What Size Wire Is Needed For A 100 Amp Service? A Complete Guide
When it comes to electrical installations, one of the most critical decisions is determining the right wire size for your service. For a 100 amp service, selecting the appropriate wire gauge is not just about meeting code requirements—it’s about ensuring safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability. Whether you’re a homeowner planning an upgrade or a contractor working on a new project, understanding the factors that influence wire size is essential. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines, but there’s more to consider than just the numbers. Factors like the distance of the run, the type of wire material, and environmental conditions all play a role in making the right choice. Getting this wrong can lead to overheating, voltage drop, or even electrical fires, which is why it’s crucial to get it right from the start.
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100 amp service involves balancing safety and practicality. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for wiring, and each has its advantages and limitations. Copper is more conductive and durable but comes at a higher cost, while aluminum is more affordable but requires larger gauges to carry the same current. Beyond material, you also need to consider insulation types, which can impact the wire’s ability to withstand heat and environmental factors. Understanding these nuances will help you make an informed decision and ensure your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
As we dive deeper into this guide, we’ll explore the technical aspects of wire sizing, the role of local codes, and practical tips for installation. Whether you’re dealing with a residential or commercial setup, knowing the answers to questions like “What size wire is needed for a 100 amp service?” will empower you to make smart decisions. So, let’s break down the complexities and provide you with a clear roadmap to ensure your electrical system meets all requirements and performs optimally for years to come.
Read also:Exploring Adam Savages Children A Glimpse Into Their Lives And Influence
Table of Contents
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 100 Amp Service?
- What Are the Factors That Influence Wire Size Selection?
- How Do You Determine the Correct Wire Gauge?
- What Are the National Electrical Code Requirements?
- Why Is Voltage Drop Important in Wire Sizing?
- How Can You Ensure a Safe and Compliant Installation?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Sizing
Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 100 Amp Service?
When it comes to electrical systems, the wire size is a critical factor that directly impacts safety and performance. For a 100 amp service, the wire must be able to handle the current load without overheating or causing voltage drop. If the wire is too small, it can overheat, leading to potential fire hazards. On the other hand, if the wire is unnecessarily large, it can lead to wasted resources and increased costs. This balance is crucial, and understanding why wire size matters can help you avoid costly mistakes.
The primary purpose of selecting the correct wire size is to ensure that the electrical system operates within safe parameters. Electrical codes, such as the NEC, provide guidelines to help electricians and homeowners determine the appropriate wire gauge for specific amperage. For a 100 amp service, the wire must be able to carry the current from the main panel to the various circuits in the home without excessive resistance. Resistance in undersized wires can lead to energy loss, reduced appliance performance, and even damage to sensitive electronics.
Beyond safety, wire size also affects the efficiency of your electrical system. Properly sized wires minimize energy loss, ensuring that your appliances and devices receive the power they need to operate efficiently. This not only saves money on utility bills but also extends the lifespan of your electrical components. By understanding the importance of wire size, you can make informed decisions that enhance the safety, efficiency, and reliability of your electrical system.
What Are the Factors That Influence Wire Size Selection?
Selecting the right wire size for a 100 amp service involves considering several key factors. These include the type of material used, the distance of the wire run, and the environmental conditions where the wire will be installed. Each of these factors plays a significant role in determining the appropriate wire gauge, and overlooking any of them can lead to suboptimal performance or safety risks.
Material Choice: Copper vs. Aluminum
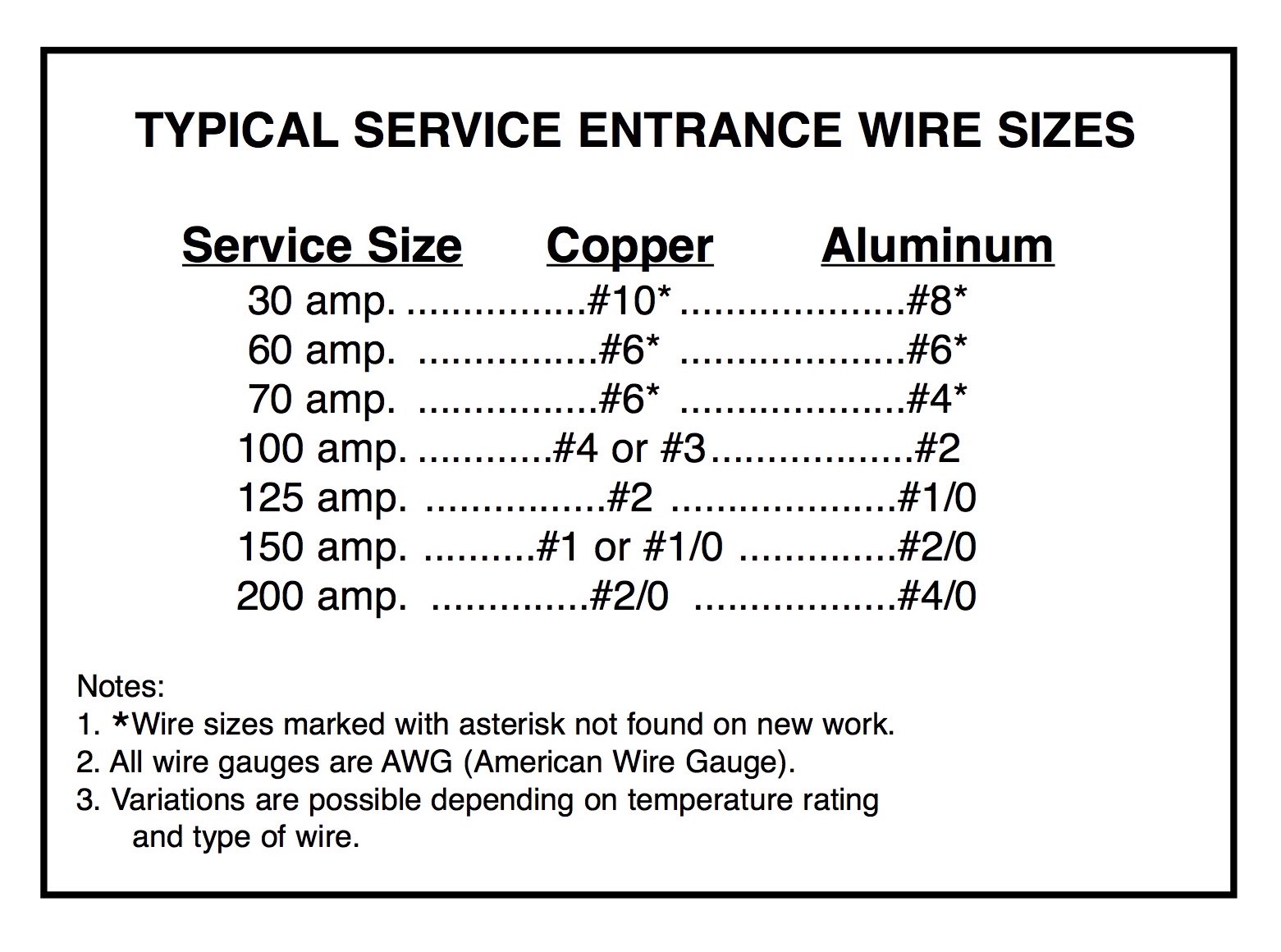
One of the first decisions you’ll need to make is whether to use copper or aluminum wiring. Copper is the preferred material for most residential applications due to its superior conductivity and durability. It can carry more current than aluminum at the same gauge, making it ideal for a 100 amp service. However, copper is also more expensive, which can be a limiting factor for some projects.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is more affordable and lighter, making it a popular choice for larger installations. However, it requires a larger gauge to carry the same current as copper. For example, a 100 amp service might require a 2/0 gauge aluminum wire, whereas a 2 AWG copper wire would suffice. Aluminum wiring also requires special connectors and anti-oxidant compounds to prevent corrosion and ensure a secure connection.
Read also:Who Is Lakiha Spicer Discover The Inspiring Story Of A Rising Star
Understanding the Impact of Distance
The distance between the main panel and the point of use is another critical factor in wire size selection. Longer runs increase resistance, which can lead to voltage drop. To compensate for this, larger wire gauges are often required for longer distances. For a 100 amp service, the NEC recommends limiting voltage drop to no more than 3% for optimal performance.
For example, if your main panel is located far from your home, you may need to upgrade to a thicker wire to maintain adequate voltage levels. This is particularly important for appliances like air conditioners, water heaters, and electric ranges, which require stable voltage to operate efficiently. By accounting for distance in your wire size calculations, you can avoid performance issues and ensure your electrical system meets all requirements.
How Do You Determine the Correct Wire Gauge?
Determining the correct wire gauge for a 100 amp service involves a combination of calculations, code compliance, and practical considerations. The process begins with consulting the NEC’s ampacity tables, which provide guidelines for wire sizes based on current load and insulation type. For a 100 amp service, the NEC typically recommends a 2 AWG copper wire or a 2/0 aluminum wire as a starting point.
However, these recommendations are just the beginning. You’ll also need to consider additional factors, such as the type of insulation and the ambient temperature where the wire will be installed. For example, wires with THHN insulation can handle higher temperatures than those with PVC insulation, allowing for smaller gauges in some cases. Similarly, wires installed in hot environments may require larger gauges to compensate for reduced conductivity.
Another important step is calculating voltage drop, especially for long runs. Voltage drop occurs when resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. To calculate voltage drop, you’ll need to know the wire’s resistance per foot, the length of the run, and the current load. If the voltage drop exceeds 3%, you may need to upgrade to a larger gauge to maintain performance. By carefully considering these factors, you can determine the correct wire gauge for your 100 amp service and ensure a safe and efficient installation.
What Are the National Electrical Code Requirements?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the cornerstone of electrical safety standards in the United States. It provides comprehensive guidelines for wire sizing, installation practices, and safety measures. For a 100 amp service, the NEC specifies minimum wire sizes based on the type of material and insulation used. These requirements are designed to ensure that electrical systems operate safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of overheating, voltage drop, and fire hazards.
For copper wiring, the NEC typically recommends a 2 AWG wire for a 100 amp service. This size is sufficient for most residential applications, provided the run length is within standard limits. For aluminum wiring, the recommendation is a 2/0 gauge wire, which compensates for the material’s lower conductivity. These guidelines are based on the assumption that the wire will be installed in a typical residential environment with standard insulation types and ambient temperatures.
It’s important to note that local codes may impose additional requirements beyond the NEC. Some jurisdictions may require larger wire gauges or specific installation practices to address unique environmental or safety concerns. Always consult with a licensed electrician or local building authority to ensure compliance with all applicable codes and regulations.
Why Is Voltage Drop Important in Wire Sizing?
Voltage drop is a critical consideration when sizing wires for a 100 amp service. It refers to the reduction in voltage that occurs as electricity travels through a conductor due to resistance. Excessive voltage drop can lead to poor performance of electrical devices, increased energy consumption, and even damage to sensitive equipment. For a 100 amp service, maintaining voltage drop within acceptable limits is essential for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your electrical system.
The NEC recommends limiting voltage drop to no more than 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders. Achieving this requires careful planning and calculation, especially for long wire runs. Factors such as wire gauge, material, and insulation type all influence voltage drop. For example, a 2 AWG copper wire may be sufficient for a short run, but a longer run may require upgrading to a 1/0 gauge to maintain acceptable voltage levels.
To calculate voltage drop, you’ll need to use a formula that accounts for the wire’s resistance, the length of the run, and the current load. Online calculators and tables are available to simplify this process, but it’s always a good idea to double-check your calculations. By addressing voltage drop during the planning stage, you can avoid performance issues and ensure your electrical system operates at peak efficiency.
How Can You Ensure a Safe and Compliant Installation?
Ensuring a safe and compliant installation for a 100 amp service involves more than just selecting the right wire size. It requires careful planning, adherence to codes, and attention to detail during the installation process. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or working with a professional electrician, following best practices is essential for achieving a safe and reliable electrical system.
One of the first steps is to obtain the necessary permits and inspections. Most jurisdictions require permits for electrical work, and inspections ensure that the installation meets all safety and code requirements. This process not only protects you from potential hazards but also adds value to your property by ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Proper installation techniques are equally important. This includes using the correct connectors, securing wires properly, and ensuring adequate ventilation for heat dissipation. For aluminum wiring, special anti-oxidant compounds must be applied to prevent corrosion and ensure a secure connection. Additionally, labeling circuits and documenting the installation can help with future maintenance and troubleshooting. By following these steps, you can ensure a safe and compliant installation that meets all requirements and performs reliably for years to come.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when sizing wires for a 100 amp service. Avoiding these common pitfalls is essential for ensuring a safe and efficient installation. One of the most frequent errors is underestimating the importance of wire size. Using a wire that’s too small for the current load can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and even fire hazards. Always consult the NEC guidelines and perform voltage drop calculations to ensure the wire size is appropriate.
Another common mistake is neglecting environmental factors. Wires installed in hot environments or exposed to moisture may require larger gauges or specialized insulation to perform safely. Failing to account for these conditions can compromise the wire’s performance and lifespan. Additionally, improper connections, such as using the wrong connectors for aluminum wiring, can lead to corrosion and loose connections, increasing the risk of electrical faults.
Finally, skipping permits and inspections is a mistake that can have serious consequences. Not only does this violate local codes, but it also puts your safety at
What Are Adepti Genshin: A Complete Guide To Their Role And Significance
Understanding BMI License Fees: A Comprehensive Guide To Music Licensing
Understanding Tabish Age: A Comprehensive Guide To His Life And Achievements

Silicone wire size vs withstand current (wire amp chart) esk8.news
What Size Wire Is Needed For 60 Amp Service