What Wire Gauge For 100 Amps: A Complete Guide To Electrical Wiring
Choosing the right wire gauge for 100 amps is a critical decision for any electrical project, whether you're wiring a home, workshop, or industrial setup. Electrical safety and efficiency depend on selecting the correct wire size to handle the current load. Using an undersized wire can lead to overheating, fire hazards, and equipment damage, while an oversized wire can unnecessarily increase costs. Understanding the relationship between amperage, wire gauge, and the type of conductor is essential to ensure compliance with electrical codes and maintain a safe environment.
When working with 100-amp circuits, the wire gauge you select must meet the National Electrical Code (NEC) standards and local regulations. These standards are designed to protect both property and lives by ensuring that electrical systems are installed correctly. Factors such as the distance of the run, the type of insulation, and the environment where the wire will be installed also play a crucial role in determining the appropriate wire gauge. By considering these variables, you can avoid common pitfalls and ensure your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about what wire gauge for 100 amps is suitable for your needs. From understanding the basics of wire gauges to exploring specific scenarios and frequently asked questions, we’ll cover all the essential details. Whether you’re a homeowner, electrician, or DIY enthusiast, this article will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and achieve optimal results for your electrical projects.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- What Is Wire Gauge and Why Does It Matter?
- How to Determine the Right Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
- What Are the Factors Affecting Wire Gauge Selection?
- Is There a Difference Between Copper and Aluminum Wires?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
- How to Ensure Compliance with Electrical Codes?
- What Are the Best Practices for Wiring a 100-Amp Circuit?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge for 100 Amps
What Is Wire Gauge and Why Does It Matter?
Wire gauge refers to the diameter of the conductor used in electrical wiring, and it is a critical factor in determining the wire's current-carrying capacity. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is the standard used to measure wire sizes in the United States. A lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire, which can carry more current without overheating. For example, a 1-gauge wire is much thicker than a 14-gauge wire and can handle significantly higher amperage.
The importance of selecting the correct wire gauge cannot be overstated. Using an undersized wire for a 100-amp circuit can result in excessive resistance, leading to overheating and potential fire hazards. On the other hand, using a wire that is too large can be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome to work with. Understanding the relationship between wire gauge, amperage, and resistance is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical installations.
In addition to amperage, other factors such as voltage drop and insulation type also influence wire gauge selection. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in a wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels through it. To minimize voltage drop, especially in long-distance runs, a thicker wire may be required. Similarly, the type of insulation affects the wire's ability to withstand heat and environmental conditions, further impacting the choice of wire gauge.
How to Determine the Right Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
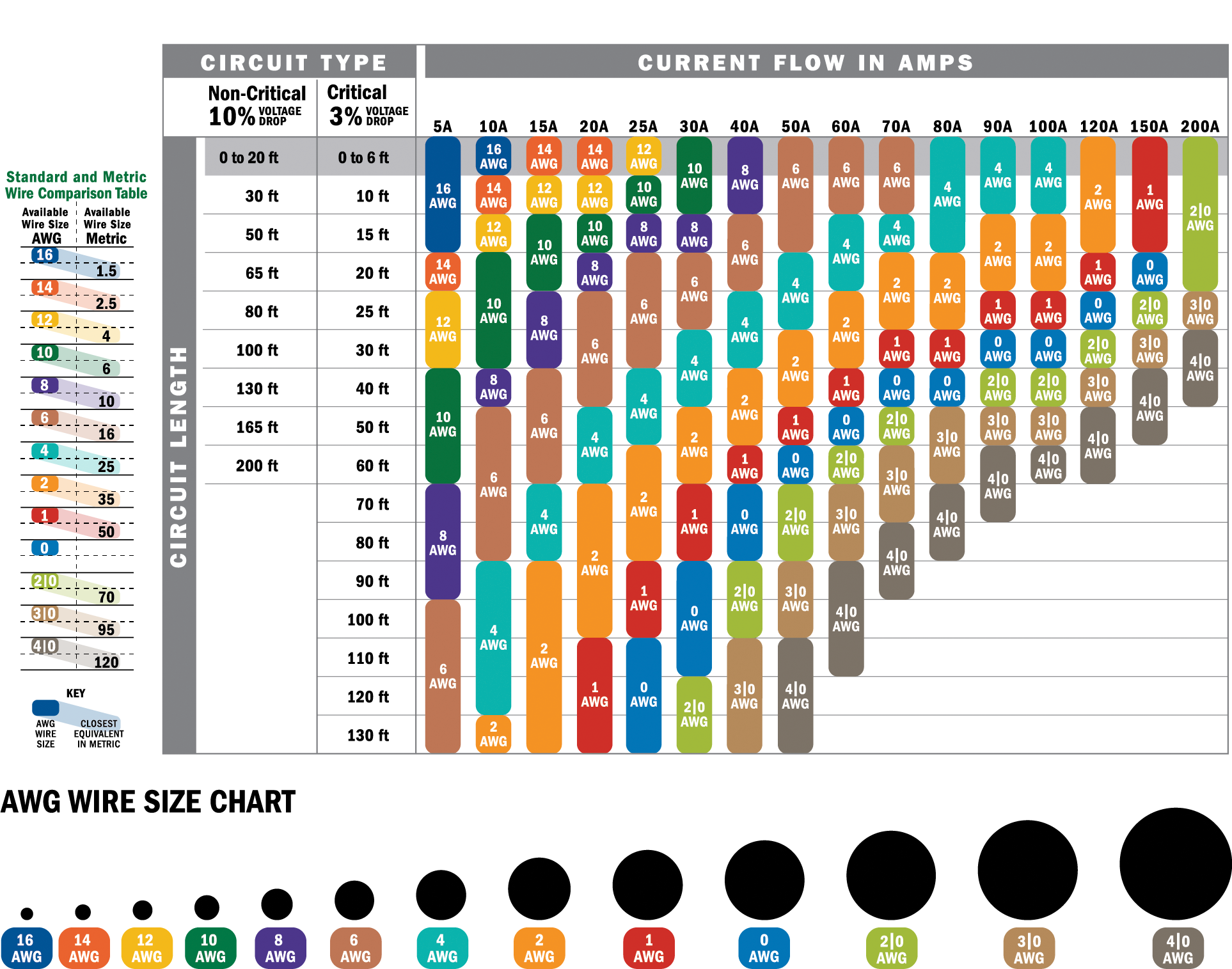
Determining the correct wire gauge for 100 amps involves understanding the NEC guidelines and considering the specific requirements of your electrical setup. For most residential applications, a 100-amp service typically requires a 3 AWG copper wire or a 1 AWG aluminum wire. These sizes are based on the assumption that the wire will be installed in a standard environment with a maximum ambient temperature of 30°C (86°F).
What Factors Influence Wire Size Selection?
Several factors influence the choice of wire gauge for a 100-amp circuit. These include:
- Distance of the Run: Longer distances require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- Type of Insulation: Wires with higher temperature ratings can handle more current without overheating.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher temperatures reduce the wire's current-carrying capacity.
- Conduit Fill: The number of wires in a conduit affects heat dissipation and may require larger wire sizes.
How Do You Calculate Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop is a critical consideration when selecting the appropriate wire gauge for 100 amps. The formula to calculate voltage drop is:
Read also:Barry Weiss The Visionary Leader Transforming Industries
Voltage Drop = (2 × Length × Current × Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length is the distance of the wire run in feet.
- Current is the amperage of the circuit (100 amps in this case).
- Resistance is the resistivity of the wire material (copper or aluminum).
By plugging in the values, you can determine whether the voltage drop exceeds the acceptable limit of 3% for branch circuits or 5% for feeders.
What Are the Factors Affecting Wire Gauge Selection?
Choosing the right wire gauge for 100 amps is not a one-size-fits-all process. Several factors can influence the selection, and understanding these variables is key to making the correct choice.
Why Is Distance Important When Selecting Wire Gauge?
The distance of the wire run plays a significant role in determining the appropriate wire gauge. For longer runs, the resistance in the wire increases, leading to a higher voltage drop. To compensate for this, a thicker wire is required to maintain the desired voltage at the load. For example, a 100-amp circuit running 100 feet may require a 1 AWG copper wire, while the same circuit running 200 feet might need a 2/0 AWG wire to minimize voltage drop.
What Role Does Insulation Type Play in Wire Selection?
The type of insulation used on the wire affects its ability to handle heat and environmental conditions. Wires with higher temperature ratings, such as THHN or XHHW, can carry more current without overheating compared to those with lower ratings. Additionally, wires installed in hot environments or exposed to sunlight may require a larger gauge to ensure safe operation.
How Does Conduit Fill Affect Wire Size?
Conduit fill refers to the number of wires placed inside a conduit and how it impacts heat dissipation. Overcrowding a conduit can lead to overheating, which reduces the wire's current-carrying capacity. The NEC provides guidelines for conduit fill, and exceeding these limits may necessitate using a larger wire gauge or splitting the circuit into multiple conduits.
Is There a Difference Between Copper and Aluminum Wires?
Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical wiring, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Copper is a superior conductor of electricity, meaning it can carry more current than aluminum for the same wire gauge. As a result, copper wires are often smaller in diameter than their aluminum counterparts for the same amperage. For example, a 3 AWG copper wire can handle 100 amps, while a 1 AWG aluminum wire is required to achieve the same capacity.
However, aluminum wires are lighter and less expensive than copper, making them a popular choice for large-scale installations. The downside is that aluminum is more prone to oxidation and requires special connectors to prevent corrosion. Additionally, aluminum wires have a higher resistance, which can lead to greater voltage drop over long distances. When selecting between copper and aluminum, it's essential to weigh the cost, performance, and specific requirements of your project.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid?
When selecting the wire gauge for 100 amps, several common mistakes can compromise safety and efficiency. Avoiding these pitfalls is crucial to ensure a successful installation.
Why Is Using an Undersized Wire Dangerous?
Using an undersized wire for a 100-amp circuit is one of the most dangerous mistakes. When a wire is too small to handle the current load, it generates excessive heat, which can lead to insulation breakdown, melting, and even fire. This risk is especially high in environments with poor ventilation or high ambient temperatures. Always consult the NEC guidelines and perform voltage drop calculations to ensure the wire can safely carry the required current.
What Are the Risks of Ignoring Voltage Drop?
Ignoring voltage drop can result in inefficient operation of electrical devices and equipment. Appliances may underperform, lights may flicker, and motors may overheat due to insufficient voltage. For long-distance runs, it's essential to account for voltage drop and select a wire gauge that minimizes it to acceptable levels. Failing to do so can lead to costly repairs and potential safety hazards.
How Can Poor Connections Affect Performance?
Poorly made connections, such as loose or corroded terminals, can increase resistance and cause overheating. This issue is particularly common with aluminum wires, which require anti-oxidant compounds and specialized connectors. Ensuring all connections are secure, clean, and compatible with the wire material is critical to maintaining a safe and reliable electrical system.
How to Ensure Compliance with Electrical Codes?
Compliance with electrical codes is not just a legal requirement but also a critical aspect of ensuring safety and reliability. The NEC provides detailed guidelines for wire gauge selection, installation practices, and safety standards. Familiarizing yourself with these codes is essential for anyone involved in electrical work.
One of the key aspects of compliance is using wires that meet the NEC's ampacity requirements. Ampacity refers to the maximum current a wire can safely carry under specific conditions. The NEC tables provide ampacity ratings for different wire sizes, materials, and insulation types. By adhering to these ratings, you can ensure that your wiring meets the necessary safety standards.
Additionally, local building codes may have specific requirements that go beyond the NEC guidelines. These codes often address regional factors such as climate, soil conditions, and building types. Consulting with a licensed electrician or local authority can help ensure that your installation complies with all applicable regulations.
What Are the Best Practices for Wiring a 100-Amp Circuit?
Wiring a 100-amp circuit requires careful planning and adherence to best practices to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with codes. Here are some tips to guide you through the process:
- Plan Ahead: Assess the electrical load, distance, and environmental conditions before selecting the wire gauge.
- Use Quality Materials: Invest in high-quality wires, connectors, and insulation to ensure durability and performance.
- Follow NEC Guidelines: Always refer to the NEC tables for ampacity ratings and installation practices.
- Hire a Professional: If you're unsure about any aspect of the installation, consult a licensed electrician to avoid costly mistakes.
By following these best practices, you can create a safe and reliable electrical system that meets your needs and complies with all relevant standards.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Gauge for 100 Amps
What Is the Minimum Wire Gauge for 100 Amps?
The minimum wire gauge for 100 amps is typically 3 AWG copper or 1 AWG aluminum, assuming standard conditions. However, adjustments may be necessary based on factors such as distance, temperature, and
Comprehensive Guide To Choosing The Right 10 Amp Wire Size For Your Projects
What Does "Enter Sandman" Mean? Exploring Its Origins And Meaning
Choosing The Right Size Wire For 100 Amp Service: A Comprehensive Guide
20 Gauge Wire Amps

Speaker wire gauge calculator vetkiza