What Wire Size For 100 Amp Service: A Complete Guide
Choosing the right wire size for a 100 amp service is critical to ensuring safety and optimal performance of your electrical system. Whether you're upgrading your home's electrical panel, installing a subpanel, or setting up a new workshop, understanding the correct wire gauge is essential. Using the wrong wire size can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or inefficient power delivery. This article will explore everything you need to know about selecting the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp service, including factors like wire material, distance, and local building codes.
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern living, powering everything from appliances to lighting. However, working with electricity requires precision and adherence to safety standards. Many homeowners and DIY enthusiasts often ask, "What wire size for 100 amp?" The answer depends on several variables, such as the type of wire material (copper or aluminum), the length of the circuit, and environmental conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down these factors and provide clear recommendations to help you make an informed decision.
Before diving into specifics, it's important to note that electrical work should always comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local regulations. Consulting a licensed electrician is highly recommended, especially for complex installations. That said, this article will equip you with the knowledge to understand wire sizing principles, empowering you to communicate effectively with professionals or tackle smaller projects confidently.
Read also:Who Is Patricia Brights Husband A Deep Dive Into Her Personal Life And Influence
Table of Contents
- What Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for 100 Amp Circuits?
- Copper vs. Aluminum Wire: Which is Better?
- How Far Can You Run a 100 Amp Wire?
- What Are the Local Codes for Wire Sizing?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100 Amp Service?
- Final Thoughts on Wire Sizing for 100 Amp Service
What Wire Size for 100 Amp Service?
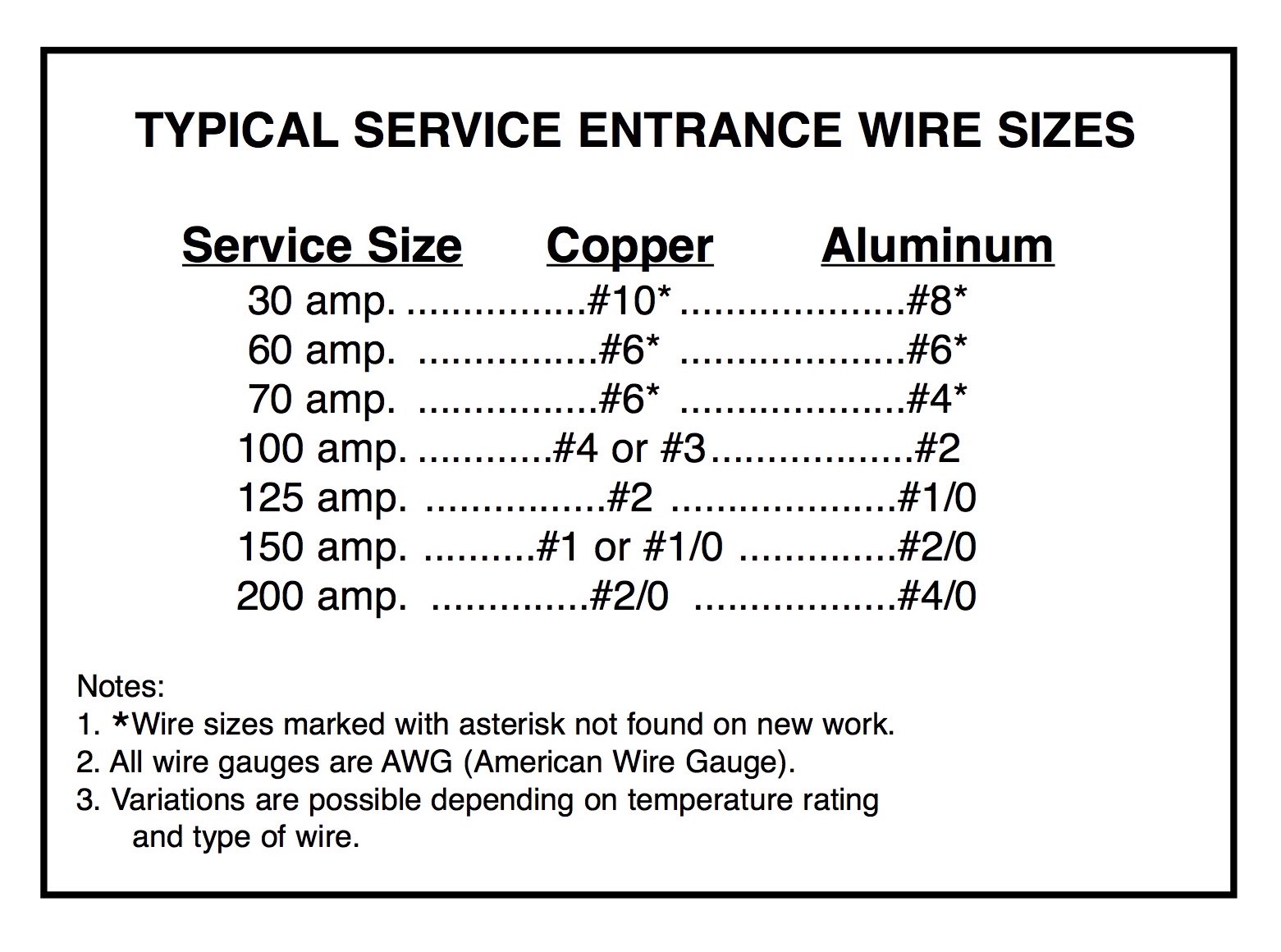
When it comes to determining the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp service, the general recommendation is to use a 3 AWG copper wire or a 1 AWG aluminum wire. These sizes are based on the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, which ensure safe and efficient electrical transmission. Copper is often preferred for its superior conductivity, while aluminum is a cost-effective alternative for longer runs.
However, these recommendations are not one-size-fits-all. The actual wire size may vary depending on the distance between the power source and the load, the type of insulation, and environmental conditions. For example, if the wire will be exposed to high temperatures or buried underground, you may need to adjust the gauge accordingly. Always consult the NEC or a licensed electrician to confirm the appropriate wire size for your specific application.
Factors Influencing Wire Size Selection
Several factors come into play when selecting the right wire size for a 100 amp service:
- Wire Material: Copper wires have better conductivity and require smaller gauges compared to aluminum wires.
- Distance: Longer runs require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- Insulation Type: Different insulation materials can handle varying temperature ranges, affecting wire size requirements.
- Environmental Conditions: Exposure to moisture, heat, or direct sunlight may necessitate specific wire types.
Why Does Wire Size Matter for 100 Amp Circuits?
Choosing the correct wire size is not just a matter of compliance; it directly impacts the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Using an undersized wire for a 100 amp service can lead to overheating, which poses a significant fire hazard. On the other hand, oversized wires can be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome to install.
The wire size determines the amount of current it can safely carry without exceeding its temperature rating. For instance, a 3 AWG copper wire is rated to handle up to 100 amps under normal conditions. If the wire is too thin, it will struggle to carry the required current, leading to excessive heat buildup. This can damage the insulation, cause shorts, or even ignite surrounding materials.
What Happens If You Use the Wrong Wire Size?
Using the wrong wire size can have serious consequences:
Read also:Exploring Adam Savages Children A Glimpse Into Their Lives And Influence
- Overheating: Undersized wires generate excessive heat, increasing the risk of fire.
- Voltage Drop: Thin wires over long distances result in significant voltage drop, affecting appliance performance.
- Code Violations: Non-compliance with NEC standards can lead to fines or insurance issues.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wire: Which is Better?
When selecting wire material for a 100 amp service, the debate often comes down to copper versus aluminum. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages, making the choice dependent on your specific needs and budget.
Copper is widely regarded as the superior option due to its excellent conductivity and durability. It can carry more current than aluminum of the same gauge, making it ideal for shorter runs or applications where space is limited. However, copper is significantly more expensive, which can be a deterrent for larger projects.
Aluminum, while less conductive, is a cost-effective alternative for longer runs. It is lighter and easier to handle, making it suitable for overhead installations. However, aluminum wires require proper connectors and anti-oxidation compounds to prevent corrosion and ensure a secure connection.
Which Material Should You Choose?
The decision between copper and aluminum ultimately depends on your project requirements:
- Short Runs: Copper is the better choice for its superior conductivity.
- Long Runs: Aluminum is more economical and practical for extended distances.
- Budget Constraints: If cost is a concern, aluminum may be the way to go.
How Far Can You Run a 100 Amp Wire?
One of the most common questions homeowners ask is, "How far can you run a 100 amp wire?" The answer depends on the wire gauge, material, and acceptable voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as the current travels over distance. For a 100 amp service, the NEC recommends limiting voltage drop to 3% or less for optimal performance.
For example, a 3 AWG copper wire can typically run up to 150 feet without exceeding the recommended voltage drop. Beyond this distance, you may need to upgrade to a thicker gauge, such as 1 AWG copper or 2/0 AWG aluminum, to maintain efficiency. Always calculate the voltage drop for your specific setup to ensure compliance with safety standards.
How to Minimize Voltage Drop?
To minimize voltage drop, consider the following tips:
- Use thicker wires for longer runs.
- Choose copper over aluminum for better conductivity.
- Install the wire in a straight path to reduce resistance.
What Are the Local Codes for Wire Sizing?
Local building codes play a crucial role in determining the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp service. While the NEC provides a national standard, local jurisdictions may have additional requirements based on climate, geography, and other factors. For instance, areas prone to extreme temperatures or high humidity may mandate specific wire types or insulation materials.
Before starting any electrical project, it's essential to consult your local building authority or a licensed electrician to ensure compliance. Failure to adhere to local codes can result in fines, project delays, or even legal liabilities.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wire Size
Even experienced DIY enthusiasts can make mistakes when selecting wire size for a 100 amp service. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Underestimating Distance: Failing to account for voltage drop over long runs.
- Ignoring Environmental Factors: Not considering temperature, moisture, or exposure to sunlight.
- Using Incorrect Connectors: Mismatched connectors can lead to poor connections and overheating.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100 Amp Service?
Calculating voltage drop is a straightforward process that involves a simple formula:
Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length: Distance of the wire run in feet.
- Current: Amperage of the circuit (100 amps).
- Resistance: Resistance per 1,000 feet of wire (available in NEC tables).
For example, if you're using a 3 AWG copper wire for a 100-foot run, the voltage drop would be approximately 2.4 volts, well within the acceptable range. Always double-check your calculations to ensure safety and compliance.
Final Thoughts on Wire Sizing for 100 Amp Service
Selecting the correct wire size for a 100 amp service is a critical step in ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. By understanding the factors that influence wire size, such as material, distance, and environmental conditions, you can make informed decisions that comply with NEC standards and local codes.
Remember, when in doubt, consult a licensed electrician. Electrical work is not something to take lightly, and professional guidance can save you time, money, and potential hazards. With the right knowledge and preparation, you can confidently tackle your next electrical project.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the minimum wire size for 100 amp service?
The minimum wire size for a 100 amp service is typically 3 AWG copper or 1 AWG aluminum, depending on the distance and environmental conditions.
Can I use aluminum wire for a 100 amp service?
Yes, aluminum wire can be used for a 100 amp service, but it requires proper connectors and anti-oxidation compounds to ensure a secure connection.
How do I know if my wire size is correct?
To verify if your wire size is correct, calculate the voltage drop and ensure it falls within the recommended 3% range. Additionally, consult the NEC and local codes for compliance.
For more information on electrical safety, visit the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) website.
Understanding Pond Vs Lake Differences: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding BMI License Fees: A Comprehensive Guide To Music Licensing
Exploring The Adepti Genshin Meaning: Origins, Significance, And More

Wire Gauge Chart
What Size Ground Wire For 100 Amp Sub Panel