Understanding The Importance Of 100 Amps Wire Size: A Complete Guide
The concept of wire size might seem technical, but it’s not as complicated as it appears. Essentially, wire size refers to the diameter of the conductor, which is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG). For a 100-amp service, the wire size must be able to handle the current load without excessive resistance, which can cause energy loss and overheating. Factors such as the distance between the electrical panel and the main service point, the type of wire material (copper or aluminum), and environmental conditions all play a role in determining the appropriate wire size. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to select the right wire size for your 100-amp service. This guide is designed to be your go-to resource for all things related to 100 amps wire size. We’ll cover everything from basic principles and calculations to common mistakes and frequently asked questions. Whether you’re planning a new installation, upgrading your current system, or simply looking to expand your knowledge, this article will provide you with the insights and tools you need to make informed decisions. Let’s dive in and explore the world of electrical wiring with confidence and clarity.
Table of Contents
- What is 100 Amps Wire Size and Why Does It Matter?
- How to Calculate the Right Wire Size for 100 Amps?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which is Better for 100 Amps?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing 100 Amps Wire Size?
- Can You Use 100 Amps Wire Size for Long-Distance Installations?
- What Regulations and Standards Govern 100 Amps Wire Size?
- Is It Worth Upgrading Your Electrical System to 100 Amps?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amps Wire Size
What is 100 Amps Wire Size and Why Does It Matter?
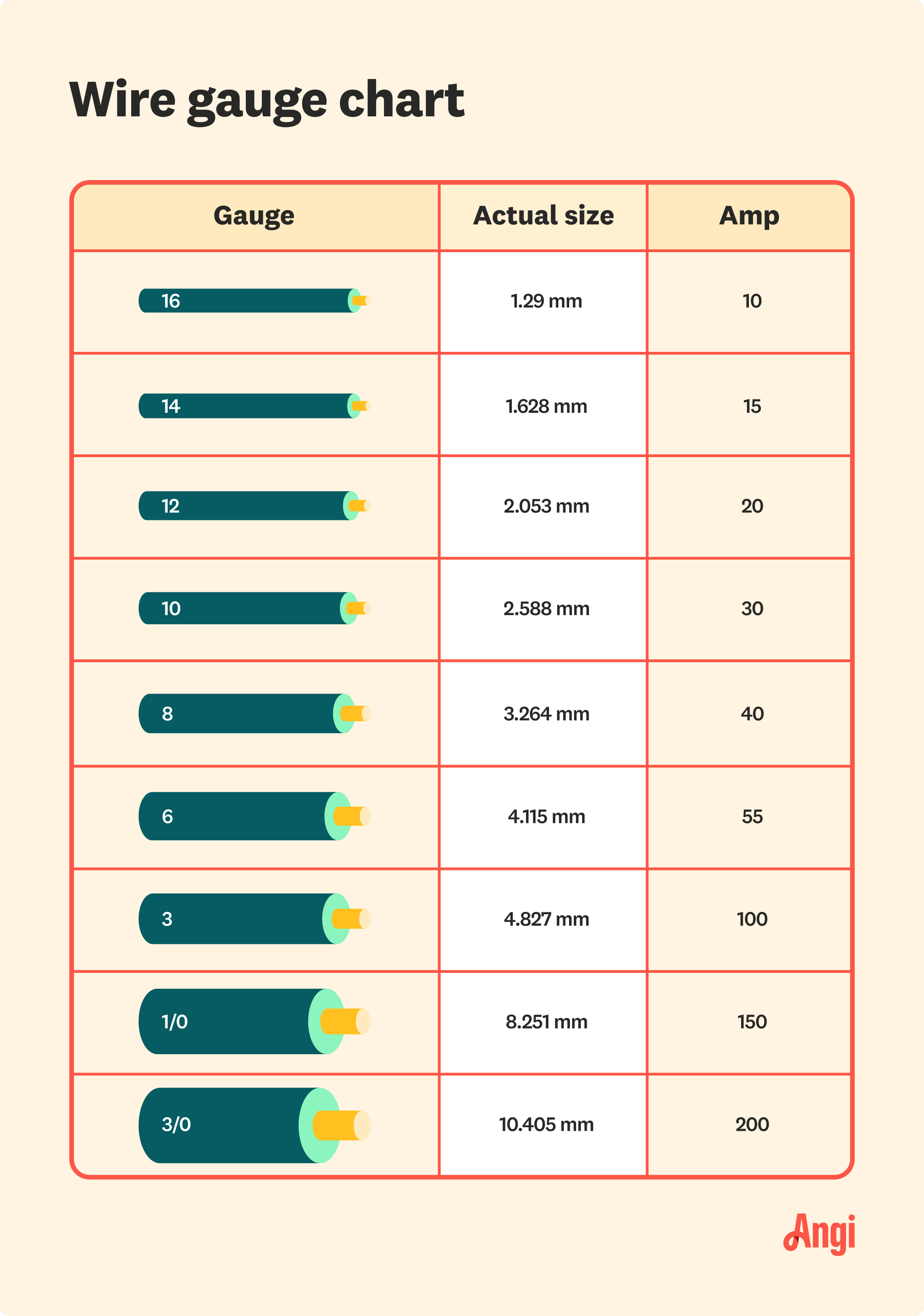
Understanding the concept of 100 amps wire size is essential for anyone dealing with electrical systems. Simply put, the wire size determines how much current the wire can safely carry without overheating. For a 100-amp service, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines on the minimum wire size required to ensure safety and efficiency. Typically, a 100-amp service requires a wire size of 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum. These sizes are designed to handle the current load while minimizing resistance and energy loss.
Why Does Wire Size Matter?
Choosing the correct wire size is not just about meeting code requirements; it’s about ensuring the safety and reliability of your electrical system. Using a wire that’s too small for the current load can result in overheating, which may lead to electrical fires. On the other hand, using a wire that’s too large can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with. The right wire size ensures that your system operates efficiently, reduces energy waste, and prolongs the lifespan of your electrical components.
Read also:Baryshnikov The Legendary Dancer Who Redefined Ballet
Factors Influencing Wire Size Selection
Several factors influence the selection of wire size for a 100-amp service. These include:
- Material: Copper wires are more conductive than aluminum, meaning they can carry the same current with a smaller diameter.
- Distance: Longer runs require larger wire sizes to compensate for voltage drop.
- Environment: Wires exposed to high temperatures or corrosive environments may need to be upsized for safety.
How to Calculate the Right Wire Size for 100 Amps?
Calculating the correct wire size for a 100-amp service involves understanding the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. The NEC provides tables and formulas to help determine the appropriate wire size based on these factors. For example, the formula for calculating voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 × Length × Current × Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length: The distance between the electrical panel and the load in feet.
- Current: The amperage of the circuit (100 amps in this case).
- Resistance: The resistance per 1,000 feet of wire, which depends on the wire size and material.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Wire Size
Here’s a simplified step-by-step guide to help you determine the correct wire size:
- Identify the total current load (100 amps).
- Measure the distance from the electrical panel to the load.
- Choose the wire material (copper or aluminum).
- Use NEC tables or online calculators to find the appropriate wire size.
- Adjust for environmental factors like temperature or conduit type.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wires: Which is Better for 100 Amps?
When it comes to selecting wire material for a 100-amp service, the debate between copper and aluminum is a common one. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice often depends on budget, application, and personal preference.
Read also:Diane Furnberg Exploring Her Life Achievements And Impact
Advantages of Copper Wires
Copper is the preferred choice for many electricians due to its superior conductivity and durability. Some key advantages include:
- Higher conductivity, allowing for smaller wire sizes.
- Greater resistance to corrosion and environmental damage.
- Longer lifespan and lower maintenance costs.
Advantages of Aluminum Wires
While aluminum is less conductive than copper, it is significantly lighter and more affordable. This makes it a popular choice for large-scale installations. Key benefits include:
- Lower cost compared to copper.
- Easier to handle and install due to its lighter weight.
- Suitable for long-distance runs where cost is a concern.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing 100 Amps Wire Size?
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when selecting wire sizes for a 100-amp service. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Ignoring Voltage Drop: Failing to account for voltage drop in long runs can lead to inefficient performance.
- Using Undersized Wires: This is a major safety hazard that can result in overheating and fires.
- Overlooking Environmental Factors: High temperatures or corrosive environments require upsized wires.
Can You Use 100 Amps Wire Size for Long-Distance Installations?
Long-distance installations pose unique challenges when it comes to selecting the right wire size. As the distance increases, so does the resistance, which can lead to significant voltage drop. For 100-amp services, it’s crucial to use larger wire sizes to compensate for this drop and ensure efficient performance.
How to Address Voltage Drop in Long Runs
To minimize voltage drop in long-distance installations:
- Use larger wire sizes than the minimum required.
- Consider upgrading to copper wires for better conductivity.
- Install intermediate junction boxes to break the run into shorter segments.
What Regulations and Standards Govern 100 Amps Wire Size?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets the standards for wire sizes in electrical installations. These regulations ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with local building codes. For a 100-amp service, the NEC specifies minimum wire sizes based on material and application.
Key NEC Guidelines for 100 Amps Wire Size
- Minimum 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum for standard installations.
- Adjustments for voltage drop and environmental factors.
- Requirements for conduit size and grounding.
Is It Worth Upgrading Your Electrical System to 100 Amps?
Upgrading to a 100-amp service can provide numerous benefits, especially for older homes or those with high electrical demands. Modern appliances, HVAC systems, and home automation devices often require more power than older 60-amp systems can provide.
Advantages of a 100-Amp Service
- Increased capacity for modern appliances and electronics.
- Improved safety and reliability of the electrical system.
- Higher resale value for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amps Wire Size
What Happens If You Use the Wrong Wire Size for 100 Amps?
Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and even electrical fires. It’s crucial to follow NEC guidelines and consult a professional if you’re unsure.
Can You Mix Copper and Aluminum Wires in a 100-Amp Service?
While technically possible, mixing copper and aluminum wires is not recommended due to differences in conductivity and expansion rates, which can lead to loose connections and safety hazards.
How Much Does It Cost to Upgrade to a 100-Amp Service?
The cost of upgrading to a 100-amp service varies depending on location, materials, and labor. On average, homeowners can expect to pay between $1,500 and $3,000 for the upgrade.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wire size for a 100-amp service is a critical decision that impacts the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical system. By understanding the factors that influence wire size selection, calculating voltage drop, and adhering to NEC guidelines, you can ensure a successful installation. Whether you’re upgrading your home or planning a new build, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions about 100 amps wire size.
External Resources
For more information on electrical codes and standards, visit the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) website.
Calories In A Slice Of Bread: Everything You Need To Know About Bread Nutrition
What’s The Difference Between A Lake And A Pond? Explained
Why The PS5 Costco Bundle Is The Ultimate Gaming Deal: Everything You Need To Know

Copper Wire For 100 Amps
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi