Understanding 6 Gauge Wire Amps: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electrical wiring, understanding the capacity and applications of different wire gauges is crucial for safety and efficiency. Among the most commonly used wires is the 6 gauge wire, which is often chosen for its ability to handle significant electrical loads. This type of wire is frequently employed in scenarios requiring high current transmission, such as in industrial settings, automotive applications, and residential wiring upgrades. The term "6 gauge wire amps" refers to the maximum amperage that this wire can safely carry, a critical factor in ensuring both performance and safety.
Choosing the correct wire gauge is not just about meeting electrical codes; it's about ensuring that your electrical system operates at its best without risking overheating or electrical fires. 6 gauge wire amps are particularly important in applications where power needs are substantial, such as when connecting large appliances, running subpanels, or setting up sound systems in vehicles. Knowing the ampacity of your wire helps in making informed decisions about the electrical components you use, ultimately leading to a more reliable setup.
While many people understand the basic concept of wire gauges, the nuances of what makes 6 gauge wire suitable for specific tasks can be less clear. Factors such as the wire’s material—whether copper or aluminum—play a significant role in determining its ampacity. Copper, being a better conductor, allows for higher ampacity compared to aluminum. Additionally, the insulation type and environmental conditions can also affect the wire’s performance. In the following sections, we will explore these aspects in detail, providing you with a thorough understanding of 6 gauge wire amps and their applications.
Read also:Rick Moranis A Comprehensive Look At The Comedy Legends Life And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What Are 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
- How Does 6 Gauge Wire Compare to Other Gauges?
- What Are the Common Applications of 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
- How to Choose the Right Wire for Your Project?
- Is 6 Gauge Wire Safe for High-Current Applications?
- What Are the Materials and Insulation Types for 6 Gauge Wire?
- How Can You Ensure Proper Installation of 6 Gauge Wire?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 6 Gauge Wire Amps
What Are 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
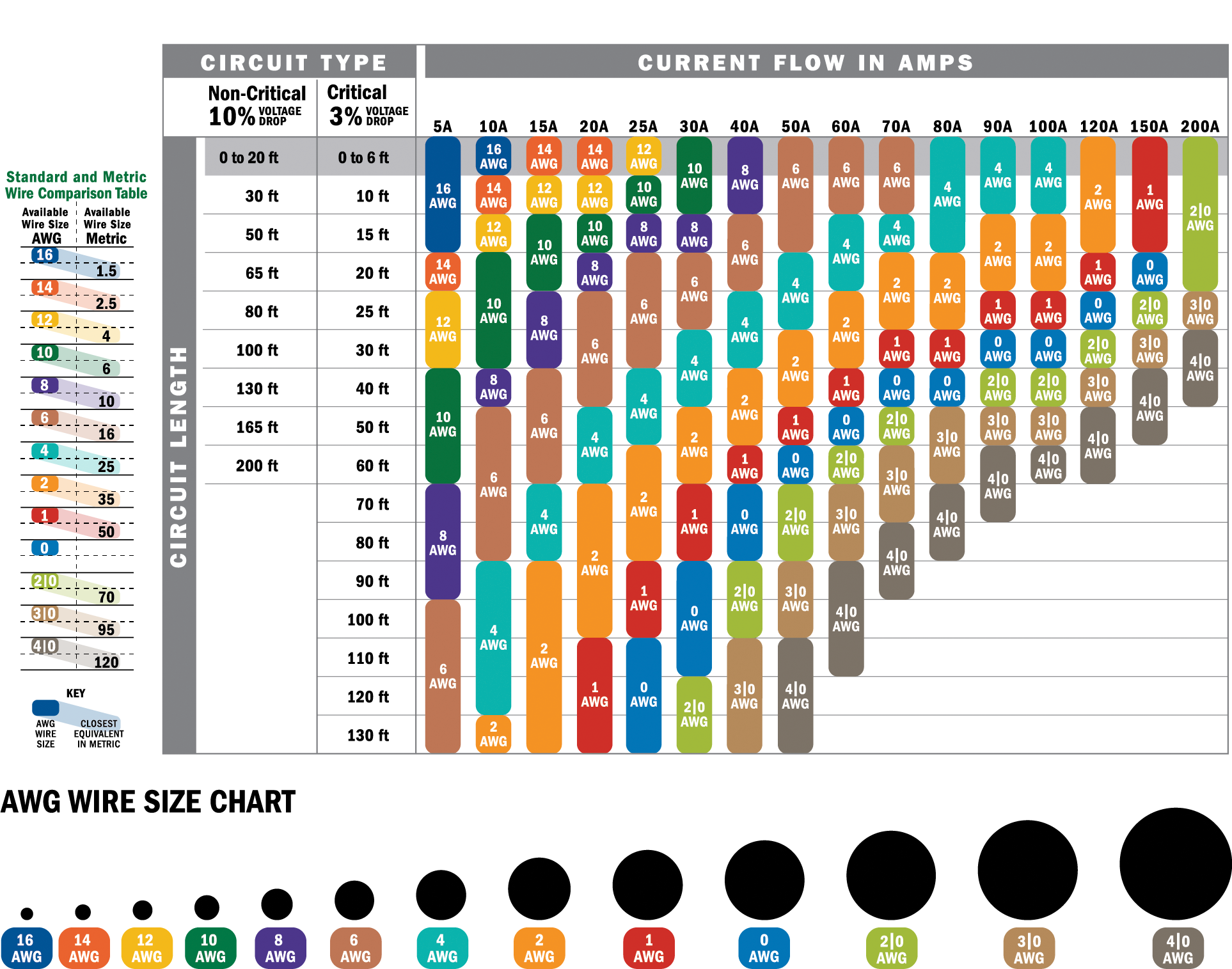
When discussing electrical wiring, the term "6 gauge wire amps" refers to the maximum current, measured in amperes (amps), that a 6 gauge wire can safely carry without overheating or causing a fire hazard. This measurement is critical for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. The ampacity of a wire depends on several factors, including its material, insulation, and the environmental conditions in which it is used. For instance, a copper 6 gauge wire typically has an ampacity of around 55 amps, while an aluminum wire of the same gauge may only handle around 40 amps.
Understanding the ampacity of 6 gauge wire is essential for anyone working on electrical projects. Overloading a wire beyond its rated capacity can lead to overheating, which poses a significant fire risk. This is why electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), provide guidelines for wire ampacity. These standards ensure that wires are used within safe limits, protecting both property and people from electrical hazards. For example, if you’re wiring a circuit that requires 50 amps, a 6 gauge copper wire would be suitable, but using an aluminum wire of the same gauge would not meet the necessary safety requirements.
Another important consideration is the length of the wire. Longer wires experience greater resistance, which can reduce their effective ampacity. This is why it’s crucial to account for the distance between the power source and the load when selecting a wire gauge. For instance, a 6 gauge wire might be perfect for a short run, but for longer distances, you might need to upgrade to a thicker gauge to maintain safe operating conditions. By understanding these factors, you can ensure that your electrical installations are both safe and efficient.
How Does 6 Gauge Wire Compare to Other Gauges?
When it comes to electrical wiring, the choice of wire gauge is critical for ensuring safety and efficiency. A 6 gauge wire is often considered a versatile option, but how does it stack up against other wire gauges? Understanding the differences can help you make informed decisions for your electrical projects. Let’s break down the comparisons between 6 gauge wire and other common wire sizes, such as 8 gauge and 4 gauge, to see how they differ in terms of ampacity, applications, and performance.
6 Gauge vs. 8 Gauge Wire: What Are the Key Differences?
One of the most common comparisons is between 6 gauge and 8 gauge wire. The primary difference lies in their ampacity. A 6 gauge wire can handle more current than an 8 gauge wire, making it suitable for higher-power applications. For instance, a copper 6 gauge wire typically has an ampacity of around 55 amps, while an 8 gauge wire is rated for approximately 40 amps. This difference is significant when you’re dealing with appliances or systems that require substantial electrical loads, such as air conditioners, water heaters, or large sound systems.
Another factor to consider is the physical size and flexibility of the wires. An 8 gauge wire is thinner and more flexible than a 6 gauge wire, which can be advantageous in tight spaces or for projects where ease of installation is a priority. However, if your project demands higher current transmission, the 6 gauge wire is the better choice despite its larger size. Additionally, the cost difference between the two gauges can be a deciding factor. While 6 gauge wire is generally more expensive, the added capacity and safety it provides often justify the investment for high-demand applications.
Read also:What Kind Of Cancer Did Melanie Olmstead Have A Comprehensive Guide
6 Gauge vs. 4 Gauge Wire: Is Bigger Always Better?
On the other end of the spectrum, comparing 6 gauge wire to 4 gauge wire reveals a different set of considerations. A 4 gauge wire can handle even more current than a 6 gauge wire, with an ampacity of around 70 amps for copper wires. This makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as connecting large subpanels, powering industrial equipment, or setting up extensive sound systems in vehicles. However, the increased capacity comes with trade-offs in terms of size, flexibility, and cost.
One of the main drawbacks of using a 4 gauge wire is its larger diameter, which can make installation more challenging, especially in confined spaces. Additionally, 4 gauge wire is significantly more expensive than 6 gauge wire, which might not be justified for projects that don’t require such high current transmission. In many cases, a 6 gauge wire strikes the perfect balance between capacity and practicality, offering sufficient ampacity for most residential and automotive applications without the added cost and installation challenges of a 4 gauge wire.
When to Choose 6 Gauge Wire Over Other Gauges
So, when should you choose a 6 gauge wire over other options? The decision largely depends on the specific requirements of your project. Here are some scenarios where 6 gauge wire is the ideal choice:
- High-Power Appliances: If you’re wiring a circuit for appliances that require 50-55 amps, such as electric ranges or large air conditioners, a 6 gauge wire is appropriate.
- Automotive Applications: In vehicles, 6 gauge wire is often used for sound systems, winches, or other high-current accessories.
- Subpanels: When running a subpanel that requires up to 55 amps, a 6 gauge wire is a safe and efficient choice.
By understanding how 6 gauge wire compares to other gauges, you can make informed decisions that ensure both safety and efficiency in your electrical projects. Whether you’re working on a home improvement project or setting up a sound system in your car, choosing the right wire gauge is crucial for optimal performance.
What Are the Common Applications of 6 Gauge Wire Amps?
Understanding the applications of 6 gauge wire amps is essential for anyone involved in electrical projects, whether you're a professional electrician or a DIY enthusiast. This type of wire is incredibly versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of uses in both residential and automotive settings. Its ability to handle significant electrical loads makes it a popular choice for various high-power applications. Let’s explore some of the most common uses of 6 gauge wire amps and how they contribute to the efficiency and safety of electrical systems.
Residential Wiring: Powering High-Demand Appliances
In residential settings, 6 gauge wire amps are often used to power high-demand appliances that require substantial electrical loads. These include electric ranges, water heaters, and air conditioning units. For instance, an electric range typically requires a dedicated circuit with a capacity of 50-55 amps, making a 6 gauge copper wire the ideal choice. This ensures that the appliance operates safely and efficiently without the risk of overheating or causing electrical fires.
Another common residential application is running subpanels. Subpanels are used to distribute power to different areas of a home, such as a garage or basement. A 6 gauge wire can safely carry the necessary current to these subpanels, ensuring that all connected devices and appliances receive adequate power. Additionally, 6 gauge wire is often used in home renovation projects where upgrading the electrical system is necessary to meet modern power demands. By using 6 gauge wire, homeowners can ensure that their electrical systems are both safe and capable of handling increased loads.
Automotive Applications: Enhancing Vehicle Performance
In the automotive world, 6 gauge wire amps are frequently employed to enhance vehicle performance and functionality. One of the most common uses is in sound systems, where high-powered amplifiers require substantial current to drive large speakers and subwoofers. A 6 gauge wire can efficiently transmit the necessary power, ensuring that the sound system operates at its best without any loss of performance.
Another popular automotive application is wiring for winches, which are often used in off-road vehicles and trucks. Winches require a significant amount of current to operate, and using a 6 gauge wire ensures that they receive the power needed for effective performance. Additionally, 6 gauge wire is used in various other automotive accessories, such as lighting systems, inverters, and battery connections. These applications benefit from the wire’s ability to handle high current loads, providing reliable and safe power transmission.
Industrial and Commercial Uses: Supporting Heavy Machinery
Beyond residential and automotive applications, 6 gauge wire amps are also widely used in industrial and commercial settings. In these environments, the wire is often employed to power heavy machinery and equipment that require substantial electrical loads. For example, in manufacturing facilities, 6 gauge wire is used to connect large motors, conveyor systems, and other industrial equipment. This ensures that these machines operate efficiently and safely, minimizing the risk of electrical failures or hazards.
Commercial buildings, such as offices and retail spaces, also benefit from the use of 6 gauge wire. It is commonly used in lighting systems, HVAC units, and backup power systems. The wire’s high ampacity makes it suitable for these applications, ensuring that all electrical components receive the power they need to function correctly. By using 6 gauge wire, businesses can maintain reliable and efficient electrical systems, supporting their daily operations and enhancing overall productivity.
In summary, the common applications of 6 gauge wire amps are diverse and critical for various electrical projects. Whether you’re powering high-demand appliances in a home, enhancing vehicle performance, or supporting heavy machinery in industrial settings, 6 gauge wire provides the necessary capacity and safety. Its versatility and reliability make it an indispensable component in modern electrical systems, ensuring optimal performance and peace of mind.
How to Choose the Right Wire for Your Project?
Selecting the appropriate wire for your project is a critical decision that impacts both safety and performance. With numerous options available, understanding the factors that influence wire selection can help you make informed choices. When it comes to 6 gauge wire amps, several considerations must be taken into account to ensure that your project meets all necessary requirements. Let’s explore the key factors you should consider when choosing the right wire for your specific needs.
Assessing Power Requirements: What Does Your Project Need?
The first step in choosing the right wire is assessing the power requirements of your project. This involves determining the amount of current, measured in amps, that your electrical system will need to handle. For instance, if you’re wiring a circuit for a high-power appliance like an electric range or a water heater, you’ll need
Nutrition In Bread Slice: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Benefits And Impact
Discover The World Of Vanilla Hift.com: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Features And Benefits
What Size Wire Is Needed For 100 Amp Service? A Complete Guide
20 Gauge Wire Amps

What Gauge Wire To Use For 240v 20 Amps