Everything You Need To Know About Nutritional Information Of White Bread
White bread is a staple food enjoyed by millions around the globe. But have you ever wondered about its nutritional content and how it impacts your health? Whether you’re enjoying a classic PB&J sandwich, dipping bread into soup, or using it as a base for avocado toast, white bread is a versatile option. However, its widespread consumption has sparked debates about its nutritional value. Understanding the nutritional information of white bread is essential for making informed dietary choices. This article dives deep into what makes white bread tick, its health implications, and how it fits into a balanced diet.
Many people assume that white bread is just empty calories, but it does offer some nutritional benefits when consumed in moderation. From carbohydrates to trace amounts of vitamins and minerals, white bread provides energy and essential nutrients. That said, it’s crucial to understand how its composition compares to other bread types, such as whole wheat or multigrain. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the nutritional profile of white bread, its pros and cons, and tips for making healthier choices without sacrificing taste.
Whether you’re a health-conscious individual or simply curious about the food you consume daily, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need to make smarter choices. From FAQs about white bread’s ingredients to its role in a balanced diet, we’ll cover all aspects of nutritional information about white bread. Let’s dive into the details and uncover the truth behind this beloved staple.
Read also:Diane Furnberg Exploring Her Life Achievements And Impact
Table of Contents
- What Are the Nutritional Benefits of White Bread?
- How Does White Bread Compare to Other Bread Types?
- Is White Bread Bad for Your Health?
- Can White Bread Be Part of a Healthy Diet?
- What Ingredients Are in White Bread?
- How Is White Bread Made?
- What Are the Common Misconceptions About White Bread?
- How Can You Make Healthier White Bread Choices?
What Are the Nutritional Benefits of White Bread?
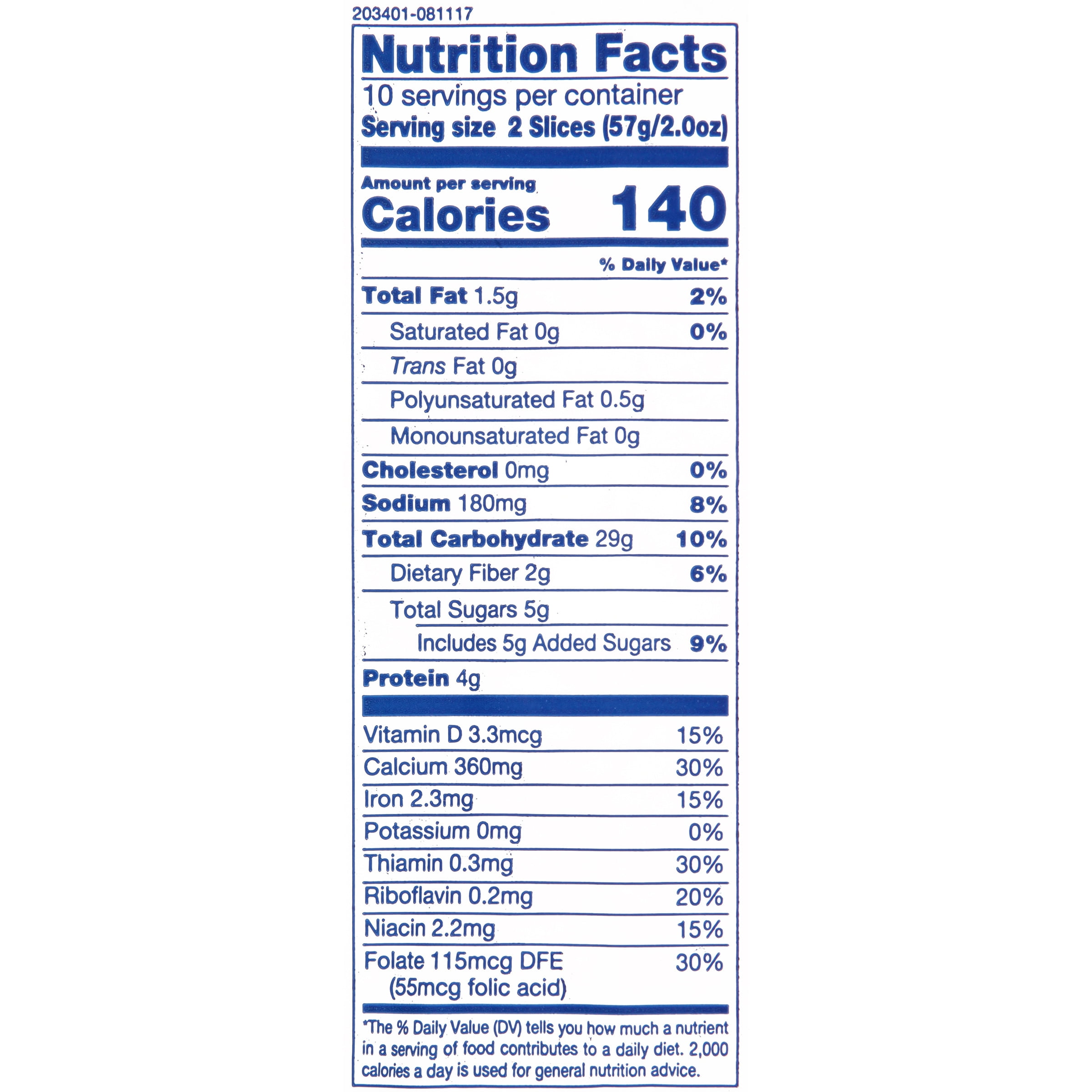
White bread is often criticized for being less nutritious than whole-grain alternatives, but it still offers some benefits. For starters, white bread is a good source of carbohydrates, which are the body’s primary energy source. A single slice typically contains around 15 grams of carbohydrates, making it a convenient option for fueling your day. Additionally, white bread is often enriched with essential nutrients such as iron, folic acid, and B vitamins, which are added during the manufacturing process.
Enrichment is a key factor in understanding the nutritional information of white bread. The process involves fortifying the bread with nutrients that may have been lost during refining. For example, folic acid, a B vitamin crucial for pregnant women, is commonly added to white bread. This enrichment makes white bread a viable option for individuals who may struggle to meet their daily nutrient requirements through other foods.
Key Nutrients Found in White Bread
- Carbohydrates: Provides quick energy for daily activities.
- Folic Acid: Supports fetal development during pregnancy.
- Iron: Essential for red blood cell production.
- B Vitamins: Aid in metabolism and energy production.
Why Is Enrichment Important?
Enrichment ensures that white bread contributes to your daily nutrient intake, even if it lacks the fiber found in whole-grain options. This makes it a practical choice for people who may not consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods. However, moderation is key, as excessive consumption can lead to unwanted health effects.
How Does White Bread Compare to Other Bread Types?
When it comes to bread, the choices can be overwhelming. From whole wheat to sourdough, each type offers unique nutritional benefits. Understanding how white bread stacks up against these alternatives is crucial for making informed dietary decisions. Let’s compare white bread to other popular bread types to better understand its role in a balanced diet.
White Bread vs. Whole Wheat Bread
One of the most common comparisons is between white bread and whole wheat bread. Whole wheat bread is made from the entire wheat kernel, including the bran, germ, and endosperm. This makes it richer in fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to white bread, which is made from refined flour. While white bread provides quick energy, whole wheat bread offers sustained energy due to its higher fiber content.
White Bread vs. Multigrain Bread
Multigrain bread is another popular option, often perceived as healthier due to its inclusion of multiple grains. However, the nutritional value depends on whether the grains are whole or refined. Multigrain bread typically contains more fiber and nutrients than white bread, but it’s essential to check the label for added sugars or preservatives.
Read also:Dawn Wells Measurements A Complete Guide To Her Life And Career
What About Gluten-Free Bread?
For individuals with gluten sensitivities, gluten-free bread is a necessity. While it may mimic the texture of white bread, gluten-free options often lack the same nutritional profile. They are usually fortified with vitamins and minerals but may contain higher levels of sugar and fat to compensate for the lack of gluten.
Is White Bread Bad for Your Health?
White bread often gets a bad rap, but is it truly harmful to your health? The answer depends on various factors, including portion size, frequency of consumption, and overall dietary habits. While white bread can fit into a healthy diet, excessive consumption may lead to health concerns such as weight gain and blood sugar spikes.
Potential Health Concerns
One of the primary criticisms of white bread is its high glycemic index (GI). Foods with a high GI can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, which may increase the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes over time. Additionally, white bread is low in fiber, which can lead to digestive issues if consumed in excess.
How Can You Minimize Risks?
To mitigate potential health risks, consider pairing white bread with protein or healthy fats. For example, adding peanut butter or avocado can slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, preventing blood sugar spikes. Moderation is key to enjoying white bread without compromising your health.
Can White Bread Be Part of a Healthy Diet?
Contrary to popular belief, white bread can be part of a healthy diet when consumed mindfully. The key is to balance it with nutrient-dense foods and maintain portion control. For instance, using white bread as an occasional treat or pairing it with vegetables and lean proteins can make it a more nutritious option.
Tips for Incorporating White Bread into Your Diet
- Choose enriched varieties to maximize nutrient intake.
- Pair with protein-rich foods like eggs or cheese.
- Limit consumption to one or two slices per day.
What About Kids and White Bread?
White bread is often a favorite among children due to its soft texture and mild flavor. While it’s fine for kids to enjoy white bread occasionally, parents should encourage a variety of whole-grain options to ensure they receive adequate fiber and nutrients.
What Ingredients Are in White Bread?
Understanding the ingredients in white bread is crucial for evaluating its nutritional information. The primary components include refined wheat flour, water, yeast, salt, and sometimes added sugars or fats. Enrichment with vitamins and minerals is also common in commercially produced white bread.
Common Additives in White Bread
- Preservatives: Extend shelf life but may have health implications.
- Emulsifiers: Improve texture and prevent staling.
- Added Sugars: Enhance flavor but contribute to calorie intake.
How Do These Ingredients Affect Nutrition?
While some additives enhance the taste and texture of white bread, they may also contribute to unnecessary calories or health risks. Reading labels carefully can help you choose healthier options.
How Is White Bread Made?
The process of making white bread involves refining wheat flour to remove the bran and germ, leaving only the starchy endosperm. This refined flour is then mixed with water, yeast, and other ingredients to form dough, which is baked into the soft, fluffy bread we know and love.
Steps in Bread Production
- Milling the wheat to produce refined flour.
- Mixing flour with water, yeast, and other ingredients.
- Allowing the dough to rise through fermentation.
- Baking the dough to achieve the final product.
What Role Does Enrichment Play?
After baking, white bread is often enriched to restore lost nutrients. This step ensures that white bread contributes positively to your diet despite the refining process.
What Are the Common Misconceptions About White Bread?
White bread is often misunderstood, with many people believing it offers no nutritional value. However, as we’ve discussed, enriched white bread provides essential nutrients like folic acid and iron. Another misconception is that all white bread is unhealthy, but moderation and mindful pairing can make it a balanced choice.
Debunking Myths About White Bread
- Myth: White bread has no nutrients. Reality: It’s often enriched with vitamins and minerals.
- Myth: All white bread is high in sugar. Reality: Sugar content varies by brand.
Why Do These Misconceptions Persist?
Misinformation and marketing often contribute to these myths. Educating yourself about nutritional information white bread can help dispel these misconceptions.
How Can You Make Healthier White Bread Choices?
Choosing healthier white bread options involves reading labels, opting for enriched varieties, and balancing consumption with nutrient-dense foods. Here are some practical tips:
Tips for Healthier Choices
- Select bread with fewer additives and preservatives.
- Look for options fortified with additional nutrients.
- Pair with vegetables, proteins, or healthy fats.
What About Homemade White Bread?
Making white bread at home allows you to control the ingredients, reducing the need for preservatives and additives. This can be a healthier alternative to store-bought options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is white bread fattening?
White bread itself is not inherently fattening, but excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain due to its calorie content. Pairing it with healthy options can mitigate this risk.
Does white bread cause bloating?
Some individuals may experience bloating due to the low fiber content in white bread. Adding fiber-rich foods to your diet can help alleviate this issue.
Can diabetics eat white bread?
Diabetics can enjoy white bread in moderation, but they should monitor their blood sugar levels and pair it with protein or healthy fats to minimize spikes.
Conclusion
Understanding the nutritional information of white bread allows you to make informed decisions about its role in your diet. While it may not be as nutrient-dense as whole-grain options, enriched white bread offers essential vitamins and minerals. By practicing moderation and pairing it with nutrient-rich foods, you can enjoy white bread as part of a balanced diet.
For further reading, check out this article on the pros and cons of white bread.
Are Fungi Autotrophic Or Heterotrophic? Unveiling The Secrets Of Fungal Nutrition
MF DOOM Unmasked: The Legacy And Mystery Of Hip-Hop's Greatest Enigma
What Size Wire Is Needed For 100 Amp Service: A Comprehensive Guide
White Wonder Bread Nutrition Facts Besto Blog

Hand drawn sketch fresh wheat bread symbol. Soft white bread being