What Size Wire For 100 Amps? A Complete Guide To Safe Electrical Wiring
When it comes to electrical wiring, safety and efficiency are paramount. One of the most common questions homeowners, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts ask is, "What size wire for 100 amps?" This question is crucial because using the wrong wire gauge can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or system inefficiencies. Understanding the correct wire size ensures that your electrical system operates safely and reliably while meeting local building codes and standards. Whether you're upgrading your electrical panel, installing a new circuit, or planning a large-scale project, knowing the appropriate wire size for 100 amps is essential. The wire gauge you choose will depend on factors such as the distance of the run, the type of wire, and the environment in which it will be installed.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern homes and businesses, powering everything from lighting to appliances and HVAC systems. A 100-amp service is a common choice for residential properties, especially for smaller homes or those with moderate electrical needs. However, the wire size you select must align with the amperage to prevent voltage drops and ensure consistent performance. This article dives deep into the topic of "what size wire for 100 amps," providing expert advice, practical tips, and detailed insights to help you make informed decisions. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of wire sizing and how to apply it in real-world scenarios.
As we explore this topic, we'll cover everything from the basics of wire gauges to advanced considerations like voltage drop calculations and material selection. Whether you're a seasoned electrician or a curious homeowner, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge you need to tackle electrical projects confidently. So, if you've ever wondered, "What size wire for 100 amps?"—you're in the right place. Let's get started!
Read also:Ant Anstead Net Worth Unveiling The Life Career And Financial Success Of A Renowned Car Expert
Table of Contents
- What Size Wire for 100 Amps?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for Electrical Safety?
- What Are the Different Types of Wires for 100-Amp Circuits?
- Factors That Affect the Choice of Wire Size
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Circuits?
- Installation Tips for 100-Amp Wiring
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Sizing
What Size Wire for 100 Amps?
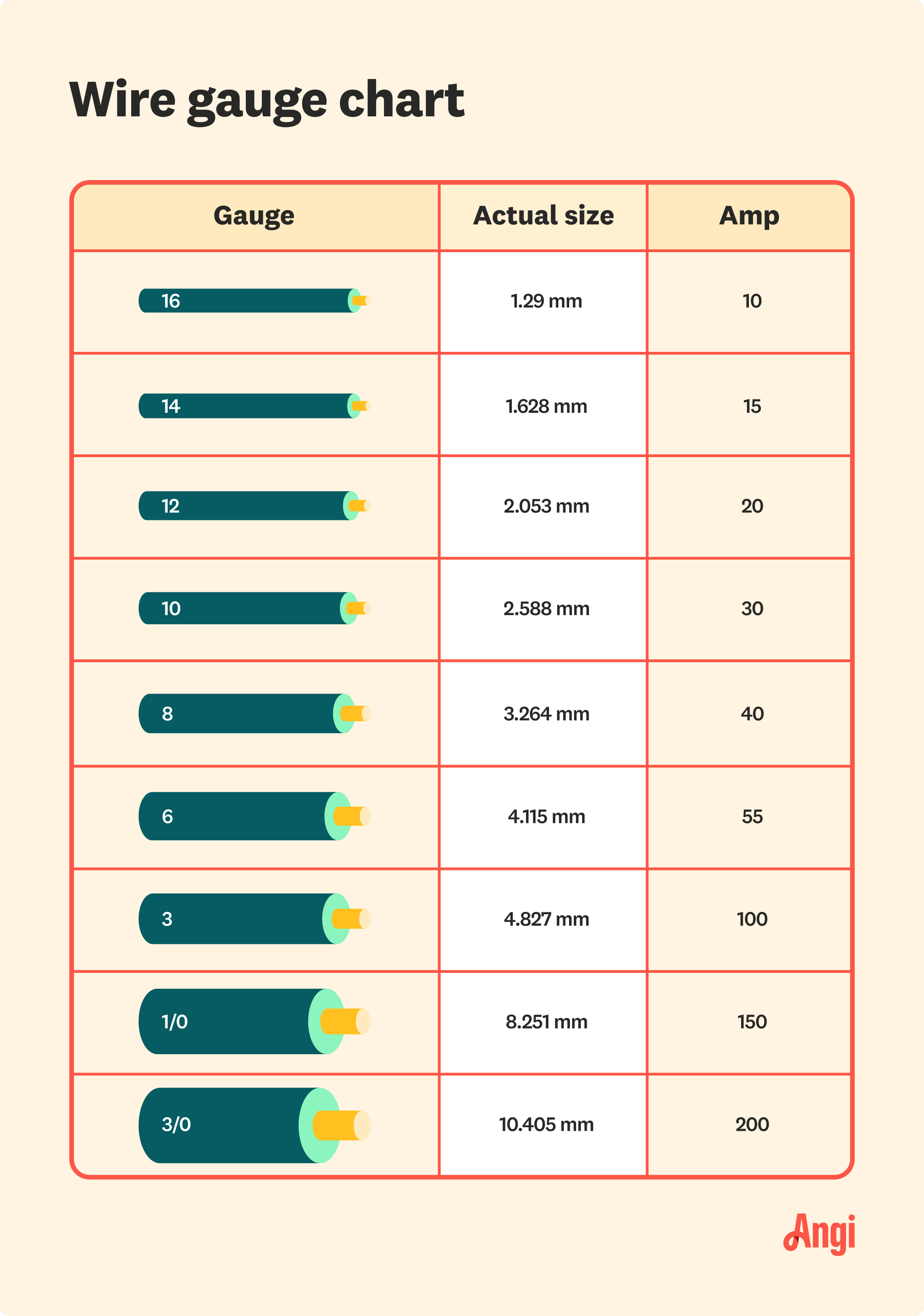
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100-amp service is a critical step in ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. For most residential applications, a 100-amp service typically requires a wire gauge of 3 AWG copper or 1 AWG aluminum. These wire sizes are designed to handle the current load without overheating or causing voltage drops. However, the specific wire size you need may vary depending on several factors, including the length of the wire run, the type of insulation, and the material of the wire.
Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical wiring. Copper is more conductive than aluminum, which means it can carry more current with a smaller gauge. For example, a 3 AWG copper wire is sufficient for a 100-amp service, while an aluminum wire would need to be thicker (1 AWG) to handle the same load. Aluminum is often chosen for larger projects due to its lower cost, but it requires careful installation to avoid issues like oxidation and overheating.
It's also important to note that local building codes and regulations may dictate specific requirements for wire sizing. Always consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) or a licensed electrician to ensure compliance. Additionally, using wires with proper insulation, such as THHN or XHHW, can further enhance safety and performance. These insulation types are designed to withstand high temperatures and resist moisture, making them ideal for a variety of environments.
Why Does Wire Size Matter for Electrical Safety?
Wire size plays a pivotal role in the safety and reliability of an electrical system. If the wire is too small for the current it needs to carry, it can overheat, leading to a host of dangerous situations. Overheating wires can cause insulation to melt, creating a fire hazard. In extreme cases, this can result in electrical fires that endanger lives and property. On the other hand, using a wire that's too large for the application is inefficient and unnecessarily expensive.
One of the key reasons wire size matters is its ability to handle the electrical load without excessive voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. A significant voltage drop can lead to poor performance of electrical devices and appliances. For a 100-amp circuit, maintaining a voltage drop of less than 3% is generally recommended to ensure optimal performance.
Another critical factor is the wire's ability to dissipate heat. Electrical current generates heat, and if the wire is too small, it cannot dissipate this heat effectively. This can lead to a buildup of heat within the wire, increasing the risk of overheating and fire. Properly sized wires, combined with appropriate circuit breakers and fuses, provide a safeguard against these risks. By understanding the importance of wire size, you can make informed decisions that prioritize safety and efficiency.
Read also:Top Unblocked Car Games For Endless Fun And Thrills
What Are the Different Types of Wires for 100-Amp Circuits?
When selecting a wire for a 100-amp circuit, it's essential to consider the type of wire and its material. The two primary materials used for electrical wiring are copper and aluminum, each with its own advantages and considerations. Copper is highly conductive, making it an excellent choice for applications where space and efficiency are critical. Aluminum, while less conductive, is lighter and more cost-effective, making it a popular choice for larger projects.
Here are some common types of wires used for 100-amp circuits:
- Copper THHN Wire: This type of wire is known for its excellent conductivity and resistance to heat. It's often used in conduit and is suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Aluminum XHHW Wire: Aluminum wires with XHHW insulation are designed for wet and dry locations, making them versatile for various environments. They are commonly used in larger installations due to their lower cost.
- SE Cable: Service entrance (SE) cables are often used for connecting a home's electrical panel to the utility meter. They are available in both copper and aluminum and are designed for direct burial or use in conduit.
Each type of wire has specific applications and is suited to different environments. For example, THHN wires are ideal for use in conduit, while SE cables are often used for service entrances. Understanding the differences between these wires can help you choose the right one for your project.
Factors That Affect the Choice of Wire Size
How Does Distance Impact Wire Size?
The distance between the power source and the load is a crucial factor in determining the appropriate wire size for a 100-amp circuit. Longer wire runs result in higher resistance, which can cause voltage drops and reduce the efficiency of your electrical system. To compensate for this, you may need to use a thicker wire to minimize resistance and maintain adequate voltage levels.
For example, a 100-amp circuit with a wire run of 50 feet may require a 3 AWG copper wire, while a run of 150 feet might necessitate a 1 AWG copper wire. The NEC provides guidelines for calculating voltage drop based on wire length, which can help you determine the correct wire size for your specific application. Always account for the total distance of the wire run when planning your project to avoid performance issues.
What Role Does the Environment Play in Wire Selection?
The environment in which the wire will be installed also affects the choice of wire size and type. Wires installed in wet or damp locations, such as basements or outdoor areas, require insulation that can withstand moisture. Similarly, wires exposed to high temperatures, such as those in attics or near heat sources, need insulation rated for higher temperatures.
Some common environmental considerations include:
- Moisture Resistance: Wires used in wet locations should have insulation like XHHW, which is designed to resist moisture and prevent corrosion.
- Temperature Ratings: High-temperature environments may require wires with insulation rated for 90°C or higher to ensure safe operation.
- Direct Burial: For underground installations, wires should be rated for direct burial or placed in conduit to protect them from damage.
Taking these factors into account ensures that your wiring is both safe and durable, capable of withstanding the conditions it will encounter.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100-Amp Circuits?
Voltage drop is an important consideration when sizing wires for a 100-amp circuit. It refers to the reduction in voltage as electricity travels through a wire, caused by the wire's resistance. Excessive voltage drop can lead to poor performance of electrical devices and appliances, making it essential to calculate and minimize it.
To calculate voltage drop, you can use the following formula:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
- Length: The distance of the wire run in feet.
- Current: The amperage of the circuit (100 amps in this case).
- Resistance: The resistance of the wire per 1,000 feet, which can be found in wire gauge charts.
For example, if you're using a 3 AWG copper wire for a 100-foot run, the voltage drop would be approximately 2.4 volts, which is within the acceptable range of 3%. By calculating voltage drop, you can ensure that your electrical system operates efficiently and reliably.
Installation Tips for 100-Amp Wiring
Proper installation is just as important as selecting the correct wire size. Here are some tips to ensure a safe and successful installation:
- Use Conduit: Running wires through conduit provides additional protection and makes future upgrades easier.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and free of corrosion to prevent overheating and voltage drops.
- Follow Codes: Always adhere to local building codes and the NEC to ensure compliance and safety.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size?
Choosing the wrong wire size is a common mistake that can lead to serious consequences. Some pitfalls to avoid include:
- Underestimating Wire Size: Using a wire that's too small for the load can cause overheating and fire hazards.
- Ignoring Voltage Drop: Failing to account for voltage drop can result in poor performance of electrical devices.
- Skipping Insulation Ratings: Using wires with inadequate insulation for the environment can lead to damage and safety risks.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Sizing
What Happens If You Use the Wrong Wire Size for 100 Amps?
Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, voltage drops, and even electrical fires. Always consult a professional or refer to the NEC for guidance.
Can I Use Aluminum Wire for a 100-Amp Circuit?
Yes, but it must be properly sized (1 AWG) and installed with care to avoid issues like oxidation and overheating.
How Do I Know If My Wire is Rated for Outdoor Use?
Check the wire's insulation type. Wires with XHHW or UF insulation are suitable for outdoor and wet locations.
In conclusion, understanding "what size wire for 100 amps" is essential for anyone involved in electrical projects. By following the guidelines and tips outlined
Understanding Lake Vs Pond: A Comprehensive Guide To Water Bodies
The Inspiring Journey Of 홀든 플레처 프레이저: A Trailblazer's Story
Understanding The CVV Of American Express Card: A Comprehensive Guide

What Size Copper Wire For 40 Amps
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi