What Size Copper Wire For 100 Amp Service: A Complete Guide
Choosing the right copper wire size for a 100 amp service is critical for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical system or installing a new one, understanding the nuances of wire sizing can save you from potential hazards like overheating or electrical fires. A 100 amp service is standard for many residential properties, but selecting the correct wire gauge involves more than just picking a random number—it requires careful consideration of factors like distance, voltage drop, and material quality.
When it comes to electrical installations, copper is often the preferred conductor material due to its superior conductivity and durability. However, not all copper wires are created equal, and selecting the wrong size can lead to inefficiencies or even catastrophic failures. For a 100 amp service, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines that electricians and homeowners must follow. These guidelines ensure that the wire can handle the current load without excessive heat buildup or energy loss. Understanding these standards is the first step toward making an informed decision.
Beyond safety, the size of the copper wire also impacts the performance and longevity of your electrical system. A properly sized wire ensures that your appliances and devices receive consistent power without voltage drops that could damage sensitive electronics. Moreover, it helps you avoid unnecessary expenses from frequent repairs or replacements. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about selecting the right copper wire size for a 100 amp service, from the basics of wire gauges to the intricacies of voltage drop calculations and code compliance.
Read also:Who Is Lakiha Spicer Discover The Inspiring Story Of A Rising Star
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics: What Size Copper Wire for 100 Amp Service?
- What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing Copper Wire?
- What Does the National Electrical Code Say About Wire Sizing?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for Your 100 Amp Service?
- Practical Tips for Installing Copper Wire in a 100 Amp Service
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size?
- Is Bigger Always Better? Balancing Cost and Efficiency in Wire Selection
- Frequently Asked Questions About Copper Wire for 100 Amp Service
Understanding the Basics: What Size Copper Wire for 100 Amp Service?
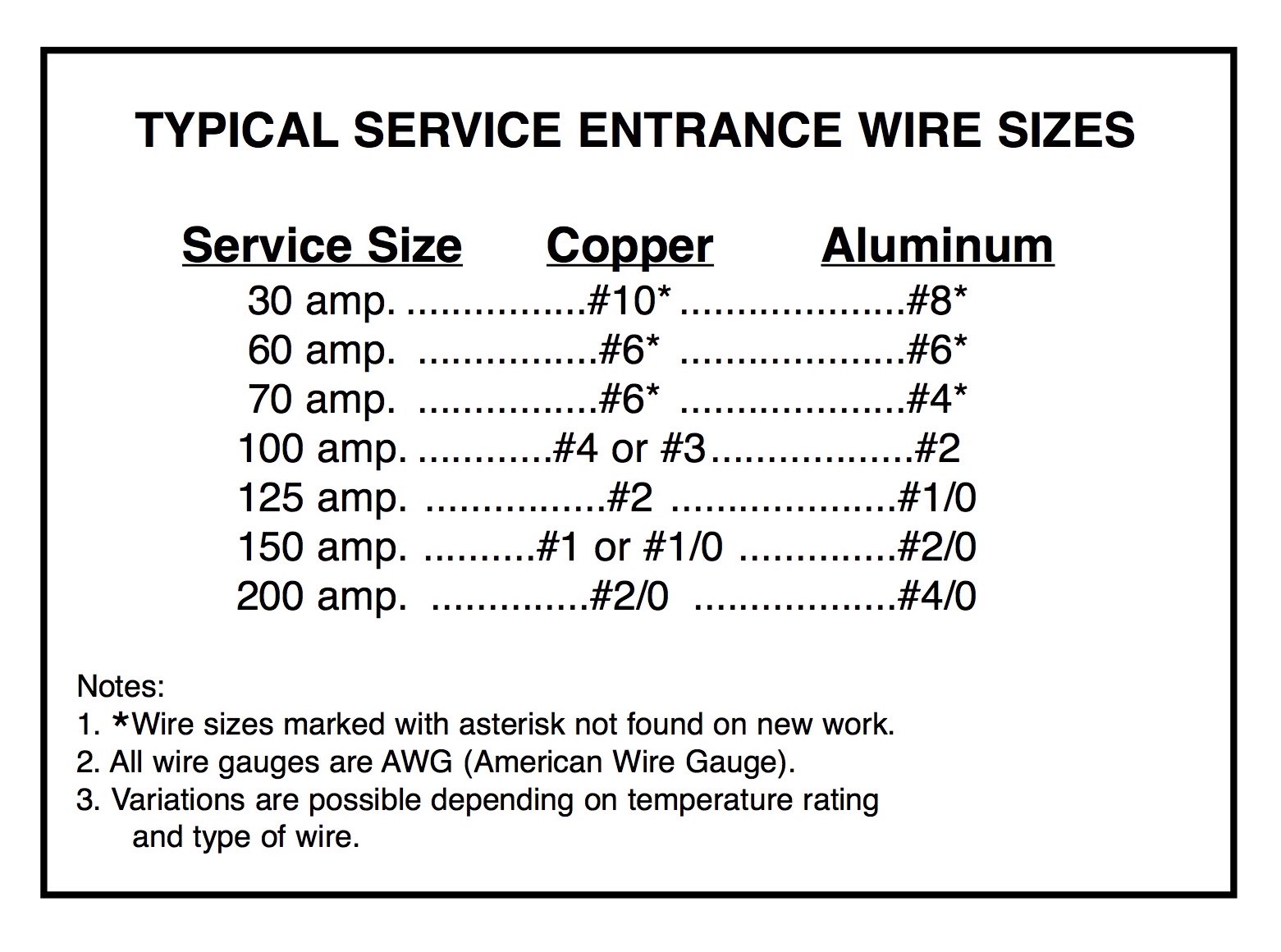
When it comes to determining the appropriate copper wire size for a 100 amp service, the process begins with understanding the fundamentals of electrical systems and wire gauges. Copper wire is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), with smaller numbers indicating thicker wires. For a 100 amp service, the most commonly recommended wire size is 2 AWG copper. This size is capable of safely carrying the current load without overheating, provided the installation adheres to standard conditions.
Why is wire size so important? The answer lies in the relationship between current, resistance, and heat. When electricity flows through a wire, it encounters resistance, which generates heat. If the wire is too small for the current it carries, the heat buildup can become excessive, leading to insulation damage, fire hazards, or even complete system failure. Conversely, using a wire that's too large can be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome to install. Therefore, selecting the correct wire size is a balancing act that ensures both safety and efficiency.
Another critical aspect to consider is the type of insulation used on the wire. Copper wires for a 100 amp service typically come with insulation rated for specific temperatures, such as THHN or XHHW. These ratings are important because they determine the wire's ability to withstand heat under load. For example, THHN insulation is rated for up to 90°C, making it suitable for high-temperature environments. Understanding these basics sets the stage for making informed decisions about wire sizing and installation.
What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing Copper Wire?
Selecting the right copper wire for a 100 amp service involves more than just picking a standard size. Several factors can influence your choice, and overlooking any of them could lead to suboptimal performance or safety issues. Let's explore these factors in detail:
How Does Distance Affect Voltage Drop?
One of the most overlooked factors is the distance between the electrical panel and the point of use. Longer distances increase resistance, which in turn leads to voltage drop. A significant voltage drop can cause appliances to underperform or even malfunction. For a 100 amp service, if the distance exceeds 100 feet, you may need to upsize the wire to compensate for the loss. For example, upgrading from 2 AWG to 1 AWG can help maintain consistent voltage levels over longer runs.
What Role Do Environmental Conditions Play?
The environment where the wire will be installed also plays a crucial role. Wires exposed to high temperatures, moisture, or corrosive substances may require special insulation or larger sizes to ensure durability. For instance, if the wire runs through a hot attic or a damp basement, choosing a wire with a higher temperature rating (e.g., XHHW) is advisable. Additionally, outdoor installations may require weatherproof conduits or direct burial cables to protect the wire from the elements.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
Other factors include the type of load the wire will carry and whether the system is single-phase or three-phase. For example, a system with heavy motor loads may require larger wires to handle the inrush current during startup. Understanding these nuances ensures that your wire selection aligns with the specific demands of your electrical system.
What Does the National Electrical Code Say About Wire Sizing?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the gold standard for electrical installations in the United States, and it provides clear guidelines for selecting wire sizes for a 100 amp service. According to the NEC, the minimum wire size for a 100 amp service is 2 AWG copper. This requirement is based on the wire's ability to safely carry the current without exceeding temperature limits or causing excessive voltage drop.
What Are Ampacity Ratings and Why Do They Matter?
Ampacity refers to the maximum current a wire can carry safely under specific conditions. The NEC provides ampacity tables that electricians use to determine the appropriate wire size for various applications. For copper wires, the ampacity depends on factors like insulation type, ambient temperature, and the number of conductors in a conduit. For example, a 2 AWG copper wire with THHN insulation has an ampacity of 115 amps at 90°C, making it suitable for a 100 amp service.
Why Is Code Compliance Essential?
Compliance with the NEC is not just a recommendation—it's a legal requirement in most jurisdictions. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in fines, insurance claim denials, or even legal liabilities in the event of an accident. Moreover, code-compliant installations ensure that your electrical system is safe, reliable, and efficient. Always consult a licensed electrician to ensure your wire selection and installation meet NEC guidelines.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for Your 100 Amp Service?
Voltage drop is a critical consideration when sizing wires for a 100 amp service. It refers to the reduction in voltage as electricity travels through a conductor, and excessive voltage drop can lead to poor performance of electrical devices. To calculate voltage drop, you can use the formula:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
In this formula, "Length" refers to the one-way distance in feet, "Current" is the load in amps, and "Resistance" is the resistance per 1,000 feet of wire, which can be found in wire resistance tables. For example, if you have a 100-foot run with a 100 amp load and are using 2 AWG copper wire, the voltage drop would be approximately 3.3%, which is within acceptable limits.
To minimize voltage drop, you can either reduce the distance or increase the wire size. For instance, upgrading to 1 AWG copper wire can reduce the voltage drop to around 2.6%, ensuring better performance and efficiency.
Practical Tips for Installing Copper Wire in a 100 Amp Service
Installing copper wire for a 100 amp service requires careful planning and execution. Here are some practical tips to ensure a smooth installation:
- Always use conduits or raceways to protect the wires from physical damage.
- Label all wires and circuits clearly to facilitate future maintenance.
- Ensure that all connections are tight and secure to prevent arcing or overheating.
Additionally, consider hiring a licensed electrician if you're unsure about any aspect of the installation. Professional expertise can save you time, money, and potential headaches down the line.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size?
Many homeowners and even some inexperienced electricians make mistakes when choosing wire sizes for a 100 amp service. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Underestimating the importance of voltage drop.
- Ignoring environmental conditions that could affect wire performance.
- Using undersized wires to save costs, compromising safety and efficiency.
By being aware of these mistakes, you can make more informed decisions and ensure a safe and reliable electrical system.
Is Bigger Always Better? Balancing Cost and Efficiency in Wire Selection
While larger wires can reduce voltage drop and improve efficiency, they also come with higher costs. Striking the right balance between cost and performance is key. For most residential applications, 2 AWG copper wire strikes this balance effectively, offering a safe and efficient solution for a 100 amp service.
Frequently Asked Questions About Copper Wire for 100 Amp Service
What Size Copper Wire for 100 Amp Service Is Recommended?
For a 100 amp service, 2 AWG copper wire is the standard recommendation, as it can safely handle the current load without excessive heat buildup.
Can I Use Aluminum Wire Instead of Copper?
Yes, but aluminum wires require larger sizes (e.g., 1/0 AWG) to match the performance of copper due to their lower conductivity.
How Do I Know If My Wire Size Is Correct?
Consult the NEC ampacity tables and perform a voltage drop calculation to ensure your wire size meets safety and performance standards.
For more detailed information on electrical codes, you can visit the National Fire Protection Association's website.
Understanding White Bread Nutrition: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring The Lives Of James McArdle Siblings: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring The Enter Sandman Meaning: Origins, Symbolism, And Cultural Impact

Ground Wire Size For 100 Amp Service (Know It Now!) PortablePowerGuides
50 Amp Wire Size Copper