What Size Wire For 100 Amp Panel: A Comprehensive Guide For Electrical Safety
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100 amp panel is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical panel or installing a new one, understanding the appropriate wire gauge can prevent overheating, reduce the risk of electrical fires, and ensure compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC). A 100 amp service is standard for many residential homes, but the wire size you need depends on factors like the distance from the main panel, the type of wire, and the environment in which it will be installed. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to make an informed decision.
When it comes to electrical systems, one size does not fit all. The size of the wire you choose directly impacts the system's performance and longevity. Using a wire that's too small for the amperage can lead to voltage drop, which may cause appliances to malfunction or even damage sensitive electronics. On the other hand, using a wire that's unnecessarily large can increase costs without providing significant benefits. In this article, we'll explore the factors that influence wire size selection, discuss the different types of wires available, and provide actionable advice to help you make the best choice for your 100 amp panel.
Electrical safety is not something to take lightly, and selecting the right wire size is a critical step in ensuring your system operates safely and efficiently. With so many variables to consider, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. However, by understanding the basics and following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can confidently choose the correct wire size for your 100 amp panel. Let's dive into the details and answer some of the most common questions homeowners and electricians face when tackling this important task.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- What Factors Influence Wire Size Selection?
- How Does Distance Affect Wire Size?
- Types of Wires for 100 Amp Panel
- Is Copper or Aluminum Wire Better?
- What Are the NEC Guidelines for Wire Sizing?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- FAQs About Wire Sizing
What Factors Influence Wire Size Selection?
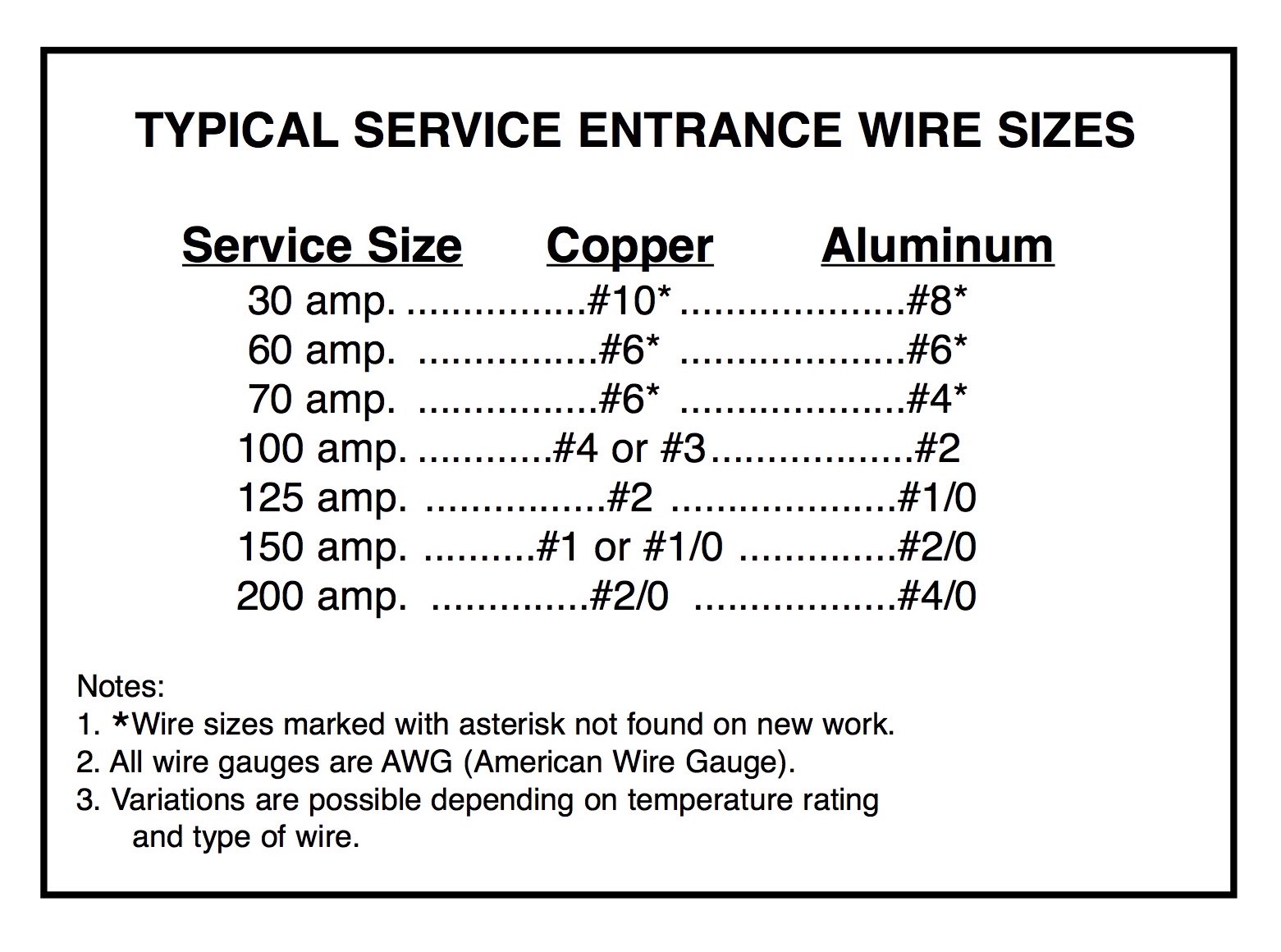
Selecting the right wire size for a 100 amp panel involves considering several key factors. The first and most important is the amperage rating of the panel itself. For a 100 amp service, the National Electrical Code (NEC) specifies minimum wire sizes to ensure safety and performance. Typically, a 100 amp panel requires either a 3 AWG copper wire or a 1 AWG aluminum wire. However, these are just starting points, and other factors can influence the final decision.
One critical factor is the length of the wire run. The longer the distance between the main panel and the subpanel or load, the larger the wire gauge you'll need to prevent voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage, which can affect the performance of your appliances and devices. To mitigate this, you may need to increase the wire size beyond the standard recommendations for a 100 amp panel.
Another consideration is the type of wire insulation. Different insulation materials have varying temperature ratings, which can affect the wire's ampacity—or its ability to carry current safely. For example, wires with THHN or THWN insulation are commonly used in residential applications and are rated for higher temperatures than older insulation types. This allows them to carry more current without overheating, potentially allowing you to use a smaller wire size for a 100 amp panel in some cases.
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which the wire will be installed also plays a significant role in determining the appropriate wire size. For instance, wires installed in hot environments, such as attics or areas with direct sunlight, may need to be larger to compensate for the increased temperature. Similarly, wires buried underground or exposed to moisture require specific types of insulation to ensure durability and safety.
Local Building Codes
Local building codes and regulations can also impact wire size selection. While the NEC provides a baseline for electrical safety, local authorities may have additional requirements based on regional conditions. Always consult with a licensed electrician or your local building department to ensure compliance with all applicable codes and regulations.
How Does Distance Affect Wire Size?
Distance is a critical factor when determining what size wire for 100 amp panel installations. As the length of the wire increases, so does the resistance, which can lead to voltage drop. Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage that occurs as electricity travels through a conductor, and it can negatively impact the performance of electrical devices. To counteract this, electricians often increase the wire size to maintain optimal voltage levels across longer distances.
Read also:Top Unblocked Car Games For Endless Fun And Thrills
For a 100 amp panel, the NEC recommends limiting voltage drop to no more than 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeder circuits. To achieve this, you may need to use a larger wire gauge than the standard 3 AWG copper or 1 AWG aluminum. For example, if the distance between the main panel and the subpanel exceeds 100 feet, you might need to upgrade to a 1 AWG copper wire or a 2/0 AWG aluminum wire to ensure adequate performance and safety.
Calculating voltage drop involves understanding the resistance of the wire and the current it will carry. While this may seem complex, there are online calculators and charts available to simplify the process. By inputting the wire length, material, and amperage, you can determine the appropriate wire size for your specific installation. This step is essential for ensuring that your electrical system operates efficiently and safely over long distances.
Why Is Voltage Drop Important?
Voltage drop is more than just a technical detail—it can have real-world consequences for your electrical system. Excessive voltage drop can cause lights to flicker, appliances to operate inefficiently, and sensitive electronics to malfunction. In extreme cases, it can even lead to equipment failure or fire hazards. By selecting the correct wire size based on distance, you can minimize voltage drop and ensure that your 100 amp panel delivers consistent power to all connected devices.
Practical Tips for Long Wire Runs
If you're dealing with long wire runs, here are some practical tips to keep in mind:
- Use a larger wire gauge than the standard recommendation to reduce resistance.
- Consider upgrading to copper wire, which has lower resistance than aluminum.
- Install a subpanel closer to the load to reduce the overall wire length.
- Consult an electrician to ensure your installation meets all safety and code requirements.
Types of Wires for 100 Amp Panel
When it comes to wiring a 100 amp panel, not all wires are created equal. The type of wire you choose can significantly impact the safety, performance, and cost of your electrical installation. Understanding the differences between the various wire types is essential for making an informed decision. Let's explore the most common types of wires used for 100 amp panels and their unique characteristics.
One of the most popular choices for residential wiring is copper wire. Copper is known for its excellent conductivity, which allows it to carry more current than aluminum wire of the same size. For a 100 amp panel, a 3 AWG copper wire is typically sufficient for most installations. Copper wire is also more durable and resistant to corrosion, making it a reliable option for long-term use. However, copper is more expensive than aluminum, which can make it less appealing for budget-conscious homeowners.
Aluminum wire is another common option for 100 amp panels. While it is less conductive than copper, aluminum is lighter and more affordable, making it a practical choice for larger installations. For a 100 amp panel, a 1 AWG aluminum wire is usually recommended. However, aluminum wire requires careful installation to prevent issues like oxidation and loosening at connection points. Using anti-oxidant compounds and ensuring proper torque on connections can help mitigate these risks.
THHN vs. THWN Insulation
The type of insulation used on the wire is another important consideration. THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated) and THWN (Thermoplastic Heat and Water-resistant Nylon-coated) are two of the most common insulation types for residential wiring. Both are suitable for use in dry and damp locations, but THWN is specifically designed to withstand moisture, making it ideal for underground or outdoor installations. These insulation types also have higher temperature ratings, which can increase the wire's ampacity and allow for smaller wire sizes in some cases.
Stranded vs. Solid Wire
Another distinction to consider is stranded versus solid wire. Stranded wire consists of multiple thin strands of conductor material, making it more flexible and easier to route through conduits. This makes it an excellent choice for installations with tight bends or long runs. Solid wire, on the other hand, is more rigid and better suited for shorter, straight runs. For a 100 amp panel, both types are acceptable, but stranded wire is often preferred for its flexibility and ease of installation.
Is Copper or Aluminum Wire Better?
When deciding between copper and aluminum wire for a 100 amp panel, it's essential to weigh the pros and cons of each material. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on your specific needs and budget. Let's take a closer look at the differences between copper and aluminum wire to help you make an informed decision.
Copper wire is widely regarded as the gold standard for electrical wiring due to its superior conductivity. It can carry more current than aluminum wire of the same size, making it ideal for installations where space is limited or where maximum efficiency is required. For a 100 amp panel, a 3 AWG copper wire is typically sufficient, and its durability ensures long-term performance. Copper is also more resistant to corrosion and oxidation, reducing the risk of connection issues over time.
However, copper's main drawback is its cost. Copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum, which can make it less appealing for large-scale installations or budget-conscious projects. Additionally, copper wire is heavier, which can make it more challenging to handle during installation, especially for long runs or in tight spaces.
Aluminum wire, on the other hand, offers a cost-effective alternative. It is lighter and more affordable than copper, making it an attractive option for larger installations. For a 100 amp panel, a 1 AWG aluminum wire is typically recommended. While aluminum is less conductive than copper, it can still perform effectively when installed correctly. However, aluminum wire requires special attention to prevent issues like oxidation and loosening at connection points. Using anti-oxidant compounds and ensuring proper torque on connections can help mitigate these risks.
When Should You Choose Copper?
Copper wire is the best choice for installations where performance and reliability are paramount. If you're wiring a home with sensitive electronics or planning a long-term installation, copper's superior conductivity and durability make it worth the investment. It's also the preferred choice for shorter runs, where its higher cost is less of a concern.
When Should You Choose Aluminum?
Aluminum wire is ideal for budget-conscious projects or installations where weight is a concern. It's also a practical choice for long runs, where its lower cost can result in significant savings. However, proper installation techniques are crucial to ensure safety and performance. If you're considering aluminum wire, consult with a licensed electrician to ensure it's the right choice for your specific application.
What Are the NEC Guidelines for Wire Sizing?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for determining what size wire for 100 amp panel installations. These guidelines are designed to ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems, and they serve as the foundation for electrical codes across the United States. Understanding the NEC's recommendations is essential for anyone involved in electrical work, whether you're a homeowner or a professional electrician.
According to the NEC, a 100 amp panel requires a minimum wire size of 3 AWG copper or 1 AWG aluminum. These recommendations are based on the ampacity—or the maximum current a wire can safely carry—of the materials. The NEC also specifies that the wire must be protected by an appropriate circuit breaker and installed in a manner that minimizes the risk of overheating or voltage drop. These guidelines apply to both residential and commercial installations, ensuring consistency and safety across different applications.
In addition to wire size,
Adele Noriega: Unveiling The Life And Legacy Of A Remarkable Personality
Do Animals Have Cell Membranes? Exploring The Basics Of Life
The World's Fattest Animals: A Fascinating Exploration Of Nature's Giants

What Size Wire 100 Amp Subpanel
What Size Ground Wire For 100 Amp Sub Panel