Unveiling The Secrets Of Slice Of White Bread Nutrition: A Complete Guide
While white bread is often criticized for its refined flour content, it also provides essential nutrients when consumed in moderation. A single slice typically contains around 70-80 calories, with carbohydrates forming the bulk of its composition. However, it’s not just about calories; white bread also contains small amounts of protein, fiber, and essential vitamins like niacin and thiamine, thanks to the enrichment process. By examining slice of white bread nutrition, we can make better decisions about its role in our diet and explore healthier alternatives if needed. To help you navigate this topic, we will break down the nutritional value of white bread, discuss its benefits and drawbacks, and answer common questions about its role in a balanced diet. This guide aims to provide clarity on whether white bread is a friend or foe in your daily meals, while also exploring ways to enhance its nutritional profile. So, let’s dive into the details and uncover the truth about slice of white bread nutrition.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Nutritional Basics of a Slice of White Bread?
- Is White Bread Bad for You? Weighing the Pros and Cons
- How Can You Make White Bread Healthier?
- What Are the Alternatives to White Bread?
- Why Is Fiber Important in Bread?
- How Does White Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
- What Are the Hidden Nutrients in a Slice of White Bread?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Slice of White Bread Nutrition
What Are the Nutritional Basics of a Slice of White Bread?
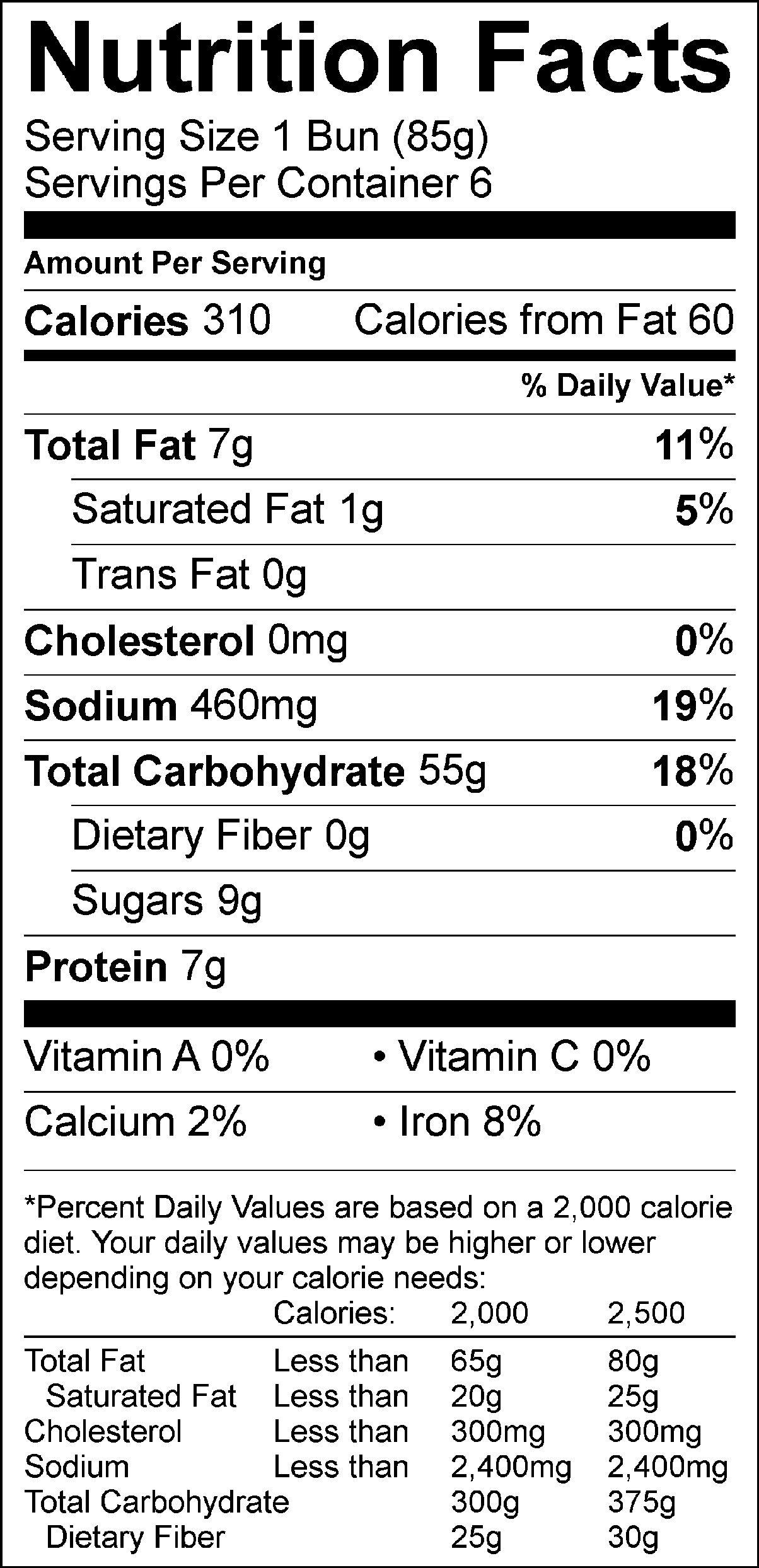
Understanding the nutritional basics of a slice of white bread is essential for making informed dietary choices. On average, a single slice of white bread contains approximately 70-80 calories. The primary macronutrient in white bread is carbohydrates, which account for about 15 grams per slice. These carbohydrates are predominantly in the form of starch, which provides a quick source of energy. However, white bread is low in fiber, with less than 1 gram per slice, which can affect digestion and satiety.
Protein content in white bread is relatively modest, with around 2-3 grams per slice. While this is not a significant source of protein, it contributes to the overall amino acid profile of your diet. Additionally, white bread is often enriched with essential vitamins and minerals, such as niacin, thiamine, riboflavin, and folic acid. These nutrients play critical roles in energy metabolism, red blood cell production, and nervous system function. Iron and calcium are also commonly added during the enrichment process, making white bread a source of micronutrients despite its refined nature.
Read also:Unblocked Games Your Ultimate Guide To Fun And Learning
Despite its enrichment, white bread lacks the natural fiber and nutrients found in whole grain alternatives. The refining process removes the bran and germ, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This is why many nutritionists recommend consuming white bread in moderation and balancing it with other nutrient-dense foods. By understanding the slice of white bread nutrition, you can better assess its role in your diet and make adjustments as needed.
Is White Bread Bad for You? Weighing the Pros and Cons
White bread often gets a bad reputation in health circles, but is it truly as harmful as some claim? To answer this question, we need to weigh the pros and cons of consuming white bread. On the positive side, white bread is a convenient and affordable source of energy. Its high carbohydrate content provides quick fuel for the body, making it a popular choice for athletes and individuals with high energy demands. Additionally, the enrichment process ensures that white bread contains essential vitamins and minerals, which can contribute to overall health.
However, there are notable drawbacks to consider. The low fiber content in white bread can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, which may not be ideal for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes. Furthermore, the lack of fiber can result in poor digestion and reduced feelings of fullness, potentially leading to overeating. Overconsumption of white bread has also been linked to an increased risk of obesity and metabolic disorders, primarily due to its high glycemic index.
Pros of White Bread
- Quick source of energy due to high carbohydrate content.
- Enriched with essential vitamins like niacin, thiamine, and folic acid.
- Affordable and widely available.
Cons of White Bread
- Low in fiber, which can affect digestion and satiety.
- High glycemic index, leading to rapid blood sugar spikes.
- Overconsumption linked to obesity and metabolic disorders.
Ultimately, whether white bread is "bad" for you depends on your individual health goals and dietary needs. For those seeking a balanced diet, moderation is key. Pairing white bread with protein-rich foods or healthy fats can help mitigate its negative effects and provide a more well-rounded meal.
How Can You Make White Bread Healthier?
While white bread may not be the healthiest option on its own, there are several ways to enhance its nutritional value. One simple strategy is to choose fortified or enriched varieties, which contain added vitamins and minerals. Additionally, you can pair white bread with nutrient-dense toppings to create a more balanced meal. For example, spreading avocado or almond butter on your toast can add healthy fats and fiber, while topping it with eggs or lean meats provides a protein boost.
Another way to make white bread healthier is to incorporate it into meals that include vegetables and whole grains. For instance, using white bread for a sandwich filled with leafy greens, tomatoes, and lean protein can create a more nutritious option. You can also experiment with homemade white bread recipes that incorporate whole wheat flour or seeds to increase fiber and nutrient content. These small adjustments can significantly improve the slice of white bread nutrition without sacrificing taste.
Read also:Rick Moranis A Comprehensive Look At The Comedy Legends Life And Legacy
What Are the Alternatives to White Bread?
If you’re looking to reduce your consumption of white bread, there are plenty of alternatives to consider. Whole grain bread, for instance, is a popular choice due to its higher fiber content and richer nutrient profile. Made from whole grains, this type of bread retains the bran and germ, providing more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Other alternatives include sprouted grain bread, sourdough, and gluten-free options, each offering unique health benefits.
Benefits of Whole Grain Bread
- Higher fiber content for improved digestion.
- Rich in essential nutrients like magnesium and selenium.
- Lower glycemic index compared to white bread.
Why Choose Sprouted Grain Bread?
- Improved digestibility and nutrient absorption.
- Higher protein content than traditional bread.
- Contains beneficial enzymes and antioxidants.
While these alternatives may have a different taste and texture, they offer a more nutritious option for those seeking to improve their dietary habits. By exploring these choices, you can enjoy the benefits of slice of white bread nutrition without relying solely on refined grains.
Why Is Fiber Important in Bread?
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health and supporting overall well-being. Unlike white bread, which is low in fiber, whole grain and high-fiber bread options provide the necessary roughage to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of carbohydrates, reducing the risk of spikes and crashes.
In addition to its digestive benefits, fiber contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management. Studies have shown that individuals who consume high-fiber diets are less likely to overeat and more likely to maintain a healthy weight. By choosing bread with higher fiber content, you can enjoy the slice of white bread nutrition while reaping the added benefits of improved satiety and metabolic health.
How Does White Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
One of the primary concerns with white bread is its impact on blood sugar levels. Due to its high glycemic index, white bread can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose, followed by a sharp decline. This rollercoaster effect can leave you feeling fatigued and hungry shortly after eating, making it challenging to maintain stable energy levels throughout the day.
For individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes, these blood sugar fluctuations can be particularly problematic. Consuming white bread in moderation and pairing it with protein or healthy fats can help mitigate its effects. Additionally, opting for lower glycemic index bread options, such as whole grain or sourdough, can provide a more stable energy source and reduce the risk of blood sugar spikes.
What Are the Hidden Nutrients in a Slice of White Bread?
While white bread is often criticized for its refined nature, it does contain some hidden nutrients that are worth noting. Thanks to the enrichment process, white bread is fortified with essential vitamins and minerals, including niacin, thiamine, riboflavin, and folic acid. These nutrients play vital roles in energy production, brain function, and red blood cell formation.
Additionally, white bread often contains small amounts of iron and calcium, which are critical for oxygen transport and bone health, respectively. While these nutrients may not be present in large quantities, they contribute to the overall slice of white bread nutrition and can be beneficial when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Frequently Asked Questions About Slice of White Bread Nutrition
Is White Bread a Good Source of Fiber?
No, white bread is not a significant source of fiber. It contains less than 1 gram of fiber per slice, which is much lower than whole grain alternatives. For better fiber intake, consider switching to whole grain or high-fiber bread options.
Can White Bread Be Part of a Healthy Diet?
Yes, white bread can be part of a healthy diet if consumed in moderation. Pairing it with nutrient-dense foods like vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help balance its nutritional profile. However, it’s important to limit intake if you have specific health concerns like diabetes or obesity.
What Are the Health Risks of Eating Too Much White Bread?
Eating excessive amounts of white bread can lead to weight gain, blood sugar spikes, and an increased risk of metabolic disorders. Its low fiber content and high glycemic index make it less ideal for long-term health compared to whole grain options.
For further reading on the topic, check out this external resource that delves deeper into the pros and cons of white bread.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding slice of white bread nutrition is key to making informed dietary choices. While white bread may not be the healthiest option, it can still be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. By exploring its nutritional basics, weighing its pros and cons, and considering healthier alternatives, you can make the most of this versatile staple. Remember, the key to a healthy diet lies in variety, moderation, and mindful consumption.
How Many Calories Are In A Slice Of Bread? A Comprehensive Guide
Marlo Thomas Net Worth: A Deep Dive Into Her Career, Achievements, And Legacy
Decoding The Enter Sandman Lyrics Meaning: A Deep Dive Into Metallica's Iconic Song
Bread slice Actual Size Image
White Bread Nutrition Label Blog Dandk