Understanding Wire Size For 100 Amp Service: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right wire size for a 100 amp service is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical system. Whether you're installing a new electrical panel, upgrading your current setup, or simply curious about electrical wiring, understanding the nuances of wire size is essential. A 100 amp service is common in residential and small commercial settings, and using the correct wire gauge ensures that the system can handle the electrical load without overheating or causing fire hazards. With numerous factors to consider, such as wire material, insulation type, and environmental conditions, it's important to approach this topic with care and precision.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern living, powering everything from lights and appliances to HVAC systems and entertainment devices. When it comes to a 100 amp service, the wire size plays a pivotal role in determining how efficiently electricity is delivered to your home or business. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for wiring, each with its own advantages and limitations. Copper wires are more conductive and durable, while aluminum wires are lighter and more cost-effective. However, the choice of material is just one piece of the puzzle. Factors like the length of the wire run, ambient temperature, and local building codes also influence the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp service.
By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of wire size for 100 amp service, including how to calculate the correct gauge, what factors to consider, and how to ensure compliance with safety standards. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your electrical wiring. Let’s dive into the details and explore everything you need to know about wire size for a 100 amp service.
Read also:Exploring The Legacy Of Norma Strait A Journey Through Time
Table of Contents
- What Is the Right Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
- How Do You Calculate Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
- What Are the Differences Between Copper and Aluminum Wires for 100 Amp Service?
- Why Is Insulation Important for 100 Amp Wire Size?
- Can Ambient Temperature Affect Wire Size Choices for 100 Amp Service?
- What Are the Safety Standards for Wire Size 100 Amp Installations?
- How to Ensure Compliance with Local Building Codes for 100 Amp Wire Size?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Size 100 Amp Service
What Is the Right Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
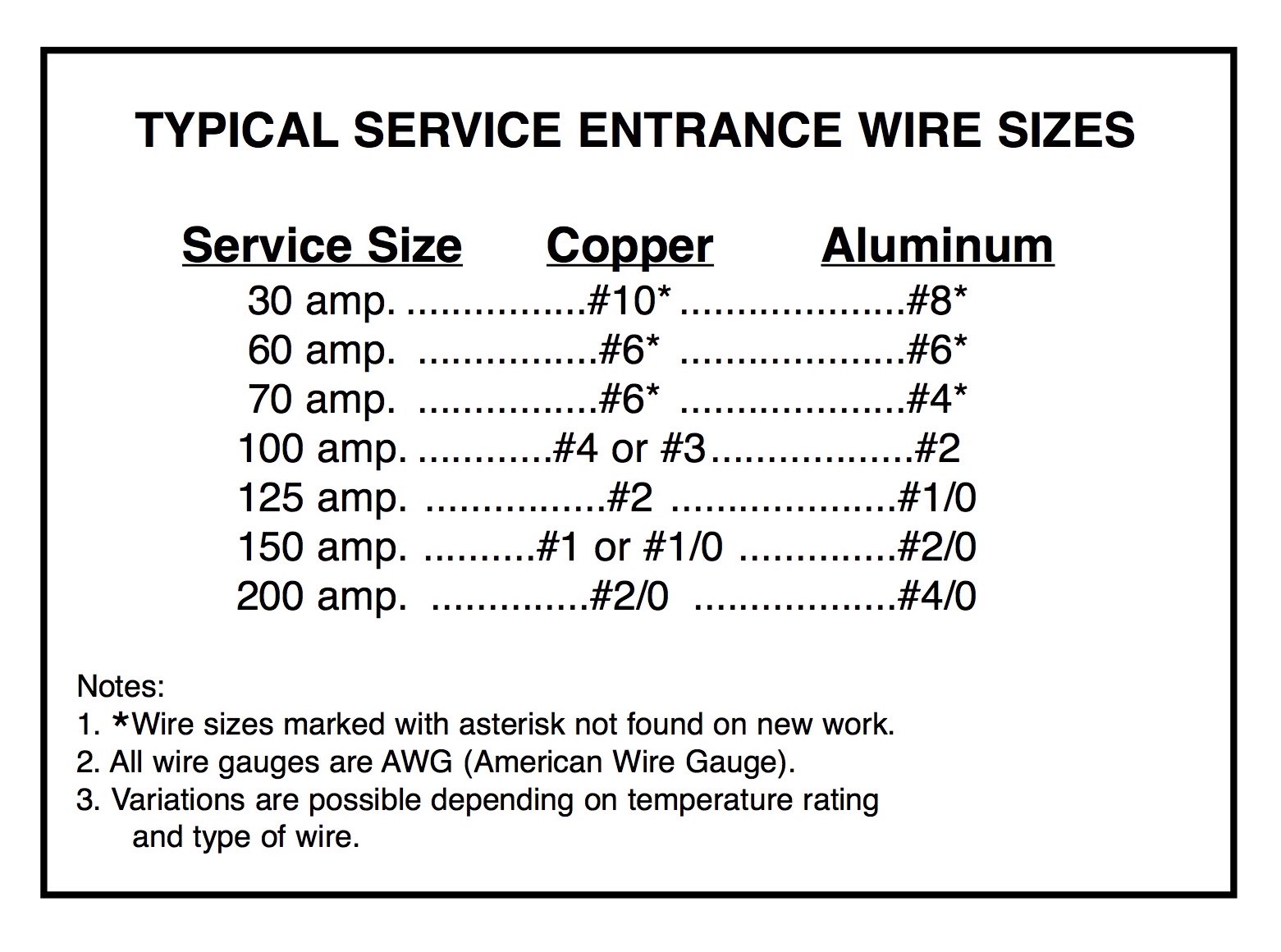
When it comes to a 100 amp service, the wire size you choose is determined by the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines and the specific requirements of your installation. For copper wires, a minimum gauge of 3 AWG is typically recommended for a 100 amp service. On the other hand, aluminum wires require a larger gauge, usually 1 AWG, due to their lower conductivity compared to copper. These recommendations ensure that the wire can safely carry the electrical load without overheating.
However, these are general guidelines, and the actual wire size may vary depending on additional factors such as the length of the wire run and the type of insulation used. For example, if the wire run is longer than 100 feet, you may need to increase the wire gauge to compensate for voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. This can lead to inefficiencies and potential damage to appliances if not addressed properly.
Another important consideration is the type of application. For instance, if the wire is being used for underground installations, it may need to be rated for direct burial or enclosed in a conduit to protect it from moisture and physical damage. Always consult a licensed electrician or refer to the NEC to ensure that your wire size selection meets all safety and performance standards.
What Factors Influence the Choice of Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
Several factors influence the choice of wire size for a 100 amp service. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision and avoid costly mistakes. Here are some key considerations:
- Wire Material: Copper and aluminum are the two primary materials used for electrical wiring. Copper is more conductive and durable, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Aluminum, while less conductive, is lighter and more affordable.
- Wire Length: Longer wire runs require larger gauges to compensate for voltage drop. For every 100 feet of wire, the gauge may need to be increased by one or two sizes to maintain efficiency.
- Insulation Type: The type of insulation used on the wire affects its ability to withstand heat and environmental conditions. Common insulation types include THHN, XHHW, and UF-B.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher ambient temperatures can reduce the current-carrying capacity of wires, necessitating larger gauges to ensure safe operation.
- Local Building Codes: Local regulations may impose additional requirements for wire size and installation methods. Always check with your local building authority before starting any electrical project.
How Does Voltage Drop Affect Wire Size Selection?
Voltage drop is a critical factor that can influence the choice of wire size for a 100 amp service. When electricity travels through a wire, some of its energy is lost due to resistance in the conductor. This loss is known as voltage drop and is expressed as a percentage of the total voltage. Excessive voltage drop can lead to inefficient operation of electrical devices and even damage to sensitive equipment.
To minimize voltage drop, you can either increase the wire gauge or reduce the length of the wire run. For example, using a 1 AWG copper wire instead of a 3 AWG copper wire can significantly reduce voltage drop over long distances. Alternatively, installing a subpanel closer to the load can shorten the wire run and improve efficiency. Calculating voltage drop requires knowledge of the wire's resistance, the current load, and the length of the wire run. Online calculators and NEC tables can help simplify this process.
Read also:What Are Examples A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Using Examples Effectively
How Do You Calculate Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
Calculating the correct wire size for a 100 amp service involves several steps and considerations. The process begins with determining the total electrical load your system will need to support. This includes all appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices that will be connected to the circuit. Once you have an estimate of the total load, you can use NEC guidelines to select the appropriate wire gauge.
The NEC provides tables that specify the maximum allowable current for different wire sizes and materials. For example, a 3 AWG copper wire is rated for up to 100 amps, while a 1 AWG aluminum wire is required to carry the same load. These ratings assume standard conditions, such as an ambient temperature of 30°C (86°F) and a wire run of less than 100 feet. If your installation deviates from these conditions, you may need to adjust the wire size accordingly.
Another important step is calculating voltage drop. As mentioned earlier, voltage drop can affect the performance of your electrical system and may necessitate a larger wire gauge. To calculate voltage drop, you'll need to know the wire's resistance, the current load, and the length of the wire run. The formula for voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Wire Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
By plugging in the appropriate values, you can determine whether your chosen wire size will result in an acceptable voltage drop. If the voltage drop exceeds 3% for branch circuits or 5% for feeders, you should consider increasing the wire gauge or reducing the wire length.
What Tools Can Help You Calculate Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
Fortunately, there are several tools and resources available to simplify the process of calculating wire size for a 100 amp service. Here are some of the most useful options:
- NEC Tables: The NEC provides comprehensive tables that specify the maximum allowable current for different wire sizes and materials. These tables are an essential reference for any electrical project.
- Online Calculators: Many websites offer free online calculators that can help you determine the correct wire size based on your specific requirements. Simply input the wire length, current load, and other parameters, and the calculator will provide a recommended wire gauge.
- Mobile Apps: Several mobile apps are available for electricians and DIY enthusiasts that include wire size calculators, voltage drop calculators, and other useful tools. These apps can be downloaded to your smartphone or tablet for easy access on the go.
- Consulting a Professional: If you're unsure about how to calculate wire size or interpret NEC guidelines, it's always a good idea to consult a licensed electrician. They can provide expert advice and ensure that your installation meets all safety and performance standards.
How Can You Use NEC Tables to Determine Wire Size?
NEC tables are an invaluable resource for determining the correct wire size for a 100 amp service. These tables provide detailed information about the maximum allowable current for different wire sizes and materials, as well as adjustments for ambient temperature and other factors. To use NEC tables effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the wire material (copper or aluminum) and insulation type (THHN, XHHW, etc.).
- Locate the appropriate table in the NEC based on your wire material and insulation type.
- Find the wire size that corresponds to your current load (100 amps in this case).
- Check for any adjustments based on ambient temperature or other conditions.
- Select the wire size that meets or exceeds the requirements for your installation.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your wire size selection is both safe and compliant with NEC standards.
What Are the Differences Between Copper and Aluminum Wires for 100 Amp Service?
When selecting a wire size for a 100 amp service, one of the first decisions you'll need to make is whether to use copper or aluminum wiring. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice often depends on your budget, application, and specific requirements. Understanding the differences between copper and aluminum wires can help you make an informed decision and ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
Copper wires are widely regarded as the gold standard for electrical wiring due to their superior conductivity and durability. They are more resistant to corrosion and can carry higher currents than aluminum wires of the same gauge. This makes copper an excellent choice for high-performance applications where reliability is paramount. However, copper wires are also more expensive and heavier than aluminum, which can make them less practical for large-scale installations or projects with budget constraints.
Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are lighter and more cost-effective than copper. They are often used in residential and commercial applications where weight and cost are significant considerations. However, aluminum has a lower conductivity than copper, which means that larger gauges are required to carry the same current. Additionally, aluminum is more prone to oxidation and expansion, which can lead to connection issues if not properly installed. To mitigate these risks, aluminum wires are often coated with an anti-oxidant compound and require special connectors designed for use with aluminum.
What Are the Advantages of Using Copper Wires for 100 Amp Service?
Copper wires offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for a 100 amp service. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Higher Conductivity: Copper is one of the most conductive materials available, allowing it to carry higher currents with less resistance. This results in more efficient energy transfer and reduced heat generation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper is highly resistant to corrosion, which extends the lifespan of the wire and reduces the need for maintenance.
Exploring Inland Bodies Of Water: Why They Don’t Develop Self-Contained Ecosystems
Exploring The Unique Geometry: What’s A Seven-Sided Shape?
Understanding 6 Gauge Wire Amps: A Comprehensive Guide

Wire Gauge Chart
What Size Ground Wire For 100 Amp Sub Panel