Understanding 0 Celsius: The Science, Effects, And Applications
This temperature, often referred to as the freezing point of water, plays a critical role in everything from weather patterns to food preservation. Whether you're a student, scientist, or simply curious, understanding 0 Celsius offers valuable insights into the natural world. This article dives deep into the science behind this temperature, its effects on the environment, and its practical applications in various industries.
0 Celsius is more than just a number on a thermometer; it's a threshold that influences countless processes. From the formation of frost on a chilly morning to the preservation of perishable goods, this temperature acts as a boundary between states of matter. Its significance extends beyond the laboratory, affecting agriculture, transportation, and even human health. As we explore the topic further, we'll uncover how this seemingly simple temperature has profound implications for both natural and man-made systems.
By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of 0 Celsius and its multifaceted role in our lives. We'll explore its scientific foundations, its impact on ecosystems, and how it is utilized in technology and industry. Whether you're preparing for an exam, conducting research, or simply looking to expand your knowledge, this guide will provide you with the tools to grasp the importance of 0 Celsius in a meaningful way.
Read also:Understanding Steve Dulcichs Illness A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What is 0 Celsius?
- Why is 0 Celsius Significant?
- How Does 0 Celsius Affect the Environment?
- What Happens to Water at 0 Celsius?
- Applications of 0 Celsius in Daily Life
- How Can 0 Celsius Impact Human Health?
- Industrial Uses of 0 Celsius
- Frequently Asked Questions About 0 Celsius
What is 0 Celsius?
0 Celsius, also known as the freezing point of water, is a fundamental reference point in the Celsius temperature scale. This scale, developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742, divides the temperature range between the freezing and boiling points of water into 100 equal intervals. At 0 Celsius, water molecules slow down enough to form a solid lattice structure, resulting in the transformation of liquid water into ice. This temperature is not just a scientific benchmark but also a practical guide for everyday activities, from cooking to weather forecasting.
Understanding 0 Celsius requires a basic grasp of thermodynamics. At this temperature, the kinetic energy of water molecules decreases significantly, allowing hydrogen bonds to lock them into a fixed position. This process is reversible, meaning that as temperatures rise above 0 Celsius, ice melts back into water. The transition at 0 Celsius is not instantaneous; it often requires additional energy, known as latent heat, to complete the phase change. This phenomenon is critical in understanding weather patterns, as it explains why frost forms overnight and melts during the day.
Beyond its scientific definition, 0 Celsius has cultural and practical significance. In many parts of the world, it serves as a dividing line between "cold" and "freezing" weather conditions. For instance, when temperatures dip below 0 Celsius, roads become icy, and frost blankets landscapes. This temperature also plays a role in food preservation, as freezing halts the growth of bacteria and extends the shelf life of perishable items. By understanding the science behind 0 Celsius, we can better prepare for its effects and harness its potential in various applications.
Why is 0 Celsius Significant?
The significance of 0 Celsius extends far beyond its role as a temperature benchmark. It serves as a critical juncture in both natural and engineered systems, influencing everything from climate dynamics to industrial processes. One of the most notable aspects of 0 Celsius is its impact on water, a substance essential for life. At this temperature, water transitions from a liquid to a solid state, a process that shapes ecosystems, weather patterns, and human activities. For example, the formation of ice at 0 Celsius plays a vital role in regulating Earth's climate by reflecting sunlight and influencing ocean currents.
How Does 0 Celsius Influence Weather Patterns?
Weather systems are heavily influenced by the behavior of water at 0 Celsius. When temperatures drop to this threshold, water vapor in the atmosphere condenses and freezes, forming frost, snow, or ice. These phenomena not only affect visibility and travel but also contribute to the Earth's energy balance. For instance, snow-covered surfaces reflect more sunlight than bare ground, a phenomenon known as the albedo effect. This reflection helps cool the planet, making 0 Celsius a key player in global climate regulation.
What Role Does 0 Celsius Play in Ecosystems?
Ecosystems are finely tuned to the changes that occur at 0 Celsius. Many plants and animals have adapted to survive in environments where temperatures fluctuate around this threshold. For example, some trees enter a dormant state during winter, while certain animals hibernate to conserve energy. The freezing and thawing cycles at 0 Celsius also influence soil composition and nutrient availability, impacting plant growth and agricultural productivity. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting how ecosystems will respond to climate change.
Read also:Exploring The Most Dangerous Cities In The World Risks Realities And Resilience
In addition to its natural significance, 0 Celsius has practical applications in technology and industry. From refrigeration systems to cryogenics, this temperature is a cornerstone of modern engineering. By leveraging the properties of water at 0 Celsius, scientists and engineers have developed innovative solutions to preserve food, transport goods, and even advance medical research. The versatility of 0 Celsius underscores its importance in both scientific exploration and everyday life.
How Does 0 Celsius Affect the Environment?
The environmental impact of 0 Celsius is profound, influencing everything from seasonal changes to long-term climate trends. As temperatures hover around this threshold, ecosystems experience a delicate balance between freezing and thawing, which shapes the natural world in significant ways. For example, the formation of ice at 0 Celsius can alter water bodies, creating barriers for aquatic life while also insulating deeper layers from extreme cold. This dual role of ice—both as a disruptor and protector—highlights the complexity of its environmental effects.
How Does 0 Celsius Impact Water Bodies?
At 0 Celsius, water bodies such as lakes, rivers, and oceans undergo significant transformations. When surface water freezes, it forms a layer of ice that can act as an insulator, preventing deeper layers from freezing completely. This phenomenon is particularly important for aquatic ecosystems, as it allows fish and other organisms to survive in liquid water beneath the ice. However, prolonged freezing can also disrupt oxygen exchange, leading to hypoxic conditions that threaten marine life. Additionally, the melting of ice during warmer periods can cause flooding, erosion, and changes in water quality, further impacting ecosystems.
What Are the Effects of 0 Celsius on Terrestrial Ecosystems?
Terrestrial ecosystems are equally affected by the dynamics of 0 Celsius. In regions where temperatures frequently dip below this threshold, plants and animals have evolved unique adaptations to survive. For instance, deciduous trees shed their leaves to conserve water and energy, while animals grow thicker fur or migrate to warmer areas. The freeze-thaw cycle at 0 Celsius also influences soil structure, breaking down rocks and organic matter to release nutrients. However, rapid temperature fluctuations around this threshold can stress ecosystems, leading to reduced biodiversity and altered food chains.
On a broader scale, 0 Celsius plays a role in shaping global climate patterns. The albedo effect, driven by snow and ice at this temperature, influences how much solar energy is absorbed or reflected by the Earth's surface. This feedback loop can amplify climate change, as melting ice reduces reflectivity and increases warming. By understanding the environmental impact of 0 Celsius, we can better predict and mitigate the effects of climate change on both local and global scales.
What Happens to Water at 0 Celsius?
At 0 Celsius, water undergoes a fascinating transformation that lies at the heart of its unique properties. This temperature marks the point where water transitions from a liquid to a solid, a process governed by the interplay of molecular forces and energy levels. Understanding this transformation is essential for grasping the broader implications of 0 Celsius in both natural and engineered systems. The behavior of water at this temperature is not just a scientific curiosity but a critical factor in everything from weather patterns to industrial processes.
What Causes Water to Freeze at 0 Celsius?
Water freezes at 0 Celsius due to the slowing down of its molecules, which allows hydrogen bonds to lock them into a fixed, crystalline structure. At higher temperatures, water molecules move rapidly, breaking and reforming these bonds continuously. However, as the temperature drops to 0 Celsius, the kinetic energy of the molecules decreases, enabling the bonds to stabilize. This process requires additional energy, known as latent heat, to complete the phase change. Latent heat is absorbed or released during the transition, ensuring that the temperature remains constant until the phase change is complete.
Why Does Ice Float on Water?
One of the most intriguing aspects of water's behavior at 0 Celsius is the fact that ice floats. This phenomenon occurs because water expands as it freezes, becoming less dense than its liquid form. The hydrogen bonds in ice create a hexagonal lattice structure that occupies more space, reducing its density. This property is crucial for life on Earth, as floating ice insulates the water beneath it, allowing aquatic ecosystems to survive in cold climates. Without this unique characteristic, lakes and rivers could freeze solid, making it impossible for marine life to endure harsh winters.
The freezing of water at 0 Celsius also has practical implications. For example, it is the foundation of refrigeration and food preservation, where freezing halts the growth of bacteria and extends shelf life. In addition, the phase change at this temperature is harnessed in technologies such as air conditioning and cryogenics, demonstrating its versatility and importance in modern engineering.
Applications of 0 Celsius in Daily Life
The practical applications of 0 Celsius are vast and varied, touching nearly every aspect of daily life. From preserving food to ensuring safe transportation in cold weather, this temperature serves as a cornerstone of modern living. Understanding how 0 Celsius is utilized in everyday scenarios not only highlights its importance but also demonstrates the ingenuity of human innovation. Whether you're storing leftovers in the freezer or navigating icy roads, the influence of 0 Celsius is undeniable.
How Is 0 Celsius Used in Food Preservation?
One of the most common applications of 0 Celsius is in food preservation. Freezing food at or below this temperature halts the growth of microorganisms, such as bacteria and mold, which are responsible for spoilage. This process extends the shelf life of perishable items, from fruits and vegetables to meats and dairy products. Freezers in homes and commercial facilities are designed to maintain temperatures at or below 0 Celsius, ensuring that food remains safe and nutritious for extended periods. Additionally, freezing preserves the texture and flavor of food, making it a preferred method for long-term storage.
What Role Does 0 Celsius Play in Cold Weather Safety?
In regions where temperatures frequently dip to 0 Celsius or lower, this temperature plays a crucial role in safety and preparedness. For example, road maintenance crews use salt and other de-icing agents to lower the freezing point of water, preventing ice from forming on roads and highways. This practice reduces the risk of accidents and ensures safe travel during winter months. Similarly, individuals take precautions such as wearing insulated clothing and using antifreeze in vehicles to mitigate the effects of freezing temperatures. Understanding the behavior of water at 0 Celsius is essential for developing effective strategies to combat its challenges.
Beyond food preservation and safety, 0 Celsius is also utilized in recreational activities and hobbies. Ice skating, for instance, relies on the properties of water at this temperature to create smooth, solid surfaces for gliding. Similarly, the production of ice sculptures and the maintenance of ice rinks depend on precise temperature control around 0 Celsius. These examples illustrate how this seemingly simple temperature enriches our lives in countless ways.
How Can 0 Celsius Impact Human Health?
The effects of 0 Celsius on human health are both direct and indirect, influencing everything from physical well-being to mental resilience. Exposure to temperatures at or below this threshold can pose significant risks, particularly if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding these impacts is essential for safeguarding health during cold weather conditions. From hypothermia to seasonal affective disorder, the influence of 0 Celsius on human health is multifaceted and warrants careful consideration.
What Are the Physical Risks of Exposure to 0 Celsius?
Exposure to 0 Celsius and colder temperatures can lead to a range of physical health issues, with hypothermia being one of the most serious. Hypother
Crackstrem 2.0: The Ultimate Guide To Unlocking Streaming Potential
Understanding The Age Of Consent In Russia: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlocking The Secrets Of The Numerology Of 1111: A Comprehensive Guide
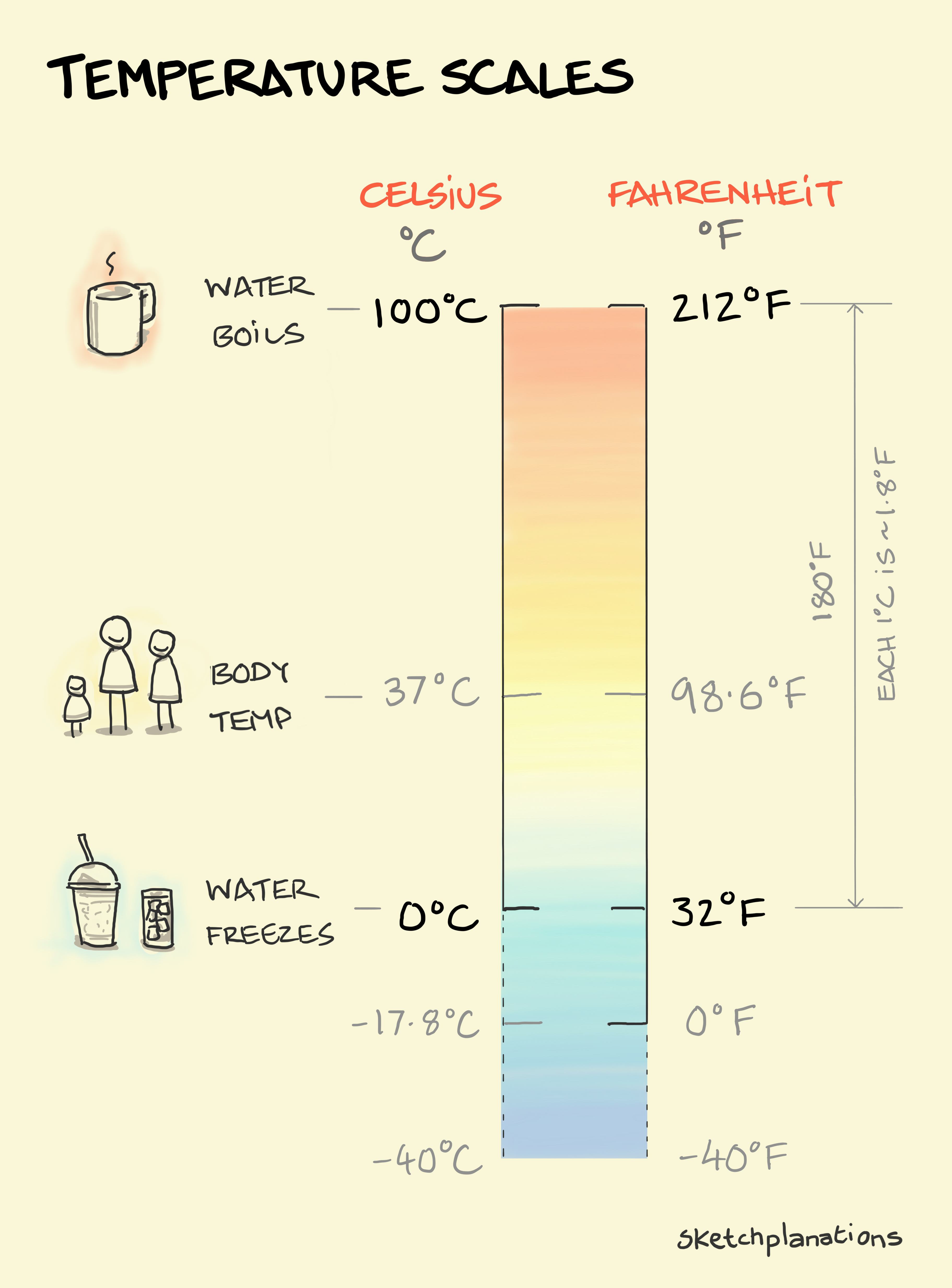
Fahrenheit and Celsius Sketchplanations

How to Convert Celsius to Kelvin 10 Steps (with Pictures)