Understanding White Bread Nutrition: A Comprehensive Guide
Whether you enjoy it as a sandwich base, toast, or a side to your favorite soup, knowing the facts about white bread nutrition can help you make informed dietary choices. In this article, we will delve deep into the nutritional aspects of white bread, explore its health implications, and provide practical tips for incorporating it into your diet without compromising your health goals. White bread is made from refined wheat flour, which undergoes processing to remove the bran and germ layers of the grain. This refining process results in a softer texture and longer shelf life but also strips away some of the natural nutrients found in whole grains. To compensate for this, many manufacturers enrich white bread with essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, thiamine, niacin, and folic acid. While these enrichments enhance its nutritional value, they do not fully replicate the benefits of whole grains. Understanding the balance between convenience and nutrition is key to evaluating white bread's role in your daily meals. In this article, we will address common questions like "What are the nutritional benefits of white bread?" and "How does white bread compare to whole grain options?" to provide a well-rounded perspective. Before we dive into the details, let’s take a moment to explore the broader context of white bread nutrition. With its widespread availability and adaptability to various cuisines, white bread remains a dietary staple for millions. However, concerns about its glycemic index, fiber content, and potential impact on health have led many to question its place in a modern diet. By examining its nutritional components, comparing it to alternatives, and addressing frequently asked questions, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about white bread consumption. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast, a busy professional, or someone simply curious about nutrition, this guide has something for everyone.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Nutritional Components of White Bread?
- How Does White Bread Compare to Whole Grain Options?
- Is White Bread Bad for Your Health?
- Can White Bread Be Part of a Balanced Diet?
- What Are the Health Benefits of Enriched White Bread?
- How Can You Make Healthier Choices with White Bread?
- What Are the Common Misconceptions About White Bread?
- Frequently Asked Questions About White Bread Nutrition
What Are the Nutritional Components of White Bread?
Understanding the nutritional components of white bread is essential for evaluating its role in your diet. A typical slice of white bread contains approximately 70-80 calories, with the majority coming from carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy, making white bread a convenient option for quick fuel. However, it is important to note that white bread is made from refined flour, which lacks the fiber content found in whole grains. This absence of fiber can lead to quicker digestion and a spike in blood sugar levels, making it less ideal for individuals managing conditions like diabetes.
Despite its refined nature, white bread is often enriched with essential nutrients. These include B vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin, which play a crucial role in energy metabolism and maintaining healthy skin and nerves. Additionally, white bread is fortified with iron, an essential mineral that supports oxygen transport in the blood. Folic acid, another enrichment component, is particularly important for pregnant women as it helps prevent neural tube defects in developing fetuses. While these enrichments enhance the nutritional profile of white bread, they do not fully compensate for the nutrients lost during the refining process.
Read also:Streameast Soccer Your Ultimate Guide To Live Soccer Streaming
Here’s a breakdown of the typical nutritional content per slice of white bread:
- Calories: 70-80
- Carbohydrates: 15-20 grams
- Protein: 2-3 grams
- Fat: Less than 1 gram
- Fiber: Less than 1 gram
- Sugar: 1-2 grams
While white bread is not a significant source of protein or healthy fats, its carbohydrate content makes it a quick and accessible energy source. For those looking to manage their weight or improve their overall health, understanding these components can help in making informed dietary choices.
How Does White Bread Compare to Whole Grain Options?
When it comes to choosing between white bread and whole grain options, the differences in nutritional value are significant. Whole grain bread retains the bran, germ, and endosperm of the wheat kernel, providing a richer source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This makes whole grain bread a more nutrient-dense choice compared to white bread, which is made from refined flour. The fiber content in whole grain bread, for instance, is about three times higher than that of white bread, promoting better digestion and a feeling of fullness.
What Are the Key Nutritional Differences?
The refining process used to make white bread removes many of the natural nutrients found in whole grains. Here’s a comparison of the key nutritional differences:
- Fiber: Whole grain bread contains 3-5 grams of fiber per slice, while white bread has less than 1 gram.
- Vitamins: Although white bread is often enriched, whole grain bread naturally contains higher levels of B vitamins and antioxidants.
- Minerals: Whole grain bread is richer in essential minerals like magnesium, zinc, and selenium, which support immune function and bone health.
- Glycemic Index: White bread has a higher glycemic index, causing a quicker spike in blood sugar levels compared to the slower, more sustained energy release from whole grain bread.
Why Should You Consider Whole Grain Bread?
Switching to whole grain bread can offer numerous health benefits. Its higher fiber content supports digestive health and reduces the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the antioxidants and phytonutrients in whole grains contribute to overall well-being. While white bread can still be enjoyed in moderation, opting for whole grain alternatives more frequently can enhance your diet's nutritional quality.
Is White Bread Bad for Your Health?
One of the most common questions about white bread nutrition is whether it is inherently bad for your health. The answer depends on various factors, including your overall diet, lifestyle, and health goals. While white bread is not inherently harmful, its refined nature and lack of fiber can pose challenges for some individuals. For instance, its high glycemic index may cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, making it less suitable for people with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Read also:Exploring The Unique Bond Of Colin Jost And Michael Che Friendship A Closer Look
What Are the Potential Health Risks?
Consuming excessive amounts of white bread without balancing it with other nutrient-rich foods can lead to several health concerns:
- Weight Gain: The low fiber content in white bread may not promote satiety, leading to overeating and potential weight gain.
- Blood Sugar Fluctuations: The rapid digestion of refined carbohydrates can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, affecting energy levels and mood.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Relying heavily on white bread as a staple food may result in insufficient intake of essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
How Can You Mitigate These Risks?
To enjoy white bread without compromising your health, consider pairing it with protein-rich or fiber-rich foods. For example, adding avocado, eggs, or lean meats to your sandwich can slow down digestion and stabilize blood sugar levels. Additionally, limiting your intake of white bread and incorporating more whole grains into your diet can help maintain a balanced nutritional profile.
Can White Bread Be Part of a Balanced Diet?
Despite its drawbacks, white bread can still be part of a balanced diet when consumed mindfully. The key lies in moderation and pairing it with nutrient-dense foods. For instance, using white bread as an occasional treat or in recipes where its texture and flavor are essential can be a practical approach. It is also important to balance white bread consumption with other food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, to ensure a well-rounded intake of nutrients.
What Are Some Healthy Ways to Enjoy White Bread?
Here are a few tips for incorporating white bread into your diet without compromising your health:
- Pair it with protein-rich spreads like peanut butter, hummus, or low-fat cheese.
- Add fiber-rich toppings like sliced vegetables or leafy greens to your sandwiches.
- Use white bread sparingly in recipes like French toast or bread pudding, where its texture enhances the dish.
What Are the Health Benefits of Enriched White Bread?
While white bread is often criticized for its refined nature, it is worth noting that many varieties are enriched with essential nutrients. This enrichment process adds back some of the vitamins and minerals lost during refining, making enriched white bread a better option than its unenriched counterpart. For example, the addition of folic acid in enriched white bread has been shown to reduce the risk of neural tube defects in newborns, making it particularly beneficial for pregnant women.
Which Nutrients Are Added During Enrichment?
Enriched white bread typically contains the following nutrients:
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1): Supports energy metabolism and nerve function.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Aids in energy production and skin health.
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): Promotes healthy digestion and nervous system function.
- Folic Acid: Essential for cell division and fetal development.
- Iron: Supports oxygen transport and prevents anemia.
How Can You Make Healthier Choices with White Bread?
Making healthier choices with white bread involves both mindful consumption and selecting the right varieties. Look for brands that offer enriched or fortified white bread, as these options provide additional nutritional benefits. Additionally, consider portion control and pair white bread with nutrient-dense foods to create a more balanced meal.
What Should You Look for on the Label?
When shopping for white bread, check the nutrition label for the following:
- Low sugar content
- Enriched with vitamins and minerals
- Minimal use of artificial additives or preservatives
What Are the Common Misconceptions About White Bread?
White bread is often misunderstood, with many people assuming it has no nutritional value. While it is true that white bread lacks the fiber and nutrient density of whole grains, it is not devoid of benefits. Enriched white bread provides essential vitamins and minerals, making it a viable option for those who enjoy its taste and texture. Another misconception is that all white bread is unhealthy, but moderation and mindful pairing can make it a part of a balanced diet.
Frequently Asked Questions About White Bread Nutrition
Is White Bread High in Calories?
No, white bread is relatively low in calories, with a typical slice containing 70-80 calories. However, portion control is key to avoiding excessive calorie intake.
Can White Bread Cause Weight Gain?
White bread itself does not cause weight gain, but its low fiber content may not promote satiety, leading to overeating. Pairing it with protein or fiber-rich foods
Exploring Ocean Energy Pros And Cons: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlocking Sukuna Mastery: The Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Achieving Excellence
Discovering Paradise: How Much Would It Cost To Live In Hawaii?
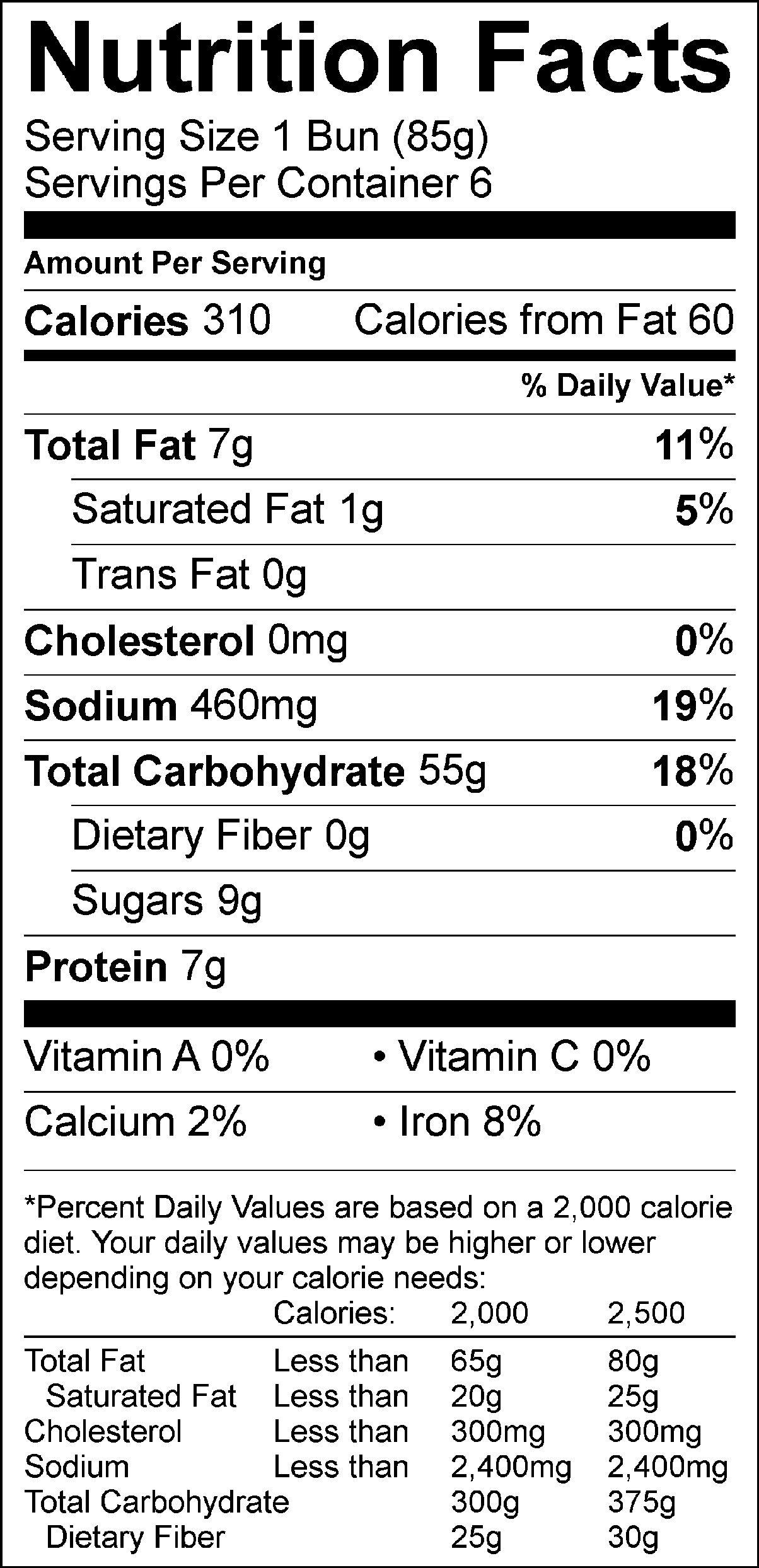
White Bread Nutrition Label Blog Dandk
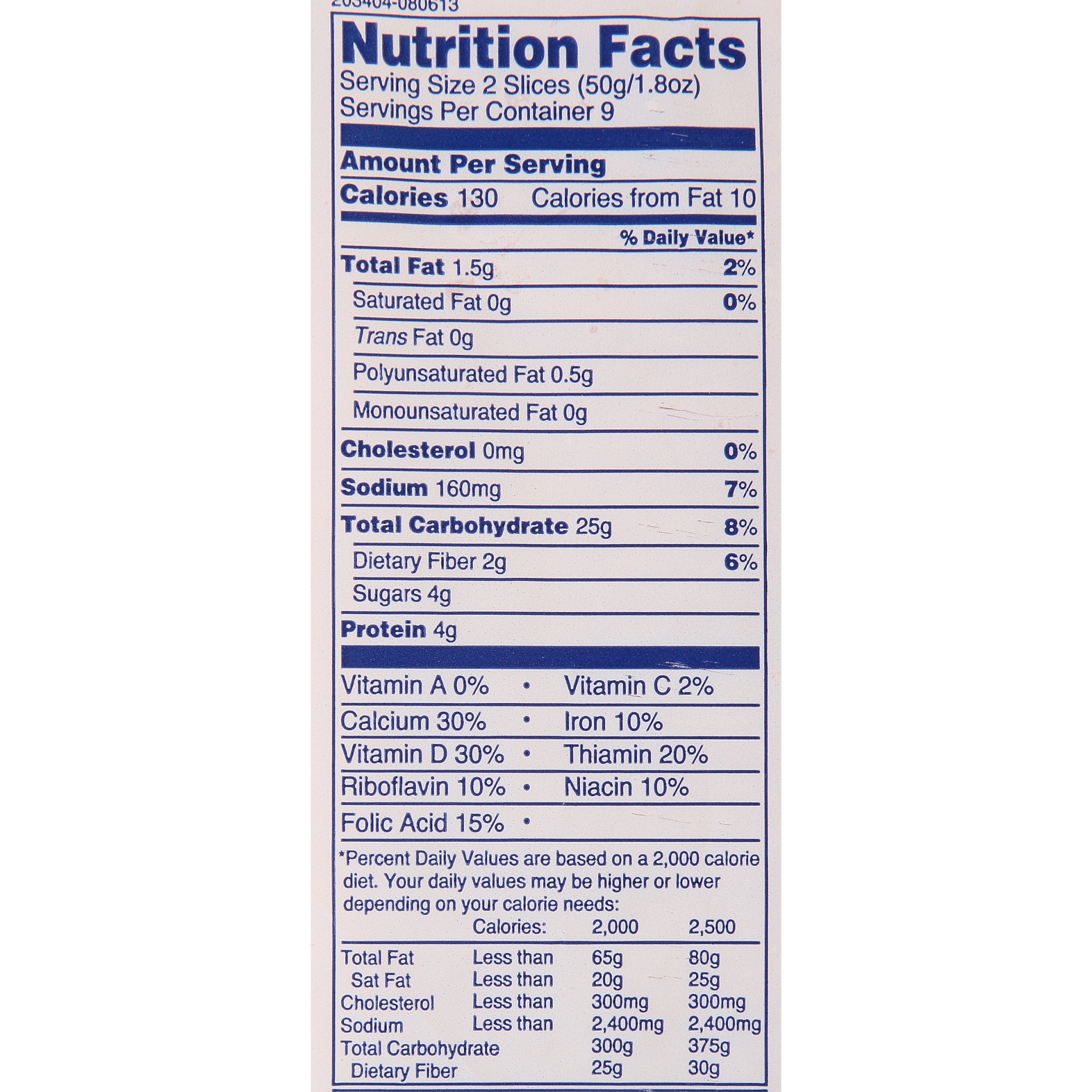
Wonder White Bread Nutrition Label Besto Blog