Exploring Lakes And Ponds Characteristics: A Comprehensive Guide
Lakes and ponds are among the most captivating natural features on Earth, serving as vital ecosystems that support diverse life forms and provide numerous benefits to humans. These water bodies are often mistaken for one another, but they possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. Understanding lakes and ponds characteristics is essential for appreciating their ecological roles, recreational value, and contributions to biodiversity. From their formation to their unique physical and biological traits, these water bodies are more than just picturesque landscapes—they are integral to the planet's health.
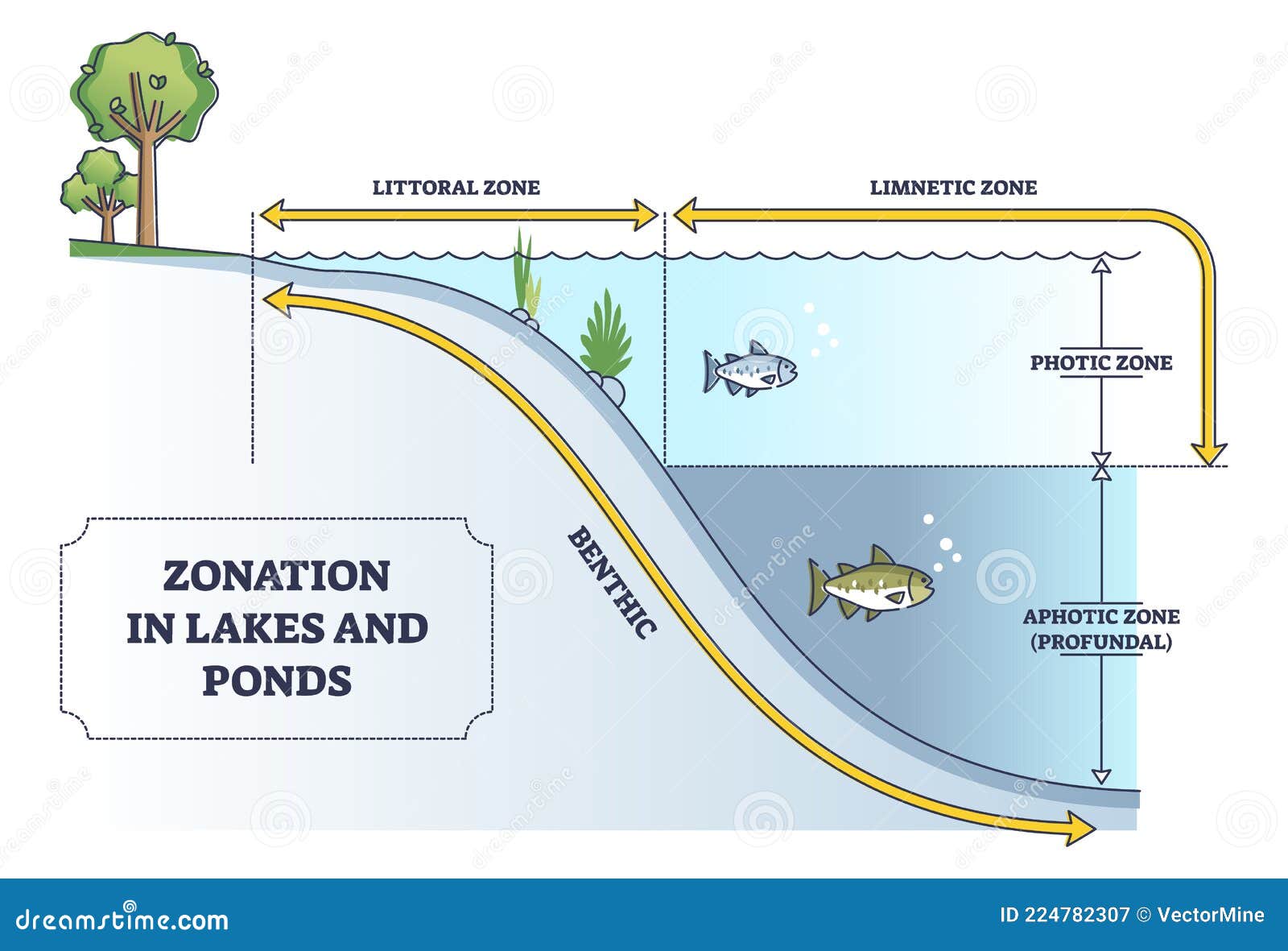
While lakes are typically larger and deeper, ponds are smaller and shallower, often allowing sunlight to penetrate their entire depth. This fundamental difference influences the types of organisms that inhabit these ecosystems and the processes that occur within them. Lakes and ponds characteristics vary depending on factors such as location, climate, and surrounding vegetation, making each one unique. Whether you're a nature enthusiast, a student, or simply curious, exploring the intricacies of these water bodies can deepen your appreciation for the natural world.
Additionally, lakes and ponds play a crucial role in regulating water cycles, supporting wildlife, and offering recreational opportunities. They are home to a wide range of species, from microscopic plankton to large fish and birds. However, these ecosystems are also vulnerable to pollution, climate change, and human activities. By understanding their characteristics, we can better protect and preserve these invaluable resources for future generations. Dive deeper into this guide to uncover the fascinating traits and significance of lakes and ponds.
Read also:Unlock The Fun Infinite Craft Unblocked Ndash The Ultimate Guide
Table of Contents
- What Are the Key Differences Between Lakes and Ponds?
- How Do Lakes and Ponds Form?
- What Are the Physical Characteristics of Lakes and Ponds?
- Biological Diversity in Lakes and Ponds
- Environmental Significance of Lakes and Ponds
- Human Impact on Lakes and Ponds Characteristics
- How Can We Protect and Restore These Ecosystems?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Lakes and Ponds
What Are the Key Differences Between Lakes and Ponds?
Understanding the distinctions between lakes and ponds is crucial for grasping their unique roles in nature. While both are inland bodies of water, they differ significantly in size, depth, and ecological functions. Lakes are generally larger and deeper, often spanning several square kilometers and reaching depths of hundreds of meters. In contrast, ponds are smaller and shallower, typically allowing sunlight to reach the bottom and support plant growth throughout the water column.
One of the most notable differences lies in their temperature stratification. Lakes often exhibit distinct layers of water with varying temperatures, especially during warmer months. These layers, known as the epilimnion (top), metalimnion (middle), and hypolimnion (bottom), influence the distribution of organisms and nutrients. Ponds, on the other hand, tend to have a more uniform temperature due to their shallowness, which allows for greater mixing of water and nutrients.
Another key difference is the biodiversity they support. Lakes, with their larger surface area and deeper waters, provide habitats for a wider range of species, including fish, amphibians, and birds. Ponds, while smaller, often serve as critical breeding grounds for amphibians and insects. The characteristics of these ecosystems influence the types of organisms that thrive in them, making each water body unique. By understanding these differences, we can better appreciate the diverse roles lakes and ponds play in the environment.
How Do Lakes and Ponds Form?
The formation of lakes and ponds is a fascinating process shaped by natural forces and geological events. These water bodies can originate through various mechanisms, including glacial activity, tectonic movements, volcanic eruptions, and human intervention. Glacial lakes, for example, are created when glaciers carve out basins in the landscape and meltwater fills them. These lakes are common in regions that were once covered by ice sheets, such as the Great Lakes in North America.
Tectonic activity is another significant factor in the formation of lakes. When the Earth's crust shifts, it can create depressions that fill with water, forming tectonic lakes. The Dead Sea and Lake Baikal are prime examples of tectonic lakes. Volcanic activity can also lead to the creation of crater lakes, which form in the calderas of extinct volcanoes. These lakes often have unique chemical compositions due to the minerals present in the volcanic rock.
Human-made lakes and ponds, such as reservoirs and ornamental ponds, are created for specific purposes like water storage, irrigation, or aesthetics. While natural lakes and ponds are shaped by geological and environmental processes, human-made water bodies are designed to meet societal needs. Regardless of their origin, the characteristics of these water bodies are influenced by their formation process, which in turn affects their ecological and environmental roles.
Read also:Barry Weiss The Visionary Leader Transforming Industries
What Are the Physical Characteristics of Lakes and Ponds?
The physical characteristics of lakes and ponds play a significant role in determining their ecological functions and the organisms they support. These characteristics include size, depth, water clarity, temperature, and surrounding vegetation. Size and depth are among the most obvious traits, with lakes being larger and deeper than ponds. This difference affects the water's ability to circulate and mix, influencing oxygen levels and nutrient distribution.
Water clarity is another important characteristic, as it determines how much sunlight penetrates the water. Clear lakes and ponds often have lower levels of suspended particles, allowing sunlight to reach greater depths. This promotes the growth of aquatic plants, which provide oxygen and habitat for other organisms. In contrast, murky waters may indicate high levels of sediment or algae, which can impact the ecosystem's health.
Temperature is a critical factor that varies with depth and season. Lakes often experience thermal stratification, where layers of water form based on temperature differences. This stratification affects the movement of nutrients and oxygen, influencing the types of organisms that can survive in each layer. Ponds, being shallower, tend to have more uniform temperatures, which allows for greater mixing and nutrient availability. The surrounding vegetation also plays a role, as it provides shade, habitat, and food for aquatic and terrestrial species.
Biological Diversity in Lakes and Ponds
Lakes and ponds are teeming with life, hosting a wide array of organisms that contribute to their ecological richness. These ecosystems support diverse species, from microscopic plankton to large fish and birds. The biological diversity in lakes and ponds is shaped by factors such as water quality, nutrient availability, and the presence of predators. Each organism plays a specific role, contributing to the balance and functionality of the ecosystem.
How Do Plants and Animals Adapt to These Ecosystems?
Plants and animals in lakes and ponds have developed unique adaptations to thrive in their aquatic environments. Aquatic plants, such as water lilies and cattails, have specialized structures like floating leaves and air-filled tissues that allow them to float and photosynthesize effectively. These plants not only provide oxygen but also serve as food and shelter for various species.
Animals in these ecosystems have also evolved remarkable adaptations. Fish, for example, have streamlined bodies and gills that enable them to swim efficiently and extract oxygen from water. Amphibians, such as frogs and salamanders, rely on both aquatic and terrestrial habitats during different stages of their life cycles. Insects like dragonflies and water beetles have developed strategies to breathe underwater or move efficiently in the water. These adaptations highlight the resilience and diversity of life in lakes and ponds.
What Role Do Microorganisms Play?
Microorganisms are the unsung heroes of lakes and ponds, playing a vital role in maintaining the health of these ecosystems. Bacteria, algae, and fungi break down organic matter, recycle nutrients, and contribute to the food web. Phytoplankton, a type of microscopic algae, are primary producers that form the base of the aquatic food chain. They convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, providing food for zooplankton and other organisms.
Microorganisms also help regulate water quality by decomposing waste and preventing the buildup of harmful substances. However, excessive nutrient inputs from human activities can lead to algal blooms, which disrupt the balance of the ecosystem. Understanding the role of microorganisms is essential for managing and preserving the health of lakes and ponds.
Environmental Significance of Lakes and Ponds
Lakes and ponds are more than just beautiful landscapes; they are vital components of the Earth's ecosystems. These water bodies play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle, supporting biodiversity, and mitigating climate change. They act as natural reservoirs, storing water and releasing it gradually to maintain streamflow and groundwater levels. This function is especially important during dry periods when water scarcity becomes a concern.
Additionally, lakes and ponds serve as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their sediments. This process helps mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations. The vegetation surrounding these water bodies also contributes to carbon sequestration, making them valuable assets in the fight against global warming.
Moreover, lakes and ponds provide critical habitats for a wide range of species, including migratory birds, fish, and amphibians. They act as breeding grounds, nurseries, and refuges for these organisms, supporting the biodiversity of the region. Protecting these ecosystems is essential for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the survival of countless species.
Human Impact on Lakes and Ponds Characteristics
Human activities have significantly altered the characteristics of lakes and ponds, often with detrimental effects. Pollution, deforestation, urbanization, and climate change are among the primary threats to these ecosystems. Runoff from agricultural fields and urban areas introduces excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, into the water. This nutrient overload can lead to eutrophication, a process that causes algal blooms and depletes oxygen levels, harming aquatic life.
Deforestation and land development around lakes and ponds can increase sedimentation, reducing water clarity and disrupting the habitat of aquatic organisms. Urbanization also contributes to habitat loss and fragmentation, making it difficult for species to survive and reproduce. Climate change exacerbates these issues by altering water temperatures, precipitation patterns, and evaporation rates, further stressing these ecosystems.
To mitigate these impacts, it is essential to adopt sustainable practices and implement conservation measures. Reducing pollution, restoring wetlands, and promoting responsible land use are critical steps in preserving the health and characteristics of lakes and ponds. By addressing these challenges, we can ensure that these vital ecosystems continue to thrive.
How Can We Protect and Restore These Ecosystems?
Protecting and restoring lakes and ponds requires a combination of individual actions, community efforts, and government policies. One of the most effective strategies is reducing pollution by limiting the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals that can runoff into water bodies. Implementing buffer zones of vegetation around lakes and ponds can also help filter pollutants and prevent erosion.
Community involvement is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. Local initiatives, such as clean-up drives and educational programs, can raise awareness about the importance of these ecosystems and encourage sustainable practices. Governments can support these efforts by enforcing regulations that protect water quality and funding restoration projects.
Restoration projects often focus on improving water clarity, reducing nutrient levels, and reintroducing native species. Techniques such as dredging, aeration, and the removal of invasive species can help restore the natural balance of lakes and ponds. By working together, we can ensure that these invaluable resources are preserved for future generations to enjoy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lakes and Ponds
What Causes Algal Blooms in Lakes and Ponds?
Algal blooms occur when excessive nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, enter the water, often due to agricultural runoff or sewage discharge. These nutrients fuel the rapid growth of algae, which can deplete oxygen levels and harm aquatic life.
What’s The Distilled Purified Water Difference? A Comprehensive Guide
Discover The Best Gifts At Vanillagift.com: Your Ultimate Gifting Destination
What’s The Real Difference Between Purified Water And Distilled Water?
Pictures Of Lakes And Ponds

How Do Lakes Differ from Ponds?