What Size Wire For 150 Amps? A Comprehensive Guide For Electrical Safety
Choosing the correct wire size for a 150-amp electrical system is not just about meeting code requirements—it’s about ensuring safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability. Whether you’re wiring a new home, upgrading an existing electrical panel, or installing heavy-duty equipment, understanding wire gauge and its implications is crucial. The wrong wire size can lead to overheating, voltage drops, and even fire hazards. With so many factors to consider, such as wire material, insulation type, and the distance of the run, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But don’t worry—this guide will walk you through everything you need to know to make an informed decision.
When it comes to electrical systems, precision matters. A 150-amp circuit is considered a high-capacity setup, often used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. For instance, a 150-amp service is common in modern homes with multiple appliances, HVAC systems, and electric vehicle chargers. But how do you determine the right wire gauge for such a system? Factors like copper versus aluminum wiring, ambient temperature, and conduit fill all play a role. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of these considerations, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to make the best choice.
By the end of this guide, you’ll not only know what size wire is suitable for a 150-amp circuit but also understand why it’s the safest and most efficient option. We’ll explore industry standards, answer common questions, and offer practical tips to ensure your electrical system operates smoothly. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, this resource will serve as your go-to reference for all things related to 150-amp wiring.
Read also:Unblocked Games Your Ultimate Guide To Fun And Learning
Table of Contents
- What Size Wire for 150 Amps?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 150-Amp Circuit?
- How to Calculate the Right Wire Size for 150 Amps?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wiring: Which is Better for 150 Amps?
- What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire for 150 Amps?
- How Does Distance Affect Wire Size for 150 Amps?
- What Are the Code Requirements for 150-Amp Wiring?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 150-Amp Wiring
What Size Wire for 150 Amps?
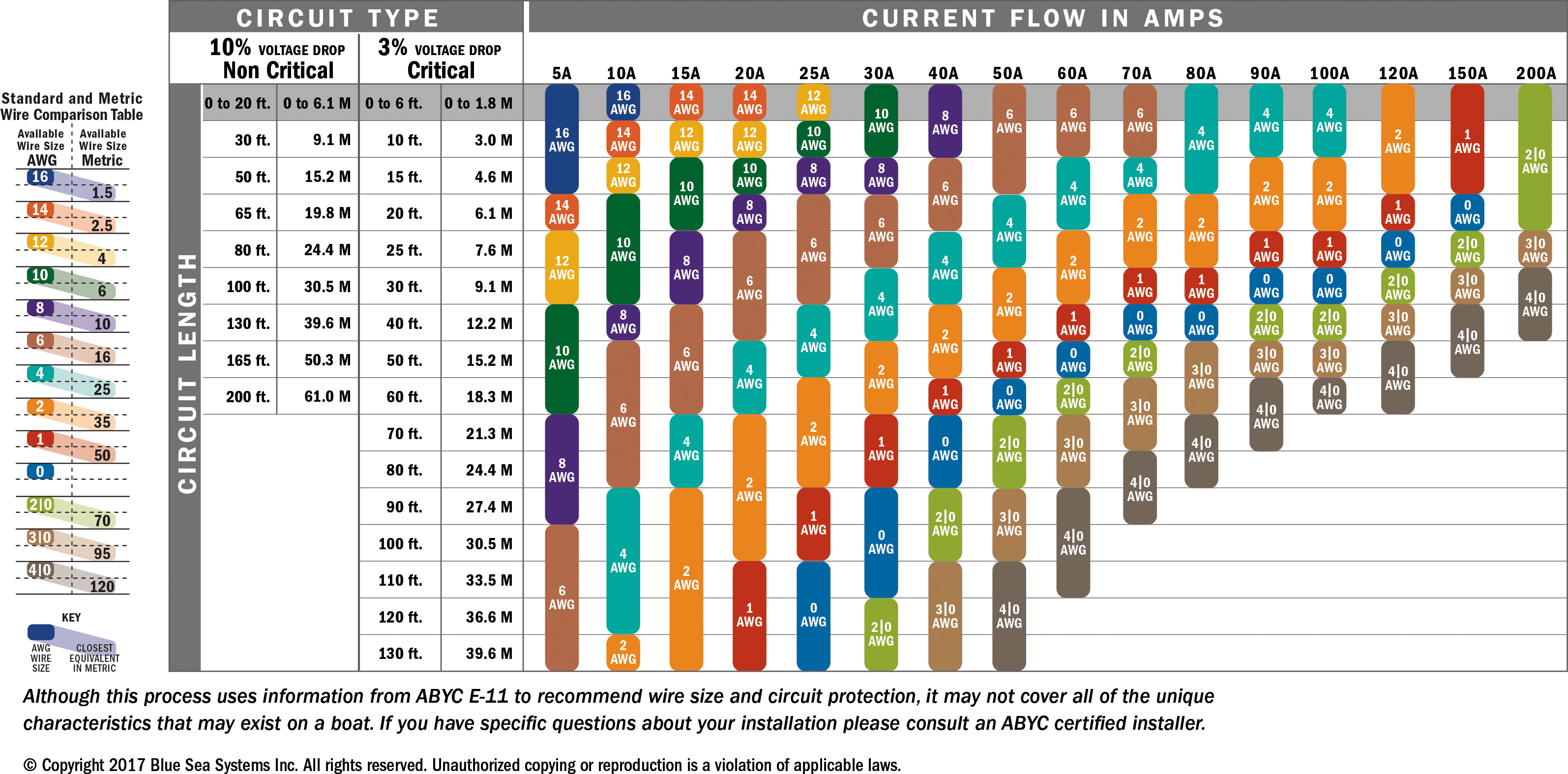
The size of the wire you need for a 150-amp circuit depends on several factors, including the material of the wire, the insulation type, and the length of the run. For most residential applications, a 150-amp service typically requires a wire gauge of 2/0 AWG (American Wire Gauge) for copper wiring or 4/0 AWG for aluminum wiring. These gauges ensure that the wire can handle the current without overheating or causing voltage drops.
Why these specific gauges? Copper wiring is more conductive than aluminum, which means it can carry the same amount of current with a smaller diameter. For example, a 2/0 AWG copper wire has a diameter of approximately 0.3648 inches, while a 4/0 AWG aluminum wire is about 0.46 inches in diameter. Both are designed to handle the maximum current load safely. However, if you’re working with longer distances, you may need to increase the wire size to compensate for voltage drop.
It’s also important to note that the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for wire sizing, but local codes may have additional requirements. Always consult a licensed electrician or your local building authority to ensure compliance. Additionally, using wires with proper insulation, such as THHN or XHHW, is essential for safety and durability.
Why Does Wire Size Matter for a 150-Amp Circuit?
Wire size is a critical factor in the performance and safety of any electrical system. For a 150-amp circuit, using a wire that’s too small can lead to excessive heat buildup, which may damage the insulation and cause a fire hazard. On the other hand, using a wire that’s too large can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with.
How Does Wire Size Affect Safety?
When a wire is too small for the current it’s carrying, resistance increases, leading to higher temperatures. This can cause the wire to overheat, melt its insulation, and potentially ignite surrounding materials. For example, a 150-amp circuit using a 1 AWG wire instead of the recommended 2/0 AWG could overheat under full load, posing a significant risk.
What Are the Efficiency Implications of Incorrect Wire Size?
Using the wrong wire size can also result in voltage drop, which affects the performance of your electrical devices. Voltage drop occurs when the resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. For a 150-amp circuit, even a small voltage drop can lead to inefficiencies, such as dimming lights or reduced motor performance.
Read also:Ant Anstead Net Worth Unveiling The Life Career And Financial Success Of A Renowned Car Expert
How to Calculate the Right Wire Size for 150 Amps?
Calculating the correct wire size for a 150-amp circuit involves several steps, including determining the load, considering the distance, and accounting for environmental factors like temperature. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Determine the Load: Identify the total amperage of the circuit. For a 150-amp service, this is straightforward—it’s 150 amps.
- Choose the Wire Material: Decide whether you’ll use copper or aluminum wiring. Copper is more conductive, so it requires a smaller gauge.
- Factor in Distance: Longer runs require larger wires to compensate for voltage drop. Use a voltage drop calculator to determine the appropriate size.
- Consider Temperature Ratings: High ambient temperatures can reduce a wire’s capacity. Ensure the insulation is rated for the environment.
What Tools Can Help You Calculate Wire Size?
There are several tools available to simplify the process. Online calculators, NEC charts, and mobile apps can provide quick and accurate wire size recommendations based on your specific needs.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wiring: Which is Better for 150 Amps?
When it comes to wiring a 150-amp circuit, the choice between copper and aluminum is a common dilemma. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages.
Why Choose Copper Wiring?
Copper is more conductive, corrosion-resistant, and durable than aluminum. It’s also easier to work with, making it a popular choice for residential applications. However, copper wiring is more expensive, which can be a deciding factor for larger projects.
Why Choose Aluminum Wiring?
Aluminum is lighter and less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective option for long runs or industrial applications. However, it’s less conductive, requires larger gauges, and is more prone to corrosion if not properly installed.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire for 150 Amps?
Even experienced electricians can make mistakes when selecting wire for a 150-amp circuit. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Underestimating Distance: Failing to account for voltage drop over long runs can lead to inefficiencies.
- Ignoring Temperature Ratings: High ambient temperatures can reduce a wire’s capacity, so always check the insulation rating.
- Using Incorrect Connectors: Mixing copper and aluminum wires without proper connectors can cause corrosion and overheating.
How Does Distance Affect Wire Size for 150 Amps?
Distance plays a significant role in determining the appropriate wire size for a 150-amp circuit. The longer the run, the greater the resistance, which increases the risk of voltage drop. For example, a 100-foot run may require a larger wire gauge than a 50-foot run to maintain efficiency.
What Are the Best Practices for Long Runs?
For long runs, consider using a wire gauge one or two sizes larger than the standard recommendation. This ensures minimal voltage drop and optimal performance.
What Are the Code Requirements for 150-Amp Wiring?
The NEC provides specific guidelines for wiring a 150-amp circuit, including wire size, insulation type, and installation methods. Always refer to the latest edition of the NEC and consult local codes to ensure compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions About 150-Amp Wiring
Can I Use a Smaller Wire for a 150-Amp Circuit if the Load is Less?
No, the wire size must be based on the circuit’s maximum capacity, not the current load. Using a smaller wire can lead to overheating and safety hazards.
What Happens if I Use the Wrong Wire Size?
Using the wrong wire size can result in overheating, voltage drop, and even fire hazards. Always follow NEC guidelines and consult a professional if unsure.
Where Can I Find Reliable Resources for Electrical Codes?
You can find reliable resources on the NFPA website, which provides access to the NEC and other standards.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wire size for a 150-amp circuit is essential for safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. By understanding the factors that influence wire size, such as material, distance, and temperature, you can make an informed decision that ensures your electrical system operates smoothly. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, this guide provides the knowledge you need to tackle 150-amp wiring projects with confidence.
Understanding And Managing Blood Pressure 160/110: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover The Best Vanilla GIDT: A Comprehensive Guide To Vanillagidt.com
Who Is Oscar Piastri's Father? A Deep Dive Into His Life And Legacy
Wire Size For 90 Amps

Wire Ratings For Amps