Do Animals Have A Cell Membrane? Exploring The Science Behind It
Have you ever wondered what keeps animals alive at the most fundamental level? Every living organism, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest mammals, is made up of cells. These cells are the building blocks of life, and they rely on various components to function properly. One of these critical components is the cell membrane, a protective barrier that separates the internal environment of a cell from the external world. But do animals have a cell membrane? The answer is yes! In animals, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular integrity, regulating the movement of substances, and enabling communication between cells. Without this essential structure, life as we know it would not be possible.
The cell membrane is not just a simple boundary; it is a dynamic and highly specialized structure. In animals, it is composed primarily of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, all of which work together to perform vital functions. For example, the lipid bilayer provides flexibility and a semi-permeable barrier, while embedded proteins facilitate the transport of molecules in and out of the cell. This intricate design ensures that animal cells can thrive in diverse environments, from the freezing Arctic to the scorching deserts. Understanding the role of the cell membrane in animals is not only fascinating but also essential for fields like medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science.
In this article, we will explore the science behind the cell membrane in animals, answering key questions such as how does it function?, what happens if it malfunctions?, and how does it compare to other organisms? We’ll also delve into the broader implications of this biological marvel, shedding light on its importance in maintaining life. Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or simply curious about the natural world, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the cell membrane and its role in animal biology. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets of this incredible cellular structure!
Read also:Diane Furnberg Exploring Her Life Achievements And Impact
Table of Contents
- What Is a Cell Membrane?
- Do Animals Have a Cell Membrane?
- How Does the Cell Membrane Function?
- What Happens If the Cell Membrane Malfunctions?
- How Does the Cell Membrane Compare to Other Organisms?
- Why Is the Cell Membrane Important for Animal Life?
- How Can We Study the Cell Membrane?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Cell Membrane?
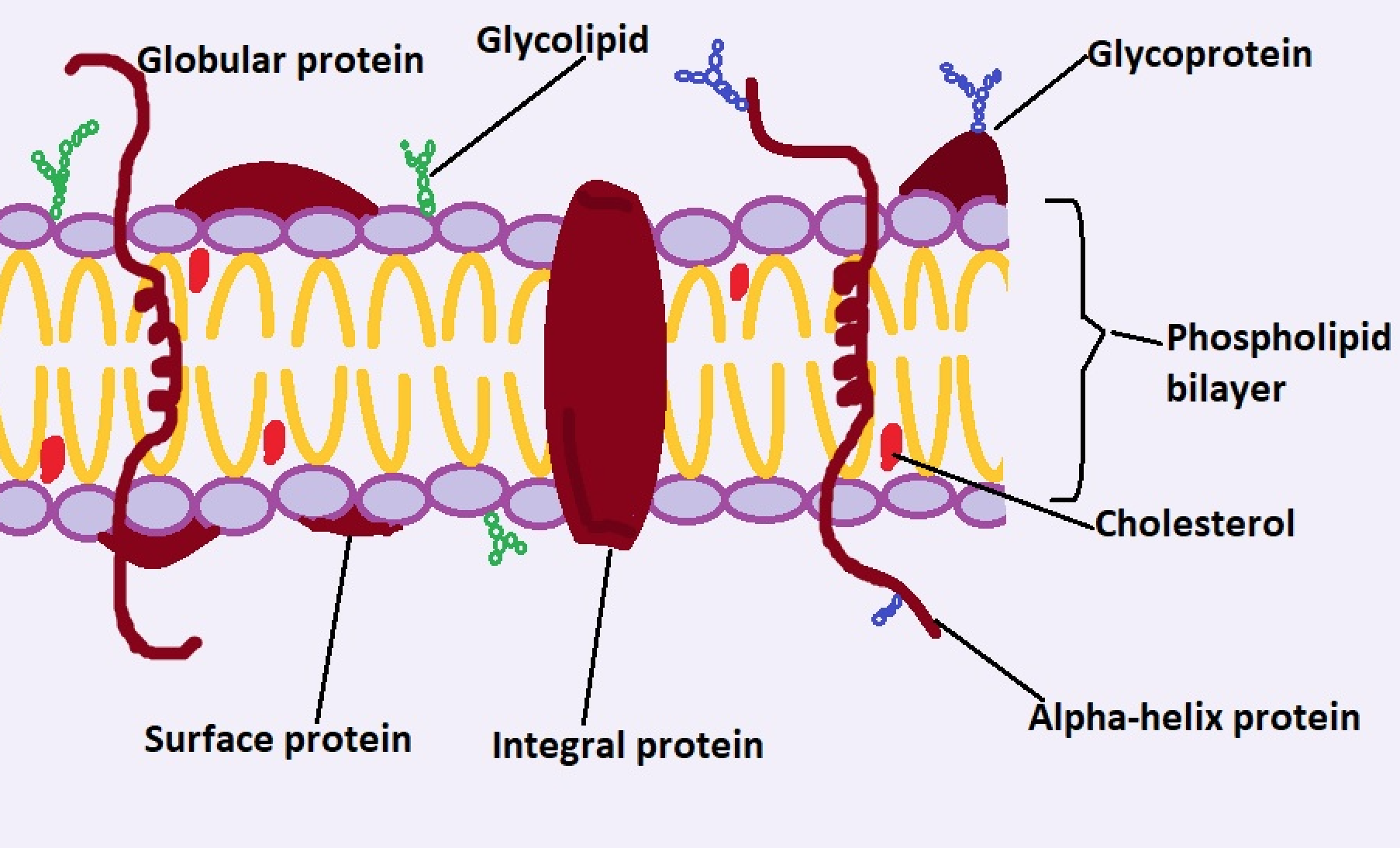
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, semi-permeable barrier that surrounds every cell in an animal’s body. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which consists of two layers of lipid molecules. These lipids have hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails, creating a structure that is both flexible and selective. Embedded within this lipid bilayer are various proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol molecules, each playing a specific role in maintaining cellular function.
One of the primary functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This is achieved through several mechanisms, including passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. For instance, small molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide can pass through the lipid bilayer freely, while larger molecules such as glucose require the assistance of transport proteins. Additionally, the cell membrane contains receptor proteins that allow cells to communicate with their environment, responding to signals like hormones and neurotransmitters.
Another fascinating aspect of the cell membrane is its ability to maintain cellular integrity. The lipid bilayer provides a stable yet flexible structure, while cholesterol molecules embedded within it help regulate fluidity and prevent the membrane from becoming too rigid or too fluid. This balance is crucial for the proper functioning of the cell. Moreover, the carbohydrates attached to the membrane’s surface play a role in cell recognition, allowing the immune system to distinguish between self and non-self cells. These features make the cell membrane an indispensable component of animal biology.
Do Animals Have a Cell Membrane?
Yes, animals do have a cell membrane. In fact, every single cell in an animal’s body is encased by this vital structure. But why is the cell membrane so important for animals? To answer this question, we need to consider the unique challenges that animal cells face. Unlike plant cells, which have a rigid cell wall, animal cells rely solely on the cell membrane for structural support and protection. This makes the cell membrane a critical component for maintaining the shape and function of animal cells.
Why Do Animal Cells Need a Cell Membrane?
Animal cells are constantly interacting with their environment, whether it’s absorbing nutrients, expelling waste, or responding to external signals. The cell membrane acts as a gatekeeper, controlling what enters and exits the cell. For example, it allows essential nutrients like glucose and amino acids to pass through while blocking harmful substances. This selective permeability is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, the delicate balance of conditions necessary for cellular survival.
Furthermore, the cell membrane plays a key role in cellular communication. Embedded proteins in the membrane act as receptors, allowing cells to detect and respond to signals from their surroundings. This is particularly important in animals, where cells must work together to form tissues, organs, and systems. For instance, nerve cells use the cell membrane to transmit electrical signals, enabling movement, thought, and sensation. Without the cell membrane, these processes would be impossible.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
What Makes the Cell Membrane Unique in Animals?
While all living organisms have cell membranes, the structure and function of these membranes can vary significantly. In animals, the cell membrane is particularly dynamic and adaptable. For example, it contains a higher concentration of cholesterol molecules compared to plant cells, which helps maintain fluidity and stability. This adaptability allows animal cells to function in a wide range of environments, from the deep sea to the highest mountains.
Another distinguishing feature of animal cell membranes is their role in cell signaling. Animal cells rely heavily on chemical signals to communicate, and the cell membrane is the interface where these signals are received and processed. This makes the cell membrane a central player in processes like growth, development, and immune response. In short, the cell membrane is not just a passive barrier; it is an active participant in the life of every animal cell.
How Does the Cell Membrane Function?
The cell membrane is a marvel of biological engineering, performing a wide range of functions that are essential for cellular survival. At its core, the membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This is achieved through several mechanisms, each tailored to specific types of molecules.
How Does the Cell Membrane Regulate Substance Movement?
One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to control the flow of materials. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse directly through the lipid bilayer, a process known as passive diffusion. However, larger or polar molecules, such as glucose and ions, require the assistance of transport proteins. These proteins act as channels or carriers, facilitating the movement of substances across the membrane.
In addition to passive transport, the cell membrane also supports active transport, which requires energy in the form of ATP. This process is used to move substances against their concentration gradient, such as pumping sodium and potassium ions in and out of the cell. Active transport is essential for maintaining the electrochemical balance necessary for processes like nerve signaling and muscle contraction.
What Role Does the Cell Membrane Play in Cell Signaling?
Cell signaling is another critical function of the cell membrane. Embedded proteins in the membrane act as receptors, detecting signals from the environment and triggering a response within the cell. For example, when a hormone binds to its receptor on the cell membrane, it can activate a cascade of reactions that lead to changes in gene expression or cellular activity. This ability to communicate is what allows cells to coordinate their actions and maintain the health of the organism.
What Happens If the Cell Membrane Malfunctions?
When the cell membrane fails to function properly, it can have serious consequences for the cell and the organism as a whole. Malfunctions can occur due to genetic mutations, environmental factors, or diseases, leading to a wide range of issues.
What Are the Consequences of Cell Membrane Damage?
Damage to the cell membrane can result in the loss of selective permeability, allowing harmful substances to enter the cell and essential nutrients to leak out. This can disrupt cellular processes and lead to cell death. For example, in conditions like cystic fibrosis, mutations in membrane proteins impair the transport of chloride ions, causing thick mucus to accumulate in the lungs and other organs.
How Can Cell Membrane Malfunctions Be Treated?
Treatment for cell membrane malfunctions depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, medications can help restore normal function, such as enzyme replacement therapy for lysosomal storage disorders. In other cases, lifestyle changes or surgical interventions may be necessary. Research into cell membrane biology continues to advance, offering hope for new treatments and therapies.
How Does the Cell Membrane Compare to Other Organisms?
While all living organisms have cell membranes, there are notable differences between animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria. For example, plant cells have a rigid cell wall in addition to the cell membrane, providing extra structural support. In contrast, animal cells rely entirely on the membrane for protection and flexibility.
Why Is the Cell Membrane Important for Animal Life?
The cell membrane is indispensable for animal life, enabling cells to maintain homeostasis, communicate, and adapt to their environment. Its unique properties make it a cornerstone of animal biology.
How Can We Study the Cell Membrane?
Scientists use a variety of techniques to study the cell membrane, including microscopy, biochemical assays, and computational modeling. These methods provide insights into its structure, function, and role in health and disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do animals have a cell membrane? Yes, every animal cell has a cell membrane.
What happens if the cell membrane is damaged? Damage can lead to loss of function and cell death.
How is the cell membrane studied? Techniques like microscopy and biochemical assays are commonly used.
For more information on cell biology, visit Cell Press.
Unlocking The Mysteries Of 1111 Meaning Numerology: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring The Differences: Pond Vs Lake – A Comprehensive Guide
What’s The Difference Between A Lake And A Pond: A Comprehensive Guide

Cell Membrane In Plant Cell Or Animal Cell
Cell Membrane Function Simple