who Redefined Ballet
Is Bread Good for Weight Loss?
One of the most common questions about bread nutrition facts is whether bread can be part of a weight loss plan. The answer largely depends on the type of bread you choose and how it fits into your overall diet. While some people avoid bread due to its carbohydrate content, others find that certain bread varieties can actually support their weight loss goals. Understanding the nutritional differences between bread types is key to making informed choices. Whole grain and sprouted breads are often recommended for weight loss because they are high in fiber and protein, both of which promote satiety and reduce hunger cravings. Fiber slows down digestion, helping you feel fuller for longer, while protein supports muscle maintenance and boosts metabolism. These breads also tend to have a lower glycemic index, meaning they cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This can help prevent energy crashes and reduce the likelihood of overeating. On the other hand, refined bread like white bread is often associated with weight gain due to its high glycemic index and lack of fiber. These factors can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, followed by crashes that trigger hunger and cravings. However, moderation is key, and even refined bread can be enjoyed occasionally as part of a balanced diet. The key takeaway is to focus on portion control and choose nutrient-dense bread options that align with your weight loss goals. By doing so, you can enjoy bread without compromising your progress.
What Are the Healthiest Bread Options?
When it comes to bread nutrition facts, not all bread is created equal. Some varieties are packed with nutrients, while others may offer little more than empty calories. To make the healthiest choice, it’s important to look beyond the packaging and examine the ingredients list. Whole grain, sprouted, and sourdough breads are often considered the healthiest options due to their nutrient density and minimal processing. Whole grain bread is made from grains that retain all parts of the kernel, including the bran, germ, and endosperm. This ensures that the bread is rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Look for bread labeled “100% whole grain” to ensure you’re getting the full nutritional benefits. Sprouted bread, on the other hand, is made from grains that have been allowed to sprout before being ground into flour. This process enhances the bread’s digestibility and increases its nutrient content, particularly in terms of protein and antioxidants. Sourdough bread is another excellent choice, thanks to its fermentation process, which breaks down phytic acid and increases the bioavailability of nutrients. This makes sourdough easier to digest and more nutritious than many other bread varieties. Additionally, sourdough has a lower glycemic index, making it a better option for those looking to manage their blood sugar levels. By choosing these healthier bread options, you can enjoy the taste and texture of bread while reaping its nutritional benefits.
What Are the Key Nutrients in Bread?
Bread is more than just a source of carbohydrates; it contains a variety of key nutrients that contribute to overall health and well-being. Understanding these nutrients can help you make informed choices about the type of bread you consume and how it fits into your diet.
Carbohydrates: The Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the main macronutrient found in bread, providing the body with its primary source of energy. Whole grain bread, in particular, contains complex carbohydrates that are digested slowly, providing a steady release of energy throughout the day. This makes it an excellent choice for maintaining energy levels and preventing fatigue. Additionally, the fiber found in whole grain bread helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of energy crashes and overeating.
Fiber and Its Digestive Health Benefits
Fiber is another key nutrient found in bread, particularly in whole grain and multigrain varieties. It plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Fiber also supports a healthy gut microbiome by feeding beneficial bacteria in the digestive tract. This can help reduce inflammation, boost immunity, and lower the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. By choosing high-fiber bread, you can enjoy both its taste and its health-promoting properties.
How Does Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
The impact of bread on blood sugar levels is a topic of great interest, especially for individuals managing conditions like diabetes or insulin resistance. Bread nutrition facts reveal that the glycemic index (GI) of bread varies depending on its ingredients and processing methods. Whole grain and sourdough breads tend to have a lower GI, meaning they cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This makes them a better choice for maintaining stable energy levels and preventing spikes and crashes. On the other hand, refined bread like white bread has a higher GI, which can lead to rapid increases in blood sugar levels. This can be problematic for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes, as it may cause energy crashes and increase hunger cravings. However, pairing refined bread with protein or healthy fats can help mitigate its impact on blood sugar levels. By understanding how different types of bread affect blood sugar, you can make smarter choices that support your overall health and well-being.
Read also:Understanding Steve Dulcichs Illness A Comprehensive Guide
What Role Does Bread Play in Global Diets?
Bread is a staple food in many cultures around the world, playing a central role in traditional diets and culinary practices. From French baguettes to Indian naan, bread takes on countless forms and flavors, reflecting the diversity of global cuisines. Its widespread popularity is a testament to its versatility, affordability, and nutritional value. In many countries, bread serves as a primary source of energy and nutrients, making it an essential component of daily meals. In Mediterranean diets, for example, whole grain bread is often paired with olive oil, vegetables, and lean proteins, creating a balanced and nutritious meal. Similarly, in Middle Eastern cuisines, flatbreads like pita and lavash are used to wrap flavorful fillings, providing both taste and sustenance. Bread’s ability to complement a wide range of ingredients makes it a versatile and indispensable food in global diets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bread Nutrition Facts the Same for All Types of Bread?
No, bread nutrition facts vary depending on the type of bread. Whole grain bread is higher in fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to refined white bread, which often lacks these nutrients unless fortified.
Can Bread Be Part of a Gluten-Free Diet?
Yes, there are many gluten-free bread options available, made from ingredients like rice flour, almond flour, or tapioca starch. These breads cater to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
How Can I Incorporate Bread into a Healthy Diet?
Choose whole grain or sprouted bread, pair it with protein or healthy fats, and practice portion control. This way, you can enjoy bread while maintaining a balanced diet.
Conclusion
Bread nutrition facts reveal that this staple food can be both delicious and nutritious when chosen wisely. By understanding its nutritional profile and making informed choices, you can enjoy bread as part of
How Can You Identify Real Gold: A Comprehensive Guide To Authenticating Precious Metals
What Size Triplex Wire Is Ideal For A 100 Amp Service?
What Size Wire For 100 Amp Service: A Complete Guide
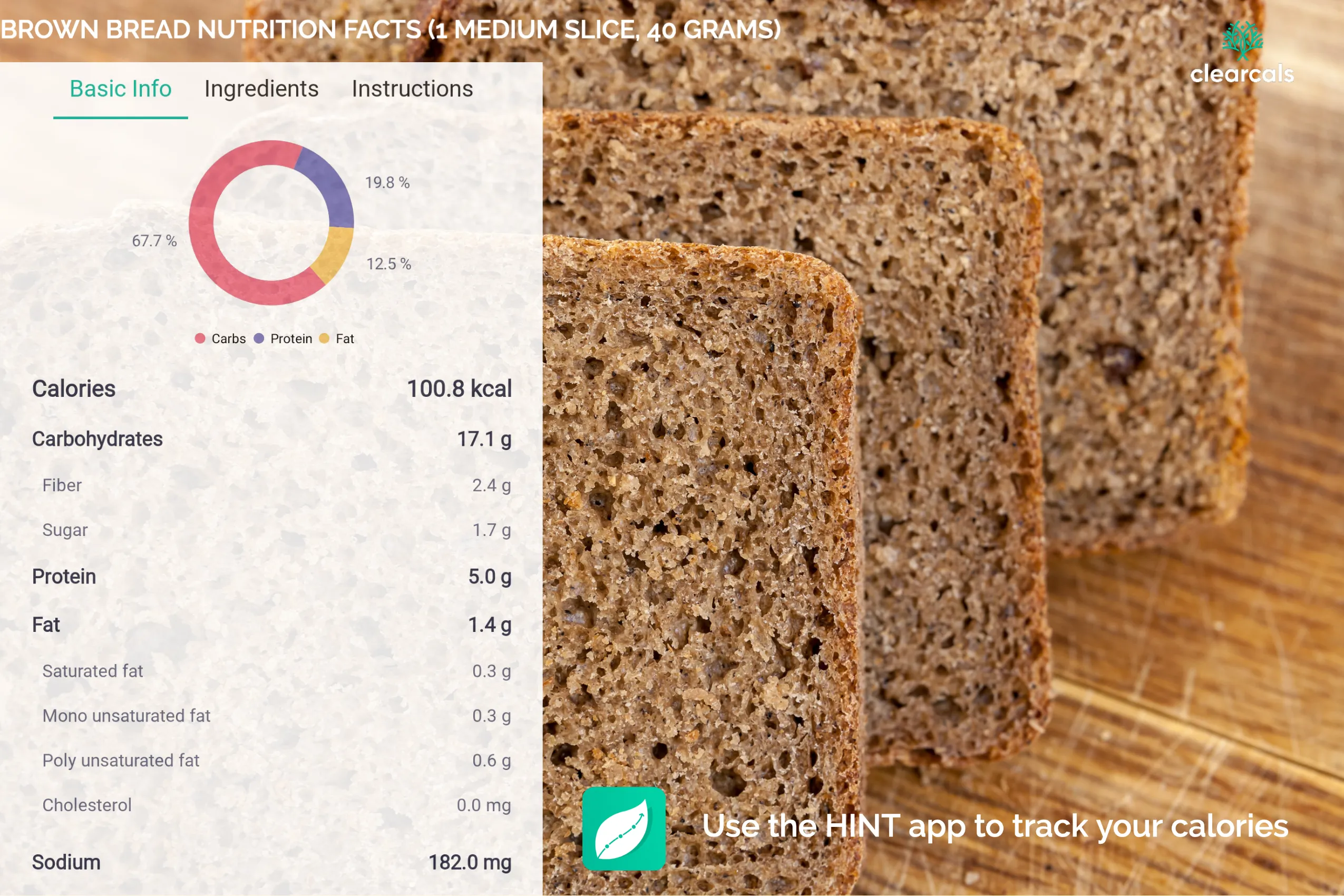
Calories In Brown Bread Nutrition Facts Science Backed I, 50 OFF

Wonder Plus Bread Nutrition Facts Nutrition Ftempo