What Size Wire For 150 Amp Service: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right wire size for a 150-amp service is critical for ensuring safety and efficiency in your electrical system. Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical panel or installing a new service, understanding the appropriate wire gauge is essential. Using an undersized wire can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or equipment damage, while an oversized wire may unnecessarily increase costs. Electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), provide guidelines for selecting the correct wire size based on the amperage and other factors like the type of wire and its insulation.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern homes, powering everything from lighting and appliances to heating and cooling systems. A 150-amp service is commonly used in residential settings, especially for larger homes or those with high energy demands. To ensure the system operates safely and efficiently, it is crucial to select the correct wire size that matches the load requirements. This involves considering factors such as the distance from the power source, the type of conductor material (copper or aluminum), and the ambient temperature conditions. Making an informed decision can prevent costly repairs, reduce energy waste, and enhance the longevity of your electrical system.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of selecting the appropriate wire size for a 150-amp service. We'll explore the role of electrical codes, the impact of wire material, and the importance of proper installation practices. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how to determine the correct wire size for your needs, ensuring a safe and reliable electrical setup. Whether you're a homeowner, electrician, or DIY enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your electrical system.
Read also:Exploring The Legacy Of Norma Strait A Journey Through Time
Table of Contents
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 150-Amp Service?
- What Are the Standard Wire Sizes for 150-Amp Service?
- How to Choose the Right Wire Material for Your 150-Amp Service?
- Factors Affecting Wire Size Selection for 150-Amp Service
- What Are the Electrical Code Requirements for 150-Amp Service?
- Installation Best Practices for 150-Amp Service Wiring
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire for 150-Amp Service
- FAQs About What Size Wire for 150 Amp Service
Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 150-Amp Service?
When it comes to electrical systems, the wire size is not just a technical detail—it’s a critical factor that impacts safety, performance, and efficiency. For a 150-amp service, the wire size determines how much electrical current can safely pass through the conductor without overheating. If the wire is too small for the amperage it carries, it can overheat, leading to insulation damage, electrical fires, or even catastrophic failures. On the other hand, using a wire that’s too large can increase costs unnecessarily and complicate the installation process.
The relationship between wire size and amperage is governed by the resistance of the conductor. Thicker wires have lower resistance, which allows them to carry more current without generating excessive heat. For a 150-amp service, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides specific guidelines on the minimum wire gauge required to handle this load safely. These guidelines take into account the material of the wire (copper or aluminum), its insulation type, and the conditions under which it will be installed. For example, copper wires are more conductive than aluminum, meaning they can carry the same current with a smaller gauge.
Another reason why wire size matters is voltage drop. Over long distances, electrical resistance in the wire can cause a drop in voltage, which can affect the performance of appliances and devices. For a 150-amp service, minimizing voltage drop is essential to ensure consistent power delivery. This is particularly important for homes with high energy demands or those located far from the power source. By selecting the appropriate wire size, you can maintain optimal voltage levels and reduce energy losses, ultimately saving money on utility bills.
What Are the Standard Wire Sizes for 150-Amp Service?
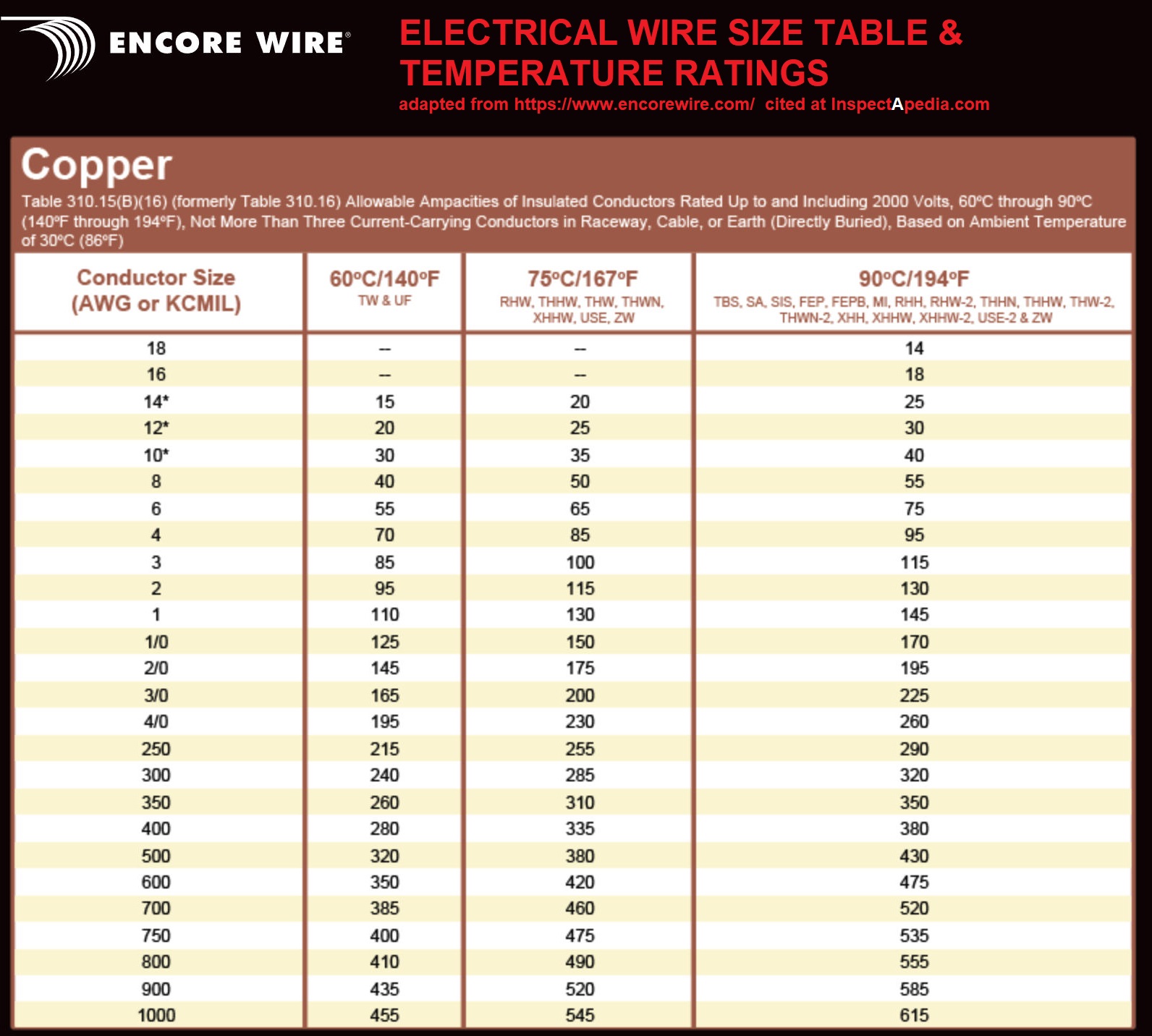
When it comes to selecting the right wire size for a 150-amp service, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides clear guidelines. For copper wires, the standard recommendation is a 1/0 AWG (American Wire Gauge) size. This gauge is specifically designed to handle the current load of a 150-amp service without overheating. Copper is highly conductive, making it an excellent choice for residential applications where space and efficiency are priorities.
For those opting for aluminum wiring, the recommended size increases to 2/0 AWG. Aluminum is less conductive than copper, which means it requires a larger diameter to carry the same amount of current safely. While aluminum wiring is often more cost-effective, it is essential to ensure proper installation to prevent issues such as corrosion or poor connections. Both copper and aluminum wires must also meet insulation standards, typically rated for 75°C or higher, to ensure they can handle the heat generated by the current.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the standard wire sizes for 150-amp service:
Read also:What Are Examples A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Using Examples Effectively
- Copper Wire: 1/0 AWG
- Aluminum Wire: 2/0 AWG
- Insulation Rating: 75°C or higher
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and specific conditions may require adjustments. For instance, if the wire run is exceptionally long, a larger gauge may be necessary to compensate for voltage drop. Consulting with a licensed electrician or referring to the NEC tables can help ensure compliance with local codes and safety standards.
How to Choose the Right Wire Material for Your 150-Amp Service?
When selecting a wire material for a 150-amp service, the choice typically comes down to copper or aluminum. Each material has its advantages and considerations, making it essential to weigh the options carefully. Copper is the preferred choice for most residential applications due to its superior conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion. It can carry the same current as aluminum with a smaller gauge, making it ideal for installations where space is limited. However, copper is more expensive, which can be a significant factor for larger projects or budget-conscious homeowners.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is a cost-effective alternative that is lighter and easier to handle, especially for long wire runs. While it is less conductive than copper, aluminum is still widely used in electrical systems, particularly for services like a 150-amp setup. The key to using aluminum effectively is ensuring proper installation, as it is more prone to oxidation and requires anti-oxidant compounds at connection points to prevent corrosion. Additionally, aluminum wires must be upsized to compensate for their lower conductivity, as mentioned earlier.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing between copper and aluminum:
- Cost: Aluminum is generally more affordable than copper, making it a budget-friendly option.
- Conductivity: Copper offers better conductivity, allowing for smaller wire sizes.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper is more resistant to corrosion, reducing maintenance needs.
- Installation Complexity: Aluminum requires special care during installation to avoid issues like loosening connections.
Ultimately, the decision depends on your specific needs, budget, and the expertise of your electrician. Consulting a professional can help you make the best choice for your 150-amp service.
Factors Affecting Wire Size Selection for 150-Amp Service
Selecting the appropriate wire size for a 150-amp service involves more than just following standard guidelines. Several factors can influence the decision, including the distance of the wire run, ambient temperature conditions, and the type of insulation used. Understanding these variables is crucial to ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system.
Distance and Voltage Drop: What You Need to Know?
One of the most significant factors affecting wire size is the distance between the power source and the load. As electrical current travels through a wire, it encounters resistance, which can lead to voltage drop. For a 150-amp service, even a small voltage drop can impact the performance of appliances and devices, particularly those sensitive to voltage fluctuations. To minimize voltage drop, it may be necessary to use a larger wire gauge than the standard recommendation.
The NEC provides guidelines for acceptable voltage drop levels, typically recommending no more than a 3% drop for branch circuits and 5% for feeder circuits. To calculate voltage drop, you need to consider the wire’s resistance, the current load, and the length of the wire run. Online calculators or NEC tables can simplify this process. For example, if your 150-amp service requires a wire run of 100 feet or more, you might need to upgrade from a 1/0 AWG copper wire to a 2/0 AWG to maintain optimal performance.
Ambient Temperature Conditions: Why Do They Matter?
The environment in which the wire is installed can also affect its performance. High ambient temperatures can increase the resistance of the wire, leading to overheating and potential safety hazards. The NEC accounts for this by specifying temperature ratings for wire insulation. For instance, wires rated for 75°C are suitable for most residential applications, but if the wire is installed in a hot attic or near heat sources, a higher-rated insulation (90°C) may be necessary.
Additionally, bundled wires or conduits can generate more heat due to the proximity of multiple conductors. In such cases, derating factors may apply, requiring the use of a larger wire size to compensate for the increased heat. Consulting the NEC derating tables or seeking advice from a licensed electrician can help ensure compliance with safety standards.
What Are the Electrical Code Requirements for 150-Amp Service?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) serves as the foundation for electrical safety standards in the United States, including guidelines for wire sizing in a 150-amp service. Adhering to these requirements is not only a legal obligation but also a critical step in ensuring the safety and reliability of your electrical system. The NEC specifies minimum wire sizes based on the amperage, material, and insulation type, providing a comprehensive framework for electricians and homeowners alike.
For a 150-amp service, the NEC mandates that copper wires must be at least 1/0 AWG, while aluminum wires must be 2/0 AWG. These sizes are designed to handle the current load without exceeding safe temperature thresholds. Additionally, the code requires that wires used in residential settings have an insulation rating of 75°C or higher. This ensures the wire can withstand the heat generated by the electrical current without degrading over time. Failure to comply with these standards can result in penalties, insurance issues, or even voided warranties.
Beyond wire size, the NEC also addresses other aspects of a 150-amp service, such as grounding, circuit protection, and conduit fill. For instance, the code specifies that all electrical systems must include a proper grounding system to protect against electrical faults. Circuit breakers must also be appropriately sized to match the wire gauge, preventing overloads and ensuring the system operates safely. Understanding and adhering to these requirements is essential for anyone involved in electrical installations or upgrades.
Installation Best Practices for 150-Amp Service Wiring
Proper installation is just as important as selecting the correct wire size for a 150-amp service. Even the best materials can fail if not installed correctly, leading to safety hazards, inefficiencies, or costly repairs. Following industry best practices ensures that your electrical system operates safely and reliably for years to come.
One of the first steps in installation is planning the wire route. Avoid sharp bends or excessive tension, as these can damage the wire and reduce its lifespan. Use conduits or raceways to protect the wire from physical damage, especially in areas prone to moisture or mechanical stress. For aluminum wires, apply anti-oxidant compounds
What Is Vanillagift.ckm? A Comprehensive Guide To This Unique Platform
Exploring The Difference Between Pond And Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring Cracks Streams 2.0: The Ultimate Guide To Streaming Innovations
Wire Size For 150 Amp Sub Panel

How To Wire 200 Amp Service Disconnect