Understanding The Nutritional Profile Of White Bread: What You Need To Know About Nutrients In White Bread
White bread is a staple in many households, often enjoyed for its soft texture and versatility in meals. However, beneath its fluffy exterior lies a nutritional profile that many may not fully understand. While it is often criticized for being less nutritious than whole-grain alternatives, white bread does contain essential nutrients that contribute to a balanced diet. Understanding what nutrients in white bread offer can help you make informed dietary choices and appreciate its role in your daily meals.
At its core, white bread is made from refined wheat flour, which undergoes a milling process that removes the bran and germ, leaving behind the starchy endosperm. This process gives white bread its characteristic light color and soft texture. Despite the refining process, manufacturers often enrich white bread with vitamins and minerals to compensate for the nutrients lost during milling. These added nutrients, combined with the natural components of wheat, make white bread a source of carbohydrates, protein, and even small amounts of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
While white bread may not match the nutrient density of whole-grain options, it still provides energy and essential nutrients that can support daily activities. From B vitamins to iron and calcium, the nutrients in white bread play a role in maintaining overall health. By exploring its nutritional composition and understanding how it fits into a balanced diet, you can better appreciate the value white bread brings to your plate while making mindful choices about its consumption.
Read also:Dawn Wells Measurements A Complete Guide To Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- What Are the Key Nutrients in White Bread?
- How Does White Bread Compare to Whole Grain Bread?
- Is White Bread Bad for Your Health?
- What Role Do Carbohydrates Play in White Bread?
- Can White Bread Support a Balanced Diet?
- How Are Nutrients in White Bread Enriched?
- What Are the Health Benefits of Nutrients in White Bread?
- How Can You Make Healthier Choices with White Bread?
What Are the Key Nutrients in White Bread?
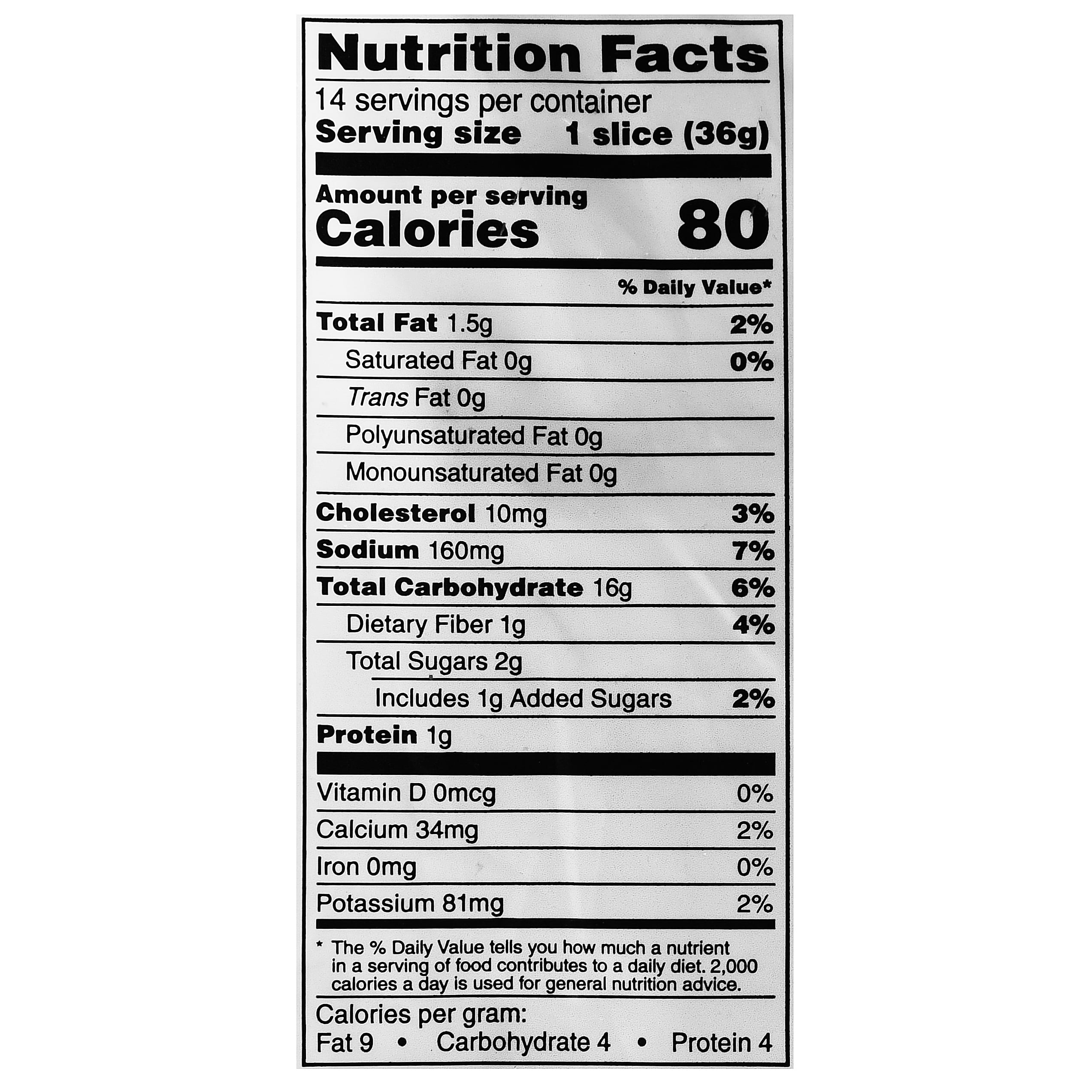
White bread contains a variety of nutrients, many of which are added during the enrichment process. These include essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health. Below is a breakdown of the key nutrients found in white bread:
- Carbohydrates: The primary macronutrient in white bread, providing energy for daily activities.
- Protein: Though not as high as whole-grain bread, white bread contains a moderate amount of protein, essential for muscle repair and growth.
- B Vitamins: Enriched white bread often contains thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), and folic acid (B9), which support energy metabolism and red blood cell production.
- Iron: An essential mineral added to enriched white bread, iron helps transport oxygen in the blood and prevents anemia.
- Calcium: Some brands fortify white bread with calcium, which is vital for bone health and muscle function.
These nutrients are carefully balanced to ensure that white bread remains a convenient and accessible source of essential vitamins and minerals, even after the refining process.
Why Are B Vitamins Important in White Bread?
B vitamins play a crucial role in converting food into energy, making them essential for maintaining vitality. Enriched white bread is a reliable source of these vitamins, which are particularly important for individuals with limited access to whole grains. By including B vitamins, white bread helps bridge nutritional gaps in modern diets.
How Does Iron Support Your Body?
Iron is a mineral that supports the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Enriched white bread provides a small but significant amount of iron, contributing to the prevention of fatigue and supporting cognitive function.
How Does White Bread Compare to Whole Grain Bread?
When comparing white bread to whole grain bread, it's essential to consider their nutritional differences. Whole grain bread retains the bran, germ, and endosperm of the wheat kernel, making it richer in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. On the other hand, white bread undergoes a refining process that removes these components, resulting in a lower fiber content and fewer naturally occurring nutrients.
Despite these differences, enriched white bread can still offer comparable levels of certain vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins and iron. However, whole grain bread provides additional benefits, including higher fiber content, which supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. The choice between the two often depends on individual dietary needs and preferences.
Read also:Discovering Kevin Beets A Journey Through His Life And Achievements
Is White Bread Bad for Your Health?
White bread has often been criticized for its high glycemic index and lower fiber content, which can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. However, it is not inherently "bad" for your health. Moderation and mindful consumption are key to incorporating white bread into a balanced diet.
For individuals with specific health conditions, such as diabetes or gluten intolerance, white bread may need to be consumed in limited quantities or substituted with alternatives. However, for most people, white bread can be part of a healthy diet when paired with nutrient-dense foods like lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats.
Can White Bread Cause Weight Gain?
Weight gain is often associated with excessive calorie intake rather than the consumption of white bread alone. While white bread is calorie-dense, it can still fit into a weight management plan when portion sizes are controlled and balanced with physical activity.
Should You Avoid White Bread if You Have Diabetes?
Individuals with diabetes should monitor their carbohydrate intake, including the consumption of white bread. Opting for whole grain alternatives or pairing white bread with protein and healthy fats can help mitigate blood sugar spikes.
What Role Do Carbohydrates Play in White Bread?
Carbohydrates are the primary macronutrient in white bread, providing the body with a quick source of energy. The refined carbohydrates in white bread are easily digestible, making them ideal for individuals who need an immediate energy boost, such as athletes or those recovering from illness.
While refined carbs have been linked to health concerns, they are not inherently harmful when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Pairing white bread with nutrient-rich foods can enhance its nutritional value and support overall health.
Can White Bread Support a Balanced Diet?
White bread can contribute to a balanced diet when consumed in moderation and paired with other nutrient-dense foods. Its versatility makes it an excellent base for sandwiches, toast, and snacks that incorporate vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
For example, a sandwich made with white bread, turkey, spinach, and avocado provides a mix of carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats, and vitamins. This combination ensures a more balanced and satisfying meal that supports overall health.
How Are Nutrients in White Bread Enriched?
During the enrichment process, manufacturers add specific vitamins and minerals to white bread to replace those lost during refining. This process ensures that white bread remains a valuable source of essential nutrients, even after the bran and germ are removed.
Commonly added nutrients include B vitamins, iron, and sometimes calcium. Enrichment helps address potential nutritional deficiencies and makes white bread a convenient option for individuals seeking fortified foods.
What Are the Health Benefits of Nutrients in White Bread?
The nutrients in white bread offer several health benefits, including improved energy metabolism, enhanced immune function, and better oxygen transport in the blood. B vitamins, iron, and calcium work together to support overall well-being and vitality.
For example, folic acid in white bread is particularly important for pregnant women, as it helps prevent neural tube defects in developing fetuses. Similarly, iron supports cognitive function and reduces fatigue, making enriched white bread a practical choice for many individuals.
How Can You Make Healthier Choices with White Bread?
Making healthier choices with white bread involves mindful consumption and pairing it with nutrient-dense foods. Here are some tips:
- Choose whole grain or multigrain options when possible.
- Pair white bread with lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats to create balanced meals.
- Control portion sizes to avoid excessive calorie intake.
By incorporating these strategies, you can enjoy the convenience and taste of white bread while maintaining a healthy diet.
FAQs
What Are the Main Nutrients in White Bread?
White bread is enriched with B vitamins, iron, and sometimes calcium. It also provides carbohydrates and a moderate amount of protein.
Is White Bread a Good Source of Fiber?
White bread contains minimal fiber compared to whole grain options. However, some brands may add fiber during the enrichment process.
Can White Bread Be Part of a Healthy Diet?
Yes, white bread can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation and paired with nutrient-dense foods.
Conclusion
Understanding the nutrients in white bread allows you to make informed decisions about its role in your diet. While it may not match the nutritional profile of whole grain bread, white bread offers essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health. By incorporating it mindfully and pairing it with other nutritious foods, you can enjoy its convenience and taste while supporting a balanced diet.
For more information on the nutritional benefits of bread, visit the Healthline website.
How To Check VanillaGift Balance: A Complete Guide To Managing Your Gift Card
Do Animal Cells Have A Cell Membrane? Discover The Key To Cellular Life
What Is Lab Cor? A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Utilizing Lab Cor
Wonder White Bread Nutrition Label Besto Blog

Hand drawn sketch fresh wheat bread symbol. Soft white bread being