Understanding The Importance Of Choosing The Right 100 Amp Wire Size For Your Electrical Needs
Choosing the correct wire size for a 100 amp electrical service is crucial for safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Whether you're installing a new circuit breaker or upgrading your home’s electrical system, understanding the nuances of wire sizing can prevent overheating, fires, and costly repairs. Electrical systems are the backbone of modern living, powering everything from lights and appliances to sophisticated smart home devices. However, a mismatched wire size can compromise the entire setup, leading to potential hazards and inefficiencies.
Electrical wires come in various gauges, each designed to handle specific current loads. For a 100 amp service, the wire must be robust enough to carry the current without excessive voltage drop, which can degrade the performance of connected devices. Using an undersized wire can result in overheating, while an oversized wire may lead to unnecessary expenses. Factors such as the distance between the power source and the load, the type of insulation, and the ambient temperature also play a significant role in determining the appropriate wire size.
Moreover, electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), provide guidelines to ensure safe installations. These regulations are not just recommendations but legal requirements that electricians and homeowners must adhere to. By understanding the importance of selecting the right 100 amp wire size, you can make informed decisions that safeguard your property and loved ones while optimizing energy efficiency. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of wire sizing and explore how to choose the best option for your specific needs.
Read also:Discover The Best Remote Iot Vpc Solutions For Your Business Needs
Table of Contents
- What Factors Determine the Right 100 Amp Wire Size?
- How Does Distance Affect Your Choice of Wire?
- Why Is Insulation Type Important for 100 Amp Wire Size?
- What Are the Common Materials Used for 100 Amp Wires?
- How Can You Ensure Compliance with Electrical Codes?
- What Are the Risks of Using Undersized or Oversized Wires?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100 Amp Services?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 100 Amp Wire Size
What Factors Determine the Right 100 Amp Wire Size?
Selecting the appropriate wire size for a 100 amp service involves evaluating several critical factors. These include the current load, distance, insulation type, and environmental conditions. Each of these elements plays a vital role in ensuring the wire can safely and efficiently carry the required current without overheating or causing voltage drop.
Current Load and Wire Gauge
The current load is perhaps the most important factor. For a 100 amp service, the wire gauge must match the amperage to prevent overheating. Typically, a 2-gauge copper wire or a 1/0-gauge aluminum wire is recommended for 100 amp circuits. Copper wires are preferred for their superior conductivity, but aluminum wires are a cost-effective alternative for longer runs.
Ambient Temperature and Heat Dissipation
Ambient temperature also influences wire size selection. Higher temperatures can reduce a wire's current-carrying capacity, necessitating a larger gauge to compensate. Additionally, wires installed in confined spaces or bundled together may generate more heat, requiring adjustments to the wire size to ensure safe operation.
Environmental Conditions and Protection
Environmental conditions such as moisture, sunlight, and exposure to chemicals can affect wire performance. Choosing wires with the appropriate insulation type, such as THHN or XHHW, ensures durability and longevity. For outdoor installations, wires with UV-resistant insulation are essential to prevent degradation from sunlight exposure.
By considering these factors, you can select the right wire size that meets your electrical needs while adhering to safety standards and regulations.
How Does Distance Affect Your Choice of Wire?
The distance between the power source and the load significantly impacts the choice of wire size. Longer distances increase the resistance in the wire, leading to voltage drop, which can affect the performance of electrical devices. To mitigate this, larger wire gauges are often required for extended runs.
Read also:Exploring The Unique Bond Of Colin Jost And Michael Che Friendship A Closer Look
Voltage Drop and Its Implications
Voltage drop occurs when the resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. For a 100 amp service, a voltage drop of more than 3% is generally considered unacceptable. Using larger wire sizes reduces resistance and minimizes voltage drop, ensuring devices receive adequate power.
Calculating Wire Size for Long Distances
To determine the appropriate wire size for long distances, you can use a voltage drop calculator or consult the NEC guidelines. For example, a 200-foot run may require a 1/0-gauge copper wire or a 2/0-gauge aluminum wire to maintain acceptable voltage levels. Proper planning and calculations are essential to avoid inefficiencies and ensure optimal performance.
Tips for Minimizing Voltage Drop
- Use larger wire gauges for extended runs.
- Install intermediate junction boxes to break up long runs.
- Choose wires with low-resistance materials, such as copper.
By accounting for distance and voltage drop, you can select the right wire size that ensures reliable and efficient power delivery.
Why Is Insulation Type Important for 100 Amp Wire Size?
The insulation type of a wire is a critical factor in determining its suitability for a 100 amp service. Insulation protects the wire from environmental factors and ensures safe operation under various conditions. Different insulation types offer varying levels of heat resistance, durability, and flexibility.
Common Insulation Types for 100 Amp Wires
THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-Resistant Nylon) and XHHW (XLPE High Heat-Resistant Water-Resistant) are two of the most common insulation types for 100 amp wires. THHN is ideal for dry and damp locations, while XHHW is suitable for wet environments and offers superior heat resistance.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Needs
When selecting insulation, consider the installation environment. For outdoor or underground installations, XHHW is often preferred due to its water-resistant properties. For indoor applications, THHN is a cost-effective and reliable choice. Proper insulation ensures the wire can withstand the conditions it will be exposed to, enhancing safety and longevity.
Key Benefits of Proper Insulation
- Protects against moisture and corrosion.
- Enhances heat resistance and durability.
- Ensures compliance with electrical codes.
By choosing the right insulation type, you can ensure your 100 amp wire performs reliably and safely under all conditions.
What Are the Common Materials Used for 100 Amp Wires?
The material of the wire is another crucial factor in determining the appropriate size for a 100 amp service. Copper and aluminum are the two most common materials used for electrical wiring, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Copper Wires: Superior Conductivity and Reliability
Copper is the preferred material for electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity and durability. It can carry more current than aluminum wires of the same gauge, making it ideal for high-load applications. Copper wires are also more resistant to corrosion and have a longer lifespan, though they come at a higher cost.
Aluminum Wires: Cost-Effective and Lightweight
Aluminum wires are a cost-effective alternative, especially for longer runs where weight is a concern. While they are less conductive than copper, aluminum wires are lighter and easier to handle. However, they require larger gauges to match the current-carrying capacity of copper wires and are more prone to corrosion if not properly insulated.
Comparison of Copper and Aluminum Wires
| Feature | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Corrosion Resistance | Better | Less |
By understanding the differences between copper and aluminum wires, you can make an informed decision based on your specific needs and budget.
How Can You Ensure Compliance with Electrical Codes?
Compliance with electrical codes is essential for safety and legal reasons. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides comprehensive guidelines for wire sizing, insulation, and installation practices. Adhering to these standards ensures your electrical system is safe, efficient, and up to code.
Understanding NEC Guidelines
The NEC specifies the minimum wire sizes for various amperages and distances. For a 100 amp service, the NEC recommends using wires that meet or exceed the specified gauge to prevent overheating and voltage drop. Familiarizing yourself with these guidelines helps ensure your installation complies with industry standards.
Working with Licensed Electricians
Hiring a licensed electrician is the best way to ensure compliance with electrical codes. Professional electricians are trained to interpret and apply NEC guidelines, ensuring your installation is safe and up to code. They can also provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their experience.
Steps to Ensure Compliance
- Review NEC guidelines for wire sizing and insulation.
- Consult with a licensed electrician for professional advice.
- Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to ensure ongoing compliance.
By following these steps, you can ensure your electrical system meets all necessary codes and standards.
What Are the Risks of Using Undersized or Oversized Wires?
Using undersized or oversized wires can lead to various risks and inefficiencies in your electrical system. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions about wire sizing.
Risks of Undersized Wires
Undersized wires can overheat, leading to fires and damage to connected devices. They may also cause excessive voltage drop, reducing the performance of electrical appliances. Ensuring the wire size matches the current load is essential for safety and efficiency.
Risks of Oversized Wires
Oversized wires, while safer, can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to work with. They may also require larger conduits and connectors, increasing installation costs. Balancing cost and safety is key to selecting the right wire size.
How to Avoid These Risks
- Consult NEC guidelines for recommended wire sizes.
- Work with a licensed electrician to ensure proper sizing.
- Regularly inspect and maintain your electrical system.
By avoiding these risks, you can ensure your electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for 100 Amp Services?
Calculating voltage drop is essential for ensuring your 100 amp service operates efficiently. By understanding the formula and factors involved, you can make informed decisions about wire sizing and installation.
Voltage Drop Formula
The voltage drop formula is: Voltage Drop = (2 x Length x Current x Resistance) / 1000. This formula helps determine the voltage loss over a given distance and current load. Using this calculation, you can select the appropriate wire size to minimize voltage drop
What's The Hardest Language To Learn? Discover The Truth Behind Language Difficulty
What’s The Difference Between A Lake And A Pond: A Comprehensive Guide
Do Animals Have A Cell Membrane? Exploring The Science Behind It
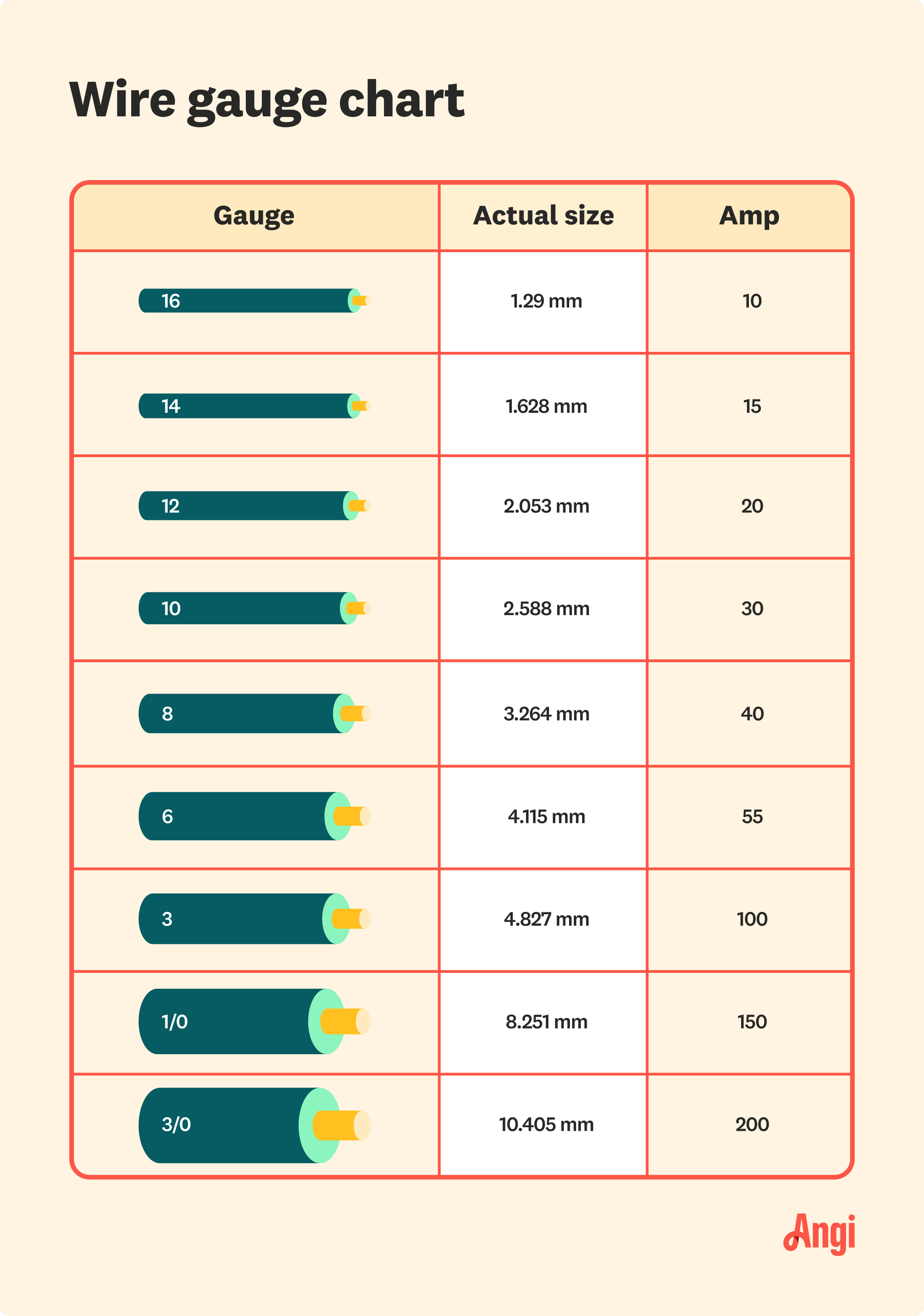
What Is the Correct Wire Size for 100Amp Service? Angi
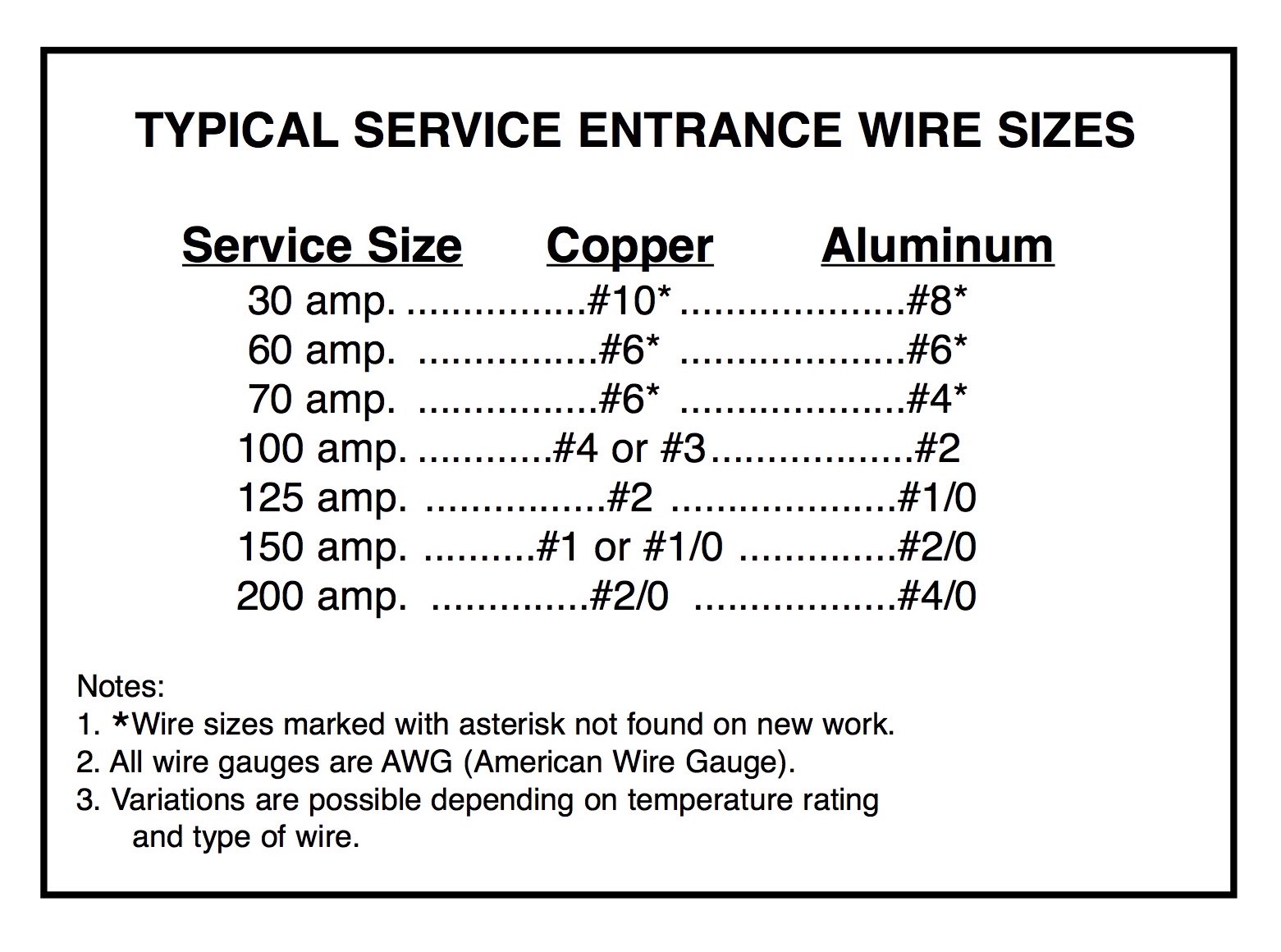
What Size Ground Wire For 100 Amp Sub Panel