What Sets Ponds Apart From Lakes? Exploring The Key Differences
Have you ever wondered what distinguishes a pond from a lake? The answer lies in their size, depth, and the ecosystems they support. While both bodies of water are essential parts of our natural environment, they serve unique purposes and exhibit distinct characteristics. Ponds are generally smaller and shallower, allowing sunlight to penetrate to the bottom, which fosters a rich variety of plant and animal life. Lakes, on the other hand, are larger and deeper, creating layered ecosystems that support diverse aquatic species. Understanding these differences is crucial for appreciating how these water bodies contribute to the environment and human life.
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds _______. a. are typically smaller and shallower, making them more accessible for recreational activities like fishing and swimming. Lakes, with their vast surface area and depth, often serve as critical water reservoirs and habitats for larger aquatic organisms. This distinction is not just a matter of size but also affects how sunlight, temperature, and nutrients interact within these ecosystems. For example, ponds are more likely to freeze entirely during winter, while lakes often maintain a liquid layer beneath their icy surface. These nuances shape the biodiversity and ecological roles of each water body.
Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a student, or someone curious about the environment, understanding the differences between ponds and lakes can deepen your appreciation for the natural world. By exploring their unique features, we can better grasp how these water bodies influence climate, support wildlife, and provide resources for human communities. In this article, we’ll delve into the defining characteristics of ponds and lakes, their ecological significance, and the factors that set them apart. So, let’s dive in and uncover what makes these aquatic wonders so special!
Read also:Exploring The Most Dangerous Cities In The World Risks Realities And Resilience
Table of Contents
- What Makes a Pond Different from a Lake?
- Why Are Ponds Shallower Than Lakes?
- How Do Ponds and Lakes Support Different Ecosystems?
- What Are the Climatic Effects of Ponds vs. Lakes?
- Can Ponds and Lakes Be Man-Made or Natural?
- What Are the Human Uses of Ponds and Lakes?
- How Do Seasonal Changes Impact Ponds and Lakes Differently?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Ponds and Lakes
What Makes a Pond Different from a Lake?
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds _______. a. are smaller in size and shallower in depth compared to lakes. This distinction is not arbitrary but rooted in ecological and hydrological factors. Ponds typically span less than 2 hectares (5 acres) and rarely exceed 2 meters (6.5 feet) in depth. In contrast, lakes are significantly larger and deeper, often spanning hundreds or thousands of hectares with depths exceeding 10 meters (33 feet). These differences influence how sunlight penetrates the water, how temperature layers form, and how aquatic life thrives.
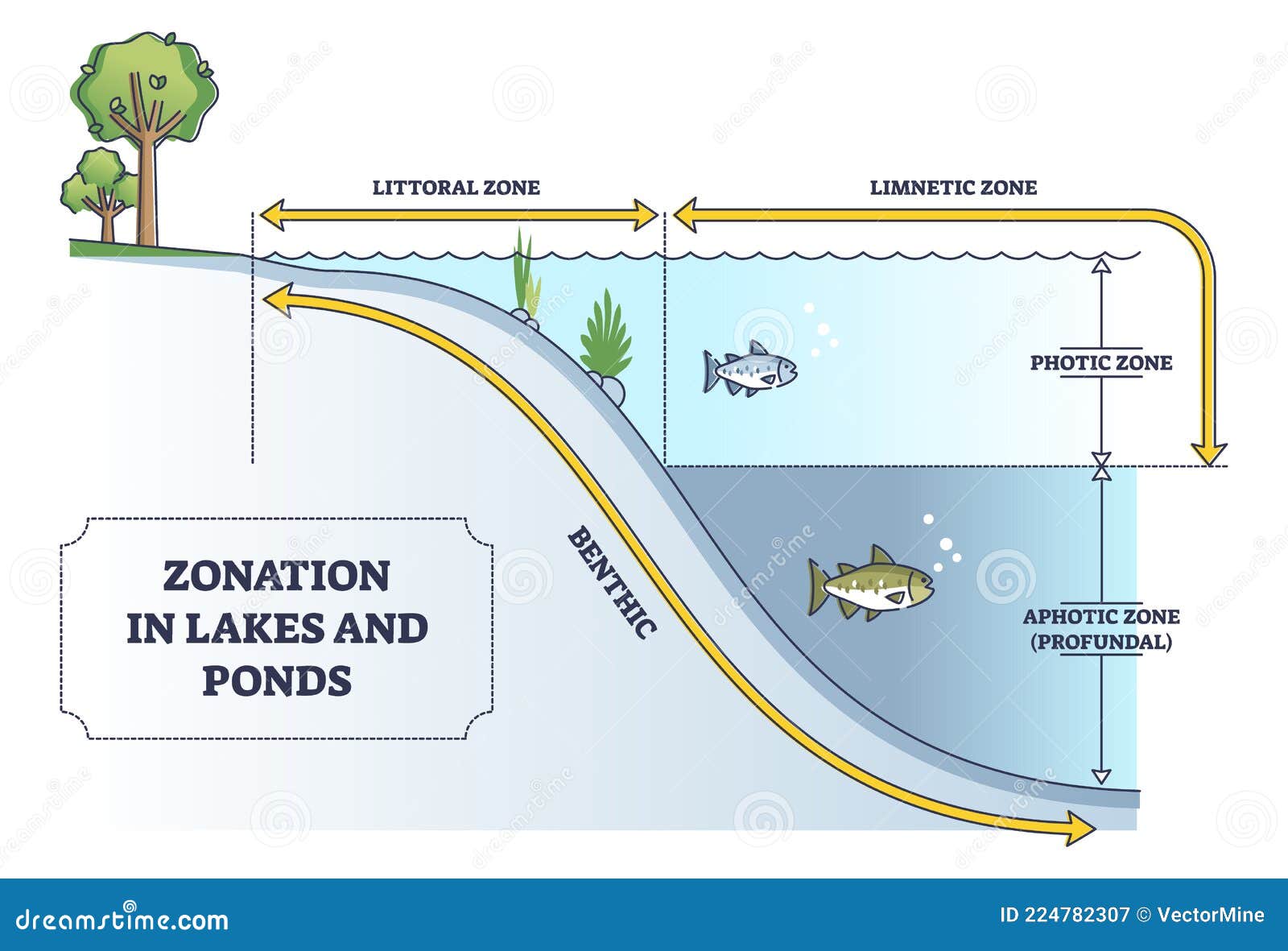
Ponds are known for their ability to support rooted aquatic plants throughout their entirety due to their shallow nature. This allows sunlight to reach the bottom, fostering a rich diversity of plant species. Lakes, on the other hand, are stratified ecosystems where sunlight may not penetrate beyond the surface layers. This stratification creates distinct zones, such as the littoral zone near the shore, the limnetic zone in open water, and the profundal zone in the deeper areas. These zones host different types of organisms, contributing to the lake’s biodiversity.
Why Do Size and Depth Matter?
Size and depth play critical roles in determining the ecological functions of ponds and lakes. The shallow nature of ponds means they are more susceptible to temperature fluctuations. During summer, ponds can warm up quickly, while in winter, they may freeze entirely. Lakes, with their greater depth, maintain more stable temperatures and often have a thermocline—a layer where the temperature changes rapidly with depth. This stability supports a wider range of aquatic life, including fish species that require cooler, deeper waters.
Why Are Ponds Shallower Than Lakes?
Ponds are shallower than lakes primarily because of their formation processes and natural characteristics. Ponds often form in low-lying areas where water collects temporarily or permanently due to rainfall, runoff, or groundwater seepage. Their shallow depth allows sunlight to penetrate the entire water column, supporting photosynthesis and creating a thriving environment for plants and microorganisms. Lakes, on the other hand, are typically formed through geological processes such as glacial activity, tectonic movements, or volcanic eruptions, which carve out deeper basins.
What Role Does Sunlight Play in Pond Ecosystems?
Sunlight is a critical factor in pond ecosystems, as it drives photosynthesis and influences water temperature. The shallow depth of ponds ensures that sunlight reaches the bottom, promoting the growth of submerged and emergent vegetation. This vegetation provides food and shelter for aquatic organisms, including fish, amphibians, and insects. Additionally, sunlight warms the water, creating a conducive environment for breeding and reproduction. Lakes, with their deeper basins, often have darker, cooler depths where sunlight cannot reach, limiting plant growth in those areas.
How Does Temperature Affect Pond and Lake Habitats?
Temperature is another key factor influenced by the depth of ponds and lakes. Ponds experience more significant temperature variations due to their shallow nature, while lakes maintain more stable conditions. During summer, ponds may become warm enough to support algae blooms, which can sometimes disrupt the ecosystem. In contrast, lakes often develop thermal stratification, where warmer water remains near the surface, and cooler water sinks to the bottom. This stratification affects oxygen levels and nutrient distribution, shaping the lake’s biodiversity.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
How Do Ponds and Lakes Support Different Ecosystems?
Ponds and lakes are home to diverse ecosystems, but their differences in size, depth, and environmental conditions lead to unique ecological dynamics. Ponds are often teeming with life, from microscopic plankton to larger species like frogs and turtles. Their shallow waters and abundant vegetation create ideal habitats for breeding and shelter. Lakes, with their larger surface area and deeper waters, support a broader range of species, including fish that require cooler, oxygen-rich environments.
What Types of Organisms Thrive in Ponds?
Ponds are hotspots for biodiversity, hosting a variety of organisms adapted to their unique conditions. Common inhabitants include:
- Frogs and toads
- Dragonflies and damselflies
- Turtles and newts
- Various fish species, such as minnows and sunfish
The abundance of sunlight and nutrients in ponds supports the growth of algae and aquatic plants, which form the base of the food chain. These plants provide food for herbivorous species and shelter for predators, creating a balanced ecosystem.
How Do Lakes Support Larger Aquatic Life?
Lakes are capable of supporting larger and more diverse aquatic life due to their depth and stratification. Fish species like bass, trout, and pike thrive in lakes, where they can find cooler waters and abundant prey. The littoral zone, where sunlight penetrates, is rich in vegetation and serves as a breeding ground for many species. Meanwhile, the deeper profundal zone supports organisms adapted to low-light conditions, such as certain types of bacteria and invertebrates.
What Are the Climatic Effects of Ponds vs. Lakes?
Ponds and lakes play important roles in regulating local climates, but their impacts differ based on their size and characteristics. Ponds, with their smaller surface area, contribute to localized cooling and humidity. They act as microclimates, supporting nearby vegetation and wildlife. Lakes, being larger, have a more significant influence on regional weather patterns. They can moderate temperatures, reduce the severity of frosts, and even generate lake-effect snow in colder regions.
How Do Lakes Influence Weather Patterns?
Lakes can significantly affect weather patterns due to their thermal properties. During summer, lakes absorb and store heat, releasing it slowly during cooler months. This moderates temperatures in surrounding areas, creating milder climates. In winter, the warm water of lakes can lead to increased evaporation, forming clouds and precipitation. In some regions, this phenomenon results in lake-effect snow, where cold air passing over warm lake waters picks up moisture and deposits it as snow downwind.
Can Ponds and Lakes Be Man-Made or Natural?
Both ponds and lakes can be either natural or man-made, depending on their origin and purpose. Natural ponds and lakes form through geological and hydrological processes, while man-made versions are created for specific uses, such as irrigation, recreation, or water storage. Understanding the origins of these water bodies helps us appreciate their roles in both nature and human society.
What Are the Characteristics of Man-Made Ponds?
Man-made ponds are often constructed for agricultural, ornamental, or recreational purposes. They may lack the biodiversity of natural ponds but still provide valuable resources and habitats. These ponds are typically smaller and shallower, making them easier to manage and maintain.
What Are the Human Uses of Ponds and Lakes?
Ponds and lakes serve a variety of human needs, from providing drinking water to supporting recreational activities. Ponds are often used for irrigation, aquaculture, and stormwater management, while lakes are critical for water supply, fishing, and tourism. Their economic and ecological value underscores the importance of conserving these vital resources.
How Do Seasonal Changes Impact Ponds and Lakes Differently?
Seasonal changes affect ponds and lakes in distinct ways, influencing their temperature, oxygen levels, and biological activity. Ponds may freeze entirely during winter, while lakes often maintain liquid water beneath their icy surface. These differences shape the survival strategies of aquatic organisms and the overall health of the ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ponds and Lakes
What Is the Main Difference Between Ponds and Lakes?
The main difference between ponds and lakes is that ponds _______. a. are smaller and shallower, allowing sunlight to penetrate the entire water column and fostering unique ecosystems.
Can Ponds Become Lakes Over Time?
While ponds and lakes are distinct, some ponds may evolve into lakes through natural processes like sedimentation or human intervention.
Why Are Lakes Important for Drinking Water?
Lakes serve as critical reservoirs of freshwater, supplying drinking water to millions of people worldwide. Their large size and depth make them ideal for water storage and purification.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between ponds and lakes enriches our appreciation of these vital water bodies. Whether natural or man-made, they play essential roles in ecosystems and human life. By conserving and protecting them, we ensure their benefits for future generations. For more information, you can explore resources like EPA Water Resources.
Exploring Marlo Thomas Net Worth: Career, Achievements, And Financial Success
Understanding Bread And Calories: A Comprehensive Guide To Nutrition And Health
Unlocking The Power Of Wave Energy: Advantages And Opportunities

Lakes+Ponds Housatonic Heritage
Pictures Of Lakes And Ponds