Understanding And Managing Blood Pressure 160/110: A Comprehensive Guide
When left untreated, these elevated readings can lead to irreversible damage to vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, and brain. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for blood pressure 160/110 is essential for anyone experiencing this condition or concerned about their cardiovascular health. Early detection and proactive management can make a substantial difference in long-term outcomes. High blood pressure, particularly at the 160/110 level, often develops gradually over time and may not present noticeable symptoms in its early stages. This "silent killer" can quietly damage blood vessels and organs without any warning signs. The systolic pressure of 160 indicates the force against artery walls during heartbeats, while the diastolic pressure of 110 represents the pressure during heart rest periods. Both numbers being elevated suggests that the heart is working harder than normal to pump blood throughout the body, potentially leading to various cardiovascular complications. Understanding these numbers and their implications is crucial for making informed healthcare decisions. Recognizing the significance of blood pressure 160/110 requires understanding how it fits into the broader context of hypertension management. This level of blood pressure falls into Stage 2 Hypertension according to medical guidelines, indicating a need for immediate medical intervention. The condition demands a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication management, and regular monitoring. By addressing blood pressure 160/110 proactively, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing serious health complications while improving their overall quality of life.
Table of Contents
- What Causes Blood Pressure to Reach 160/110?
- How Dangerous Is Blood Pressure 160/110?
- Effective Lifestyle Changes to Lower Blood Pressure
- What Are the Best Medication Options?
- Tips for Monitoring Your Blood Pressure at Home
- How Does Diet Impact Blood Pressure Levels?
- The Benefits of Regular Exercise for Hypertension
- Stress Management Techniques for Blood Pressure Control
What Causes Blood Pressure to Reach 160/110?
Several factors contribute to blood pressure readings reaching the critical level of 160/110. Understanding these causes is essential for developing effective prevention and management strategies. The primary contributors can be categorized into lifestyle factors, genetic predispositions, and underlying health conditions.
Unhealthy lifestyle choices often play a significant role in elevating blood pressure to dangerous levels. These include:
Read also:Exploring The Most Dangerous Cities In The World Risks Realities And Resilience
- Consuming excessive amounts of sodium, particularly from processed foods and restaurant meals
- Leading a predominantly sedentary lifestyle with minimal physical activity
- Being overweight or obese, which puts additional strain on the cardiovascular system
- Chronic heavy alcohol consumption and smoking habits
- Poor sleep patterns and untreated sleep disorders like sleep apnea
Genetic factors also contribute significantly to the development of severe hypertension. Family history of high blood pressure, particularly when multiple close relatives have experienced blood pressure 160/110 or similar levels, increases an individual's risk. Certain ethnic groups, particularly African Americans, show higher prevalence rates of severe hypertension due to genetic predispositions.
Underlying Health Conditions That Elevate Blood Pressure
Several medical conditions can directly lead to blood pressure readings of 160/110:
- Chronic kidney disease and renal artery stenosis
- Thyroid disorders, both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
- Cushing's syndrome and other endocrine disorders
- Obstructive sleep apnea and other respiratory conditions
- Diabetes and insulin resistance
Environmental and Psychological Factors
Modern lifestyle stressors significantly contribute to elevated blood pressure levels. Chronic work-related stress, financial pressures, and social isolation can all lead to sustained blood pressure elevation. Environmental factors such as air pollution and noise pollution have also been linked to increased hypertension rates.
How Dangerous Is Blood Pressure 160/110?
Blood pressure readings at 160/110 represent a severe health risk that requires immediate attention. The dangers associated with this level of hypertension extend far beyond just cardiovascular concerns, affecting multiple systems throughout the body. Understanding these risks is crucial for motivating appropriate medical intervention and lifestyle changes.
Cardiovascular complications pose the most immediate threat. At this pressure level, the heart must work significantly harder to pump blood through the body, leading to:
- Increased risk of heart attack and heart failure
- Higher likelihood of developing coronary artery disease
- Accelerated atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Elevated risk of aneurysms and other vascular complications
Impact on Vital Organs
The sustained pressure of 160/110 can cause progressive damage to major organs:
Read also:Understanding The Connection Between Melania Trump And Vladimir Putin A Comprehensive Insight
- Kidneys: Reduced blood flow can lead to chronic kidney disease and eventual kidney failure
- Brain: Increased risk of stroke, transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes), and vascular dementia
- Eyes: Hypertensive retinopathy can cause vision problems and potential blindness
Long-Term Consequences
If left untreated, blood pressure 160/110 can lead to:
- Metabolic syndrome development
- Memory problems and cognitive decline
- Peripheral artery disease
- Sexual dysfunction in both men and women
Effective Lifestyle Changes to Lower Blood Pressure
Implementing comprehensive lifestyle modifications can significantly impact blood pressure levels, even when starting at 160/110. These changes work synergistically to create a healthier cardiovascular environment and can often reduce the need for medication or enhance its effectiveness.
Dietary adjustments form the foundation of blood pressure management:
- Adopt the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan
- Increase consumption of potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach
- Reduce daily sodium intake to less than 1,500 mg
- Incorporate more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into meals
- Limit saturated fats and cholesterol-rich foods
Physical Activity Recommendations
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in blood pressure management:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly
- Include strength training exercises twice weekly
- Incorporate daily walking sessions of 30-60 minutes
- Practice flexibility and balance exercises
Weight Management Strategies
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for blood pressure control:
- Set realistic weight loss goals of 1-2 pounds per week
- Monitor waist circumference regularly
- Use portion control techniques
- Keep a food diary to track eating patterns
What Are the Best Medication Options?
When lifestyle changes alone aren't sufficient to manage blood pressure 160/110, medication becomes an essential component of treatment. Various classes of antihypertensive medications offer different mechanisms of action, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatment to individual needs.
The most commonly prescribed medication classes include:
- ACE inhibitors (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors)
- ARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Beta-blockers
Factors Influencing Medication Choice
Several considerations determine the most appropriate medication:
- Age and overall health status
- Presence of other medical conditions
- Potential side effects and drug interactions
- Cost and insurance coverage
- Personal preferences and lifestyle
Combination Therapy Approaches
In many cases, especially with blood pressure 160/110, combination therapy proves more effective:
- Two or more medications working through different mechanisms
- Lower doses of multiple medications to minimize side effects
- Fixed-dose combination pills for convenience
- Gradual adjustment of medication regimen
Tips for Monitoring Your Blood Pressure at Home
Regular home monitoring of blood pressure 160/110 or similar readings provides valuable information for both patients and healthcare providers. Proper technique and consistent measurement practices ensure accurate readings that can guide treatment decisions and track progress over time.
Essential equipment and preparation guidelines include:
- Using a validated automatic upper arm monitor
- Ensuring proper cuff size for accurate readings
- Measuring at the same time each day
- Avoiding caffeine, exercise, and smoking 30 minutes before measurement
- Sitting quietly for 5 minutes before taking readings
Recording and Tracking Readings
Effective documentation practices help identify patterns and trends:
- Maintain a written log or use digital tracking apps
- Record both systolic and diastolic readings
- Note the time of day and any relevant circumstances
- Share regular updates with healthcare providers
- Identify triggers that affect blood pressure levels
Interpreting Home Monitoring Results
Understanding home readings in context is crucial:
- Recognize normal fluctuations throughout the day
- Identify consistently high readings requiring attention
- Track response to medication and lifestyle changes
- Understand the difference between home and clinical measurements
How Does Diet Impact Blood Pressure Levels?
Nutritional choices play a fundamental role in managing blood pressure 160/110, with specific dietary components directly influencing blood pressure regulation. Understanding the relationship between food and blood pressure can help create effective dietary strategies for hypertension management.
Key dietary elements that impact blood pressure include:
- Sodium: Excessive intake leads to water retention and increased pressure
- Potassium: Helps balance sodium levels and relax blood vessel walls
- Magnesium: Supports proper muscle function and blood vessel relaxation
- Calcium: Essential for proper blood vessel contraction and relaxation
- Fiber: Improves overall cardiovascular health and cholesterol levels
Specific Foods to Embrace and Avoid
Incorporating beneficial foods while limiting harmful options:
- Include more leafy greens, berries, and whole grains
- Choose low-fat dairy products and lean proteins
- Limit processed foods, canned soups, and salty snacks
- Reduce consumption of red meat and full-fat dairy
- Avoid sugary beverages and high-calorie desserts
Meal Planning Strategies
Creating a sustainable eating pattern:
- Prepare meals at home using fresh ingredients
- Practice mindful eating techniques
- Plan weekly menus and grocery shopping
- Use herbs and spices instead of salt for flavor
The Benefits of Regular Exercise for Hypertension
Physical activity serves as a powerful tool in managing blood pressure 160/110, offering both immediate and long-term benefits. Regular exercise helps strengthen the heart, improve circulation, and reduce stress, all of which contribute to better blood pressure control.
Various types of exercise provide distinct advantages:
- Aerobic activities like walking, cycling, and swimming
- Strength training exercises using weights or resistance bands
- Flexibility and stretching routines
- Yoga and tai chi for mind-body connection
- High-intensity interval training (under medical supervision)
Exercise Intensity and Frequency Guidelines
Recommended exercise parameters for blood pressure management:
- Moderate-intensity exercise: 150 minutes weekly
- Vigorous-intensity exercise: 75 minutes
Exploring Norah O'Donnell's Height And Career: A Comprehensive Look
Discover The Best Gift Ideas At Banilla Gift.com: Your Ultimate Gifting Destination
Understanding Green Mold On Chocolate: Causes, Prevention, And Solutions
Blood Pressure MARIAM ELECTROPATHY HOSPITAL
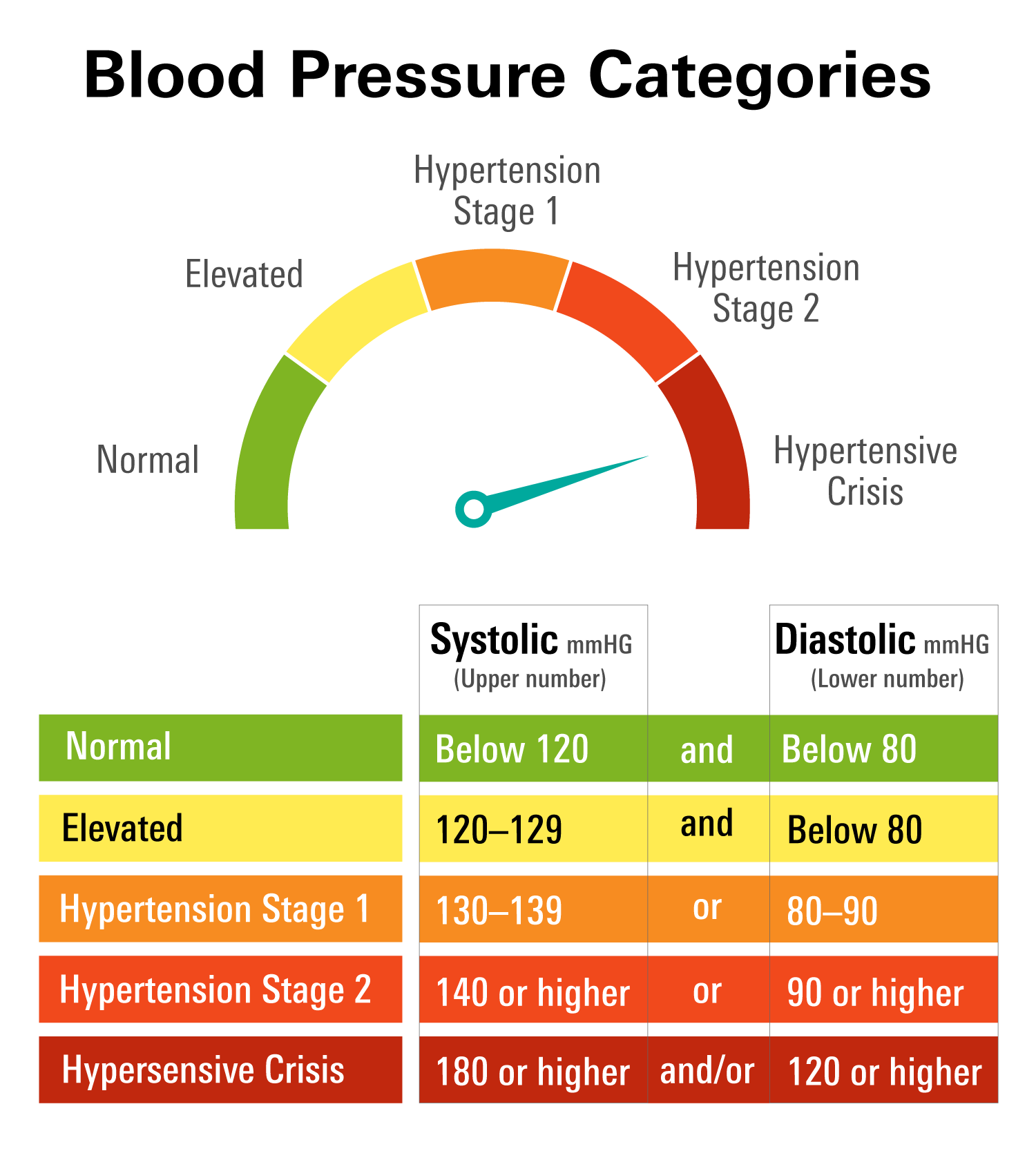
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings