What You Need To Know About 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size For Safe Electrical Installations
When it comes to electrical installations, choosing the right wire size is crucial for safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations. A 100 amp feeder wire size is commonly used in residential and commercial settings to supply power from the main panel to subpanels or specific appliances. However, selecting the wrong size can lead to overheating, voltage drops, or even electrical fires. This is why understanding the nuances of wire sizing, material types, and load requirements is essential for electricians, DIY enthusiasts, and homeowners alike.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern living, powering everything from lighting to heavy appliances. A 100 amp feeder wire is designed to handle a significant load, but its performance depends on factors such as the distance of the run, the type of insulation, and the environment in which it is installed. Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical system or planning a new construction project, knowing how to calculate and choose the correct wire size ensures that your system operates safely and efficiently.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we'll explore the technical aspects of 100 amp feeder wire size, including material options, National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, and practical tips for installation. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to select and install the appropriate wire size for your needs, ensuring both safety and compliance with industry standards.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- What is 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size and Why Does It Matter?
- How to Choose the Right Wire Size for a 100 Amp Feeder?
- What Are the Material Options for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
- Understanding NEC Guidelines for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
- What Factors Affect the Choice of 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
- Installation Tips for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
What is 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size and Why Does It Matter?
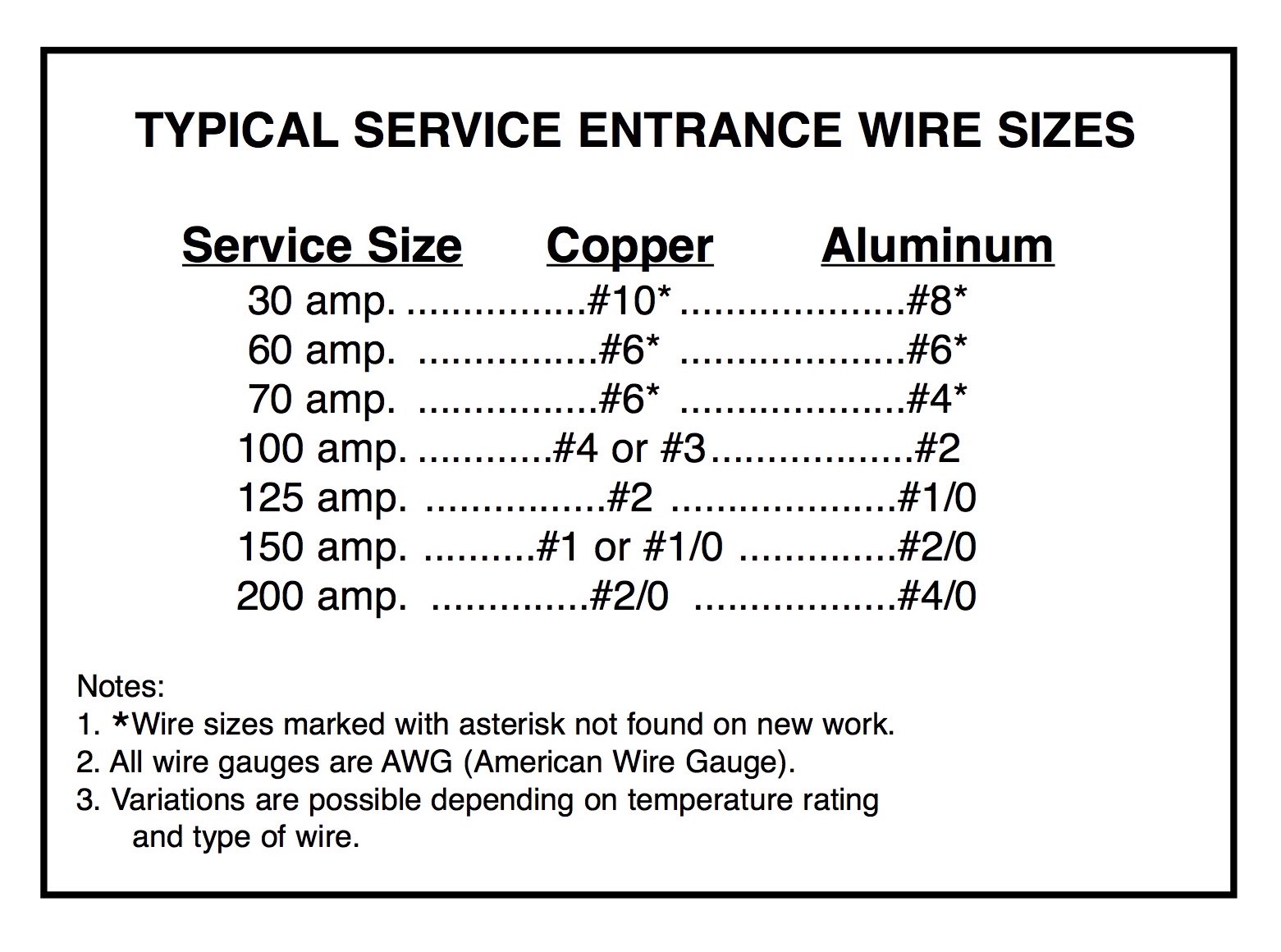
A 100 amp feeder wire size refers to the gauge and type of wire used to carry electrical current from a main panel to a subpanel or specific appliance. This wire is rated to handle up to 100 amps of current, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including powering entire sections of a home or commercial building. The size of the wire is determined by its diameter, which is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG). For a 100 amp feeder, the most common wire sizes are 2 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum.
The importance of selecting the correct wire size cannot be overstated. If the wire is too small for the load it carries, it can overheat, leading to insulation damage and potential fire hazards. On the other hand, using a wire that is unnecessarily large can result in wasted materials and increased costs. Therefore, understanding the relationship between wire size, current capacity, and load requirements is essential for safe and efficient electrical installations.
Additionally, the choice of wire size impacts voltage drop, which refers to the reduction in voltage as electricity travels through a conductor. A significant voltage drop can cause appliances to underperform or malfunction. By selecting the appropriate 100 amp feeder wire size, you can minimize voltage drop and ensure that your electrical system operates at optimal efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Wire Size for a 100 Amp Feeder?
Choosing the right wire size for a 100 amp feeder involves several considerations, including the length of the run, the material of the wire, and the specific requirements of your electrical system. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
1. Calculate the Load Requirements
Before selecting a wire size, it's essential to calculate the total load that the feeder will need to handle. This includes the combined amperage of all appliances, lighting, and outlets connected to the subpanel. Use the following formula to estimate the load:
- Voltage (V) x Amperage (A) = Wattage (W)
For example, if you're working with a 120-volt system and need to supply 100 amps, the total wattage would be 12,000 watts.
Read also:Rick Moranis A Comprehensive Look At The Comedy Legends Life And Legacy
2. Consider the Length of the Run
The distance between the main panel and the subpanel affects the choice of wire size. Longer runs require larger wires to minimize voltage drop. As a general rule, for every 100 feet of run, you may need to increase the wire size by one gauge to compensate for resistance.
3. Choose the Right Material
Wire materials, such as copper and aluminum, have different conductivity levels, which influence their size requirements. Copper is more conductive and can carry the same load with a smaller diameter compared to aluminum. However, aluminum is often more cost-effective, making it a popular choice for longer runs.
What Are the Material Options for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
When selecting a wire for a 100 amp feeder, you have two primary material options: copper and aluminum. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages, which we'll explore below.
1. Copper Wire
Copper is the preferred choice for many electricians due to its superior conductivity and durability. A 2 AWG copper wire is typically sufficient for a 100 amp feeder, making it a compact and efficient option. Copper wires are also less prone to corrosion, which extends their lifespan and reduces maintenance needs.
2. Aluminum Wire
Aluminum is a more affordable alternative to copper, but it requires a larger diameter to carry the same current. For a 100 amp feeder, a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is often recommended. While aluminum is lighter and easier to work with, it is more susceptible to oxidation and requires special anti-oxidant compounds during installation to ensure a secure connection.
Understanding NEC Guidelines for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides comprehensive guidelines for selecting and installing electrical wires, including those for a 100 amp feeder. These guidelines are designed to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
1. Ampacity Ratings
The NEC specifies ampacity ratings for different wire sizes and materials. For example, a 2 AWG copper wire is rated for 115 amps, while a 1/0 AWG aluminum wire is rated for 120 amps. These ratings take into account factors such as insulation type and ambient temperature.
2. Voltage Drop Considerations
The NEC recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders to ensure optimal performance. This can be achieved by selecting the appropriate wire size based on the length of the run and the expected load.
What Factors Affect the Choice of 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size?
Several factors influence the choice of wire size for a 100 amp feeder, including environmental conditions, insulation type, and installation method. Understanding these factors ensures that your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
1. Ambient Temperature
Higher ambient temperatures can reduce the ampacity of a wire, requiring a larger size to compensate. The NEC provides temperature correction factors to help electricians adjust their calculations accordingly.
2. Insulation Type
Different insulation materials, such as THHN, XHHW, and UF, have varying temperature and moisture resistance properties. Choosing the right insulation ensures that the wire can withstand the conditions of its installation environment.
Installation Tips for 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
Proper installation is just as important as selecting the right wire size. Here are some tips to ensure a safe and efficient installation:
- Always use conduit for protection, especially in exposed or high-traffic areas.
- Secure connections with anti-oxidant compounds when using aluminum wire.
- Label wires clearly to avoid confusion during future maintenance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when working with 100 amp feeder wires. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Underestimating the load requirements and selecting a wire that is too small.
- Ignoring voltage drop considerations, especially for long runs.
- Using improper insulation for the installation environment.
Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Feeder Wire Size
1. What Happens If You Use a Wire That Is Too Small for a 100 Amp Feeder?
Using a wire that is too small can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards. Always ensure that the wire size matches the load requirements.
2. Can You Use Aluminum Wire for a 100 Amp Feeder?
Yes, aluminum wire can be used for a 100 amp feeder, but it requires a larger diameter compared to copper. Proper installation techniques, such as using anti-oxidant compounds, are essential.
3. How Do You Calculate Voltage Drop for a 100 Amp Feeder?
Voltage drop can be calculated using the formula: Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Resistance x Current) / 1000. Adjust the wire size to keep the drop within acceptable limits.
In conclusion, selecting the right 100 amp feeder wire size is a critical step in ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. By understanding the factors that influence wire size, adhering to NEC guidelines, and avoiding common mistakes, you can create a reliable and compliant installation. For more information on electrical safety, visit the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) website.
Unlocking The Mysteries Of 1111 Angel Number Today: What It Means For You
Allen Iverson Net Worth: A Complete Guide To The Legendary Basketball Star
Fortnite Default Icon: The Ultimate Guide To Its Evolution And Significance

Wire Gauge Chart
What Size Ground Wire For 100 Amp Sub Panel